NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj
NCERT Question And Answers
Question 1. What problem did the villagers in Hardas village face? What did they do to solve this problem?
Answer:
- The villagers in Hardas village faced the problem of water. This problem has become very acute. The water level in the hand pump was below the point to which the ground was drilled.
- Also, there was no water in the taps and the women had to go to the Suru River to get water. They solved this problem by deepening two handpumps and cleaning one well.
- They sought information about the scheme of watershed development from the Block Development Officer.
Question 2. What, in your opinion, is the importance of the Gram Sabha? Do you think all members should attend Gram Sabha meetings? Why?
Answer:
In my opinion, the importance of the Gram Sabha is
- The Gram Sabha is the elected body at the village level. It seeks to develop the programs for the village. It controls the funds received by the Gram Panchayat.
- The Gram Sabha is a key factor in making the Gr Panchayat play its role and be responsible.
- Yes, I think all members should attend the meeting of the Gram Sabha because it works for the welfare of the village and people’s direct participation also influences the Gram Sabha to do for the welfare of the village.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Civics Chapter 4
Question 3. What is the link between a Gram Sabha and a Gram Panchayat?
Answer:
The link between a Gram Sabha and a Gram Panchayat are
- Gram Sabha is a meeting of all adult people who live in the area covered by the Panchayat.
- Members of the Gram Sabha elect the Gram Panchayat for a period of years.
- The Gram Panchayat’s Secretary is also the Secretary of Gram Sabha.
- The Gram Sabha is a key factor in the working of the Gram Panchayat.
- Gram Sabha prevents the Panchayat from doing wrong things like misusing money or favoring certain people.
Question 4. Take an example of any one task done by a Panchayat in your area/nearby rural area and find out the following
- Why it was taken up?
- Where does the money come from?
- Whether or not the work has been completed.
Answer:
- In my locality, Panchayat has taken up repairs of drains.
- It was taken up because the drains were in damaged condition. Dirty water was spreading onto the streets and busy roads.
- The money came from taxes, funds, grants, and donations.
- The work is in process, it will be finished by the end of the year.
Question 5. What Is the difference between a Gram Sabha and a Gram Panchayat?
The difference between a Gram Sabha And A Gram Panchayat is

Question 6. Read the following news item.
Nimone is a village on the Chauphula-Shirur road. Like many others, this village has also been facing a severe water shortage for the last few months villagers depend on tankers for all their needs. Bhagvan Mahadeo Lad (35) of this village was beaten with sticks, iron rods, and axes by a group of seven men.
The incident came to light when some villagers brought a badly injured Lad to hospital for treatment. In the FIR recorded by the police, Lad said that he was attacked when he insisted that the water in the tanker must be emptied into the storage tanks, constructed as part of the water supply scheme by Nimone Gram Panchayat so that there would be equal distribution of water. However, he alleged that the upper caste men were against this and told him that the tanker water was not meant for the lower castes. Adapted from Indian Express, 1st May, 2004.
(1) Why was Bhagvan beaten?
Answer:
Bhagavan was beaten because he asked to empty the water from the tanker into the storage tanks constructed as a part of the water supply scheme by Nimone Gram Panchayat so that there would be an equal distribution of water.
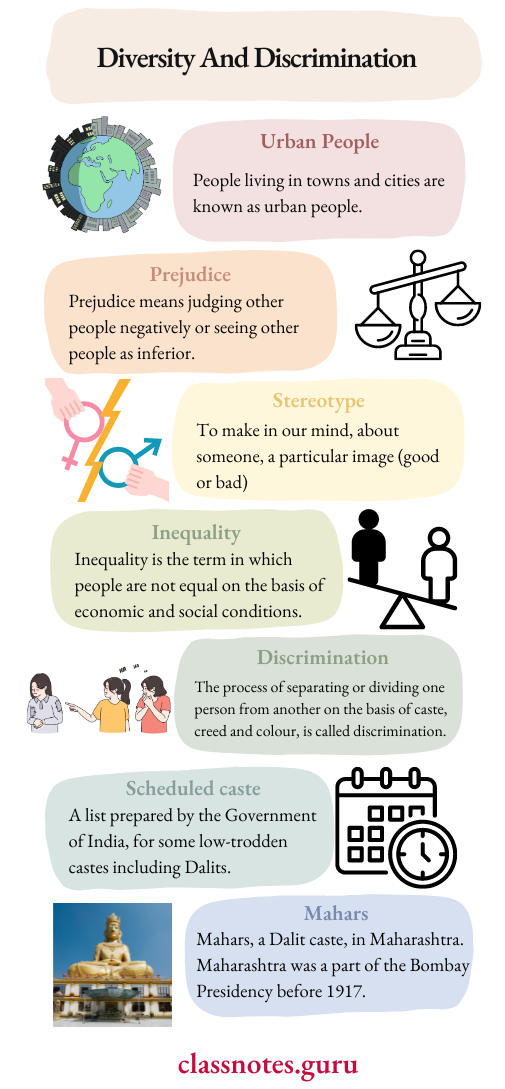
(2) Do you think that the above is a case of discrimination? Why?
Answer:
Yes, it is a clear case of discrimination as the Bhagavan was beaten because he insisted on fair distribution of water. This was because the higher caste men were against sharing water with the lower castes.
Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions
Question 7. Find out more about watershed development and how it benefits an area.
Answer:
The way of conserving water and recharging (refilling) is called watershed development.
It benefits an area in the following ways
- Trees are planted to check dams.
- Tanks are constructed to harvest rainwater.
- Barren lands are turned into green meadows.
- Water is easily available for drinking as well as for irrigation.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Who among the following Isa members of the Gram Sabha?
- Every citizen
- Villagers
- Every villager who has the right to vote
- President of India
Answer: 3. Every villager who has the right to vote
Question 2. The right to vote is given to any citizen above the age of
- 15
- 18
- 21
- 25
Answer: 2. 18
Question 3. Who Is the President of Gram Panchayat?
- Taluqdars
- Zamindars
- Sarpanch
- Mayor
Answer: 3. Sarpanch
Question 4. Who among the following elects the Panchayat President?
- Secretary
- Members of the Legislative Assembly
- Villagers
- Members of Gram Sabha
Answer: 4. Members of Gram Sabha
Question 5. Whose name should be Included In BPL families?
- Very poor person
- Middle-class family person
- High-income group
- All of these
Answer: 1. Very poor person
NCERT Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj
Question 6. Panchayat Samiti which level of a democratic government?
- Second level
- First level
- Fourth level
- Third level
Answer: 1. Second level
Question 7. Which of the following is the first tier of democratic government in rural areas?
- Gram Panchayat
- Panchayati Raj
- Zila Parishad
- Panchayat Samiti
Answer: 1. Gram Panchayat
Question 8. At which level does Zila Parishad actually make development plans?
- District level
- Village level
- Block level
- Central level
Answer: 1. District level
Question 9. Name the officer who implements the plans of Block Samiti.
- Tehsildar
- Patwari
- Sarpanch
- Block Development Officer
Answer: 4. Block Development Officer
Question 10. “Rahul wants to develop his village and build hospitals, and schools and provide water and electricity to his villagers’’. What according to you should be the best option for him to do these things?
- Enter politics as a member of Parliament.
- Enter politics as Sarpanch.
- Do not enter politics and do it by collecting donations.
- Do not enter politics and do it at his own expense.
Answer: 2. Enter politics as Sarpanch.
Question 11. Identify the level of government from the statements below.
- It facilitates participatory democracy.
- It promotes rural development.
- It implements government schemes and empowers communities at the district level in India.
Options
- Gram Sabha
- Mandal Parishad
- Zila Parishad
- State Government
Answer: 3. Zila Parishad
Question 12. Which of the following statements are correct regarding the Panchayati Raj System?
- Zila Parishad is the apex body of the Panchayati Raj.
- Gram Panchayat has a system of direct election.
Codes
- 1 and 2
- Only 1
- Only 2
- None of these
Answer: 1. 1 and 2
NCERT Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj
Question 13. Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- Sarpanch appoints the Secretary of Gram Sabha.
- Gram Sabha has no role in making Gram Panchayat.
- Gram Sabha prevents the Panchayats from doing wrong things.
Codes
- 1,2 and 3
- Both 1 and 2
- Both 2 and 3
- Only 3
Answer: 2. Both 1 and 2
Question 14. Arrange the following levels of government from bottom to top.
- Zila Parishad
- Gram Panchayat
- Gram Sabha
Codes
- 1,2,3
- 2,1,3
- 3,2,1
- 2,3,1
Answer: 4. 2,3,1
Question 15. Arrange the following according to the level of power they hold in the Panchayati Raj System.
- Block Development Officer
- Sarpanch
- Panch
Codes:
- 1,2,3
- 3,2,1
- 2,3,1
- 3,1,2
Answer: 1. 1,2,3
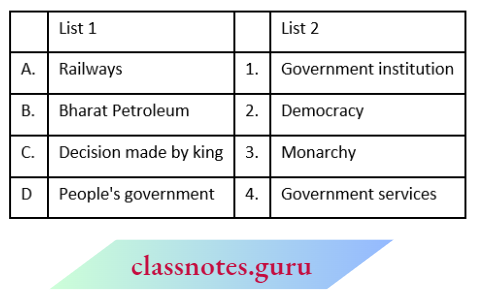
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Match The Following
Question:

Answer: 2.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Fill In The Blanks:
Question 1. The _____ problem in Hardas village has become very acute.
Answer: Water
Question 2. Amirchand was the earlier _______ of the village and still has control over a lot of _______.
Answer: Zamindar, Land
Question 3. With the help of Panchayat Samitis, ________ also regulates the money distribution.
Answer: Zila Parishad
Panchayati Raj Civics Class 6 Solutions
Question 4. The idea behind the Panchayati Raj System is to provide more and more space for people to ________ and _____ their voices.
Answer: Participate, Raise
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj True Or False
Question 1. The Gram Sabha forms committees to get the work done.
Answer: True
Question 2. The Zila Parishad actually makes development plans at the village level.
Answer: False
Question 3. Every village Panchayat is divided into wards, i.e. smaller areas.
Answer: True
Question 4. Sarpanch is directly elected by the members of the Gram Sabha.
Answer: True
Question 5. The Gram Panchayat does not collect local taxes
Answer: False
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Assertion Reason
Question 1. Assertion (A) Gram Sabha has many things to do like construction and maintenance of water bodies, roads, drainage, etc.
Reason (R) Gram Sabha collects taxes and receives government funds and donations.
Codes
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Roth A and R are true, but R Is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- A is false, but R is true
Answer: 2. Roth A and R are true, but R Is not the correct explanation of A
Question 2. Assertion (A) The Gram Sabha Secretary calls the meeting of Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat
Reason (R) The Gram Sabha Secretary is not elected but appointed by the Sarpanch.
Codes
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- A is false, but R is true
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Picture Based Questions
Question 1. Look at the picture given below and answer the question that follows.

The picture above is the scene of Gram Sabha discussing various things. Which of the following is not a work of Gram Sabha?
- Electing members of gram Panchayat
- Initiating development projects.
- Approving the budget of the government.
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
NCERT Solutions for Civics Chapter 4 Class 6
Question 2. Look at the picture below and mark the tier of government responsible for watershed management.

- First tier
- Second tier
- Third tier
- Fourth tier
Answer: 1. First tier
Question 3. Look at the picture given below and answer the questions that follow.

(1) Who is seen in the picture?
Answer:
The village Panchs from Maharashtra are seen in the picture.
(2) What award were they given?
Answer:
They were awarded with the Nirmal Gram Puruskar.
(3) When and why was this award given?
Answer:
This award was given in 2005 for the excellent work done by them in the Panchayat.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Case Based Questions And Answers
Question 1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions.
During a Gram Sabha meeting in Hardas village, Tijia highlights the severe water scarcity issue. A suggestion to pipe water from the Suru River is met with concerns about expenses. Tijia emphasizes the need for a long-term solution due to declining groundwater levels. Anwar suggests watershed development, mentioning government funding. The meeting also discusses the BPL lists; objections arise over wealthy individuals being included. After debates, Om Prakash, a genuinely needy person, is considered for inclusion. The Sarpanch instructs a re-evaluation of his income for eligibility.
(1) The main barrier to piped water from the Suru River was
- Distance from the village
- Lack of technical expertise
- Financial limitations
- Environmental concerns
Answer: 3. Financial limitations
(2) What solution is suggested for increasing the water supply in the village?
- Piping water from a distant river.
- Constructing check dams and tanks.
- Deepening handpumps and cleaning wells.
- Planting more trees in the village.
Answer: 1. Piping water from a distant river.
Panchayati Raj Civics Class 6 NCERT Notes
(3) What concept does Anwar introduce to the Gram Sabha as a possible solution for water conservation?
- Tree plantation
- Watershed development
- Education programmes
- Healthcare initiatives
Answer: 2. Watershed development
(4). The discussion on BPL lists highlighted the issue of
- Pension schemes for senior citizen
- Fund collection
- Involvement of ineligible people
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Involvement of ineligible people
Question 2. Read the passage given and answer the following questions.
- The Gram Sabha meeting begins with the Panchayat President (who is also called the Sarpanch) and the members of the Panchayat (the Panchs) presenting a plan for repairing the road that connects the village to the main highway. After this, the discussion moves to the subject of water and water shortages.
- A villager called Tijia begins the meeting by saying, “The water problem in Hardas has become very acute. The handpump water has gone well below the point up to which the ground has been drilled. We hardly get any water in the taps. Women have to go to the Suru River which is 3 km away to get water.”
- One of the members suggests piping water from the Suru and making an overhead tank in the village to increase the supply. But the others think that this will be expensive. It’s better, they feel, to deepen the handpumps and clean the wells for this season. Tijia says, “This is not enough”.
(1) What is described about the role of Gram Sabha in the above passage?
Answer:
From the above passage, we get to know that a Gram Sabha meeting is organized to discuss various needs and development projects to be taken up in the village. It also discusses new ideas and solutions to the problems.
(2) What problem can arise if there is a decline in the water level in handpumps?
Answer:
If the water level goes below the level of the hand pump it could create a shortage of water. The people would have to walk for long distances to bring water.
(3) Why piping water from Suru is not a sustainable option for the village?
Answer:
Piping water from the Suru River would require the construction of an overhead tank and this will prove to be expensive. Hence, it is not a sustainable option.
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 PDF
(4) Why is cleaning of wells and deepening of handpumps not enough?
Answer:
Cleaning of wells and deepening of handpumps is riot enough because it is a temporary option. The groundwater is going down every year. More water is used than is seeping into the ground.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Very Short Type Questions And Answers
Question 1. Who approves the list of people Below the Poverty Line (BPL) in a village?
Answer:
The Gram Sabha approves the list of people Below the Poverty Line (BPL) in the village.
Question 2. What are the three organs of the village Panchayat?
Answer:
Sarpanch, Panch and Secretary are the three organs of the village Panchayat.
Question 3. How are members of the village Panchayat elected?
Answer:
Members of the village Panchayat are elected through Universal Adult Franchise
Question 4. Who calls the meeting of the Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat?
Answer:
It is the Secretary, who calls the meeting of the Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat.
Question 5. Why is Nirmal Gram Puruskar awarded?
Answer:
The Nirmal Gram Puruskar is awarded to the village Panchs for the excellent work done in the Panchayat.
Question 6. Who received the Nirmal Gram Puruskar in 2005?
Answer:
This award was awarded to two village Panchs from Maharashtrain in 2005.
Question 7. Who is answerable to Gram Sabha?
Answer:
Gram Panchayat and Panchs are answerable to Gram Sabha.
Question 8. What is a Block Samiti?
Answer:
Block Samiti is called Panchayat Samiti or Janpad Panchayat under which many, Gram Panchayats work.
Question 9. How many levels of people’s participation are there In the Panchayati Raj System?
Answer:
There are three levels of people’s participation in the Panchayati Raj System, i.e. at the village level, at the block level, and at the district level.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Short Type Questions And Answers
Question 1. How is Gram Sabha important? Dlksha
Answer:
Gram Sabha is important for various reasons like
- It carries out functions like maintaining peace and order.
- It controls the work of village Panchayats.
- It helps in the implementation of developmental Programmes.
2. What is the work of Gram Panchayat in the Panchayati Raj System?
Answer:
The work of gram Panchayat in the Panchayati Raj System includes
- The construction and maintenance of water resources, roads, drainage, school buildings, and other common property resources.
- Levying and collecting local taxes.
- Executing government schemes related to generating employment in the village.
Question 3. From what sources does the Panchayat receive funds?
Answer:
The Panchayat receives funds from the following sources
- Collection of taxes on houses, marketplaces, etc.
- Government scheme funds are received through various departments of the government through the Janpad and Zila Panchayat.
- Donations for community works, etc.
Question 4. What are the three levels of Panchayats?
Answer:
Three levels of Panchayats are
- The Gram Panchayat is the first level of democratic government or the first tier of the Panchayats Raj system.
- The block level is the second level, which is also called the Janpad Panchayat or the Panchayat Samiti.
- The third level is the District Panchayat or the Zila Parishad, which makes developmental plans at the district level.
Question 5. What Is the importance of the Panchayati Raj system?
Answer:
The importance of the Panchayati Raj System is
- It teaches people the first lesson of democracy.
- It brings political awareness to rural India.
- People are able to solve their problems through mutual cooperation.
Question 6. Explain why we need local self-government.
Answer:
We need local self-government because
- To solve disputes among the villagers.
- To maintain peace in the village
- To have transparency between villagers and the government.
- To involve the people in the decision-making process.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Civics Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj Long Type Questions And Answers
Question 1. What do you mean by Gram Sabha? How can anybody Dlksha
Answer:
The Gram Sabha is a meeting of all adults who live in the area covered by a Panchayat. This area could include only one village or more than one village.
- To be a member of the Gram Sabha, one must meet the following criteria
- A person must be an adult, meaning a person must be at least 18 years old.
- A person must be a resident of the village or group of villages that the Gram Sabha represents.
- The name of the person must be included in the electoral rolls of the Gram Panchayat.
Question 2. Describe the composition of a Gram Panchayat.
Answer:
- Gram Panchayat is a basic governing institution in Indian villages. Every village Panchayat is divided into wards, i.e. smaller areas.
- Each ward elects a representative who is known as the Ward Member (Panch). The Ward Panchs and the Sarpanch form the Gram Panchayat.
- The Sarpanch is the Panchayat President who is elected by all the members of the Gram Sabha. The Gram Panchayat has a Secretary who is also the Secretary of the Gram Sabha.
- This person is not elected but appointed by the government. The Secretary is responsible for calling the meeting of the Gram Sabha and Gram Panchayat and keeping a record of the proceedings.
Question 3. “The Panchayat Samiti is the intermediate level of the Panchayati Raj System in India. It is responsible for the coordination of development activities at the block level and coordinates development activities at the block level, such as agriculture, education, health, and sanitation.” What is the main responsibility of the Panchayat
Samiti?
Answer:
- The Panchayat Samiti is the intermediate level of the Panchayati Raj System in India and is responsible for coordinating development activities at the block level.
- This includes agriculture, education, health, sanitation, and other important services. The Panchayat Samiti also plays a role in planning and implementing development projects and in monitoring the progress of these projects.
Chapter 4 Panchayati Raj NCERT Solutions
Question 4. A Gram Sabha discusses matters related to development projects, budgets, social welfare programs, etc. It is the primary body of the Panch.”
(1) What is the purpose of a Gram Sabha?
Answer:
A Gram Sabha is a village assembly where all adults can come together to discuss and decide on matters related to their community, such as development projects, budgets, and social welfare programs.
(2) What is the significance of the Gram Sabha in the Panchayati Raj System?
Answer:
- The Gram Sabha is the primary body of the Panchayati Raj System, which is a system of decentralized government in India.
- This means that the Gram Sabha has the power to make decisions about the development of its community, and its decisions are binding on the elected representatives of the Panchayati Raj.