Genetics In Orthodontics Short Essays
Question 1. Genetic malocclusions.
Answer.
- Disturbance in tooth size: Micrognathia, macrognathia
- Disturbance in tooth number:
- Hypodontia
- Anodontia
- Oligodontia etc.
- Disturbance in alignment of teeth:
- Abnormal overjet and overbite
- Open bite
- Effecting other structures:
- Cleft lip and palate
- High arched palate
- Bimaxillary protrusion
- Bimaxillary atresia
- Cleft lip and palate
- Syndromes associated with it:
- Down’s syndrome
- Gardner’s syndrome
- Marfan’s syndrome
- Cleido-cranial dysplasia
- Mandibulo facial dysostosis
- General conditions:
- Cherubism
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Retarded tooth eruption
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Question 2. Importance of Genetics in Orthodontics.
Answer.
- First recognized by Frederick G. Kussel in 1836
- He found that some of the malocclusions are transmitted from one generation to other
- The cause of relapse also has a hereditary influence
- Occlusal malrelations, jaw positioning and pressure habits are all results of genetic alteration
- Some of examples of genetic malocclusions are
- Disturbance in tooth size: Micrognathia, macrognathia
- Disturbance in tooth number:
- Hypodontia
- Anodontia
- Oligodontia etc.
- Disturbance in alignment of teeth:
- Abnormal overjet and overbite
- Open bite
- Effecting other structures:
- Cleft lip and palate
- High arched palate
- Bimaxillary protrusion
- Bimaxillary atresia
- Syndromes associated with it:
- Down’s syndrome
- Gardner’s syndrome
- Marfan’s syndrome
- Cleidocranial dysplasia
- Mandibulo facial dysostosis
- General conditions:
- Cherubism
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Retarded tooth eruption
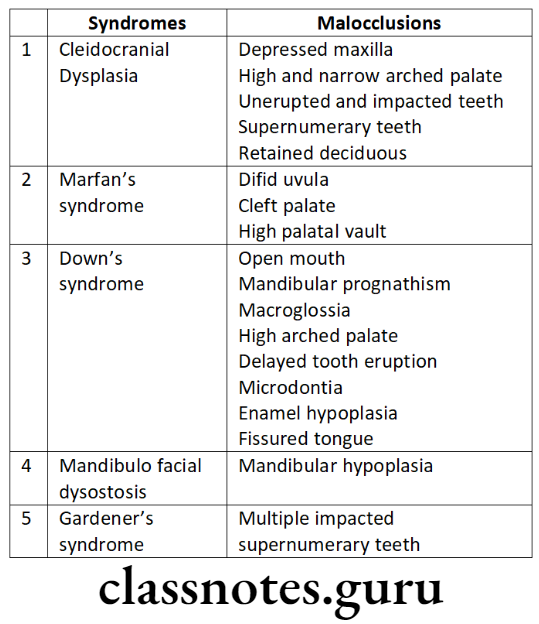
Question 3. Syndromes and malocclusions.
Answer.
Genetics In Orthodontics Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Genetic Counselling.
Answer.
It is communication between the counsellor and the patients having hereditary disease which enables the parents to decide to continue pregnancy/to abort
- It is carried out only between counsellor and parents’ confidential
- Decisions must be on the patient, the counsellor must not force the patient
- Counsellor must be confirmed about the diagnosis and severity of the disease
- Counsellor must reveal all the possible sequelae of the hereditary diseases
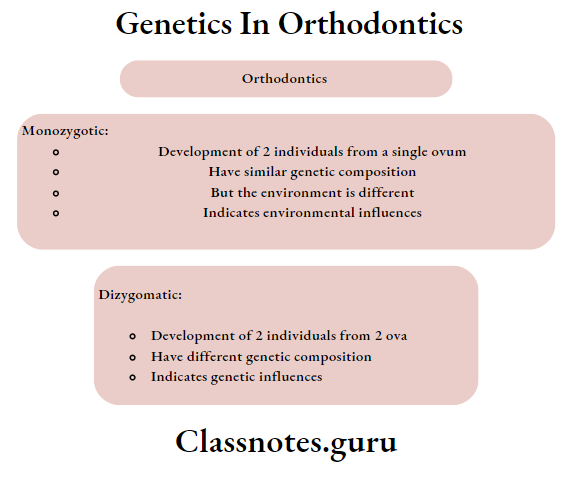
Question 2. Twin Studies
Answer.
It involves the study of human things
Human twins are of 2 types