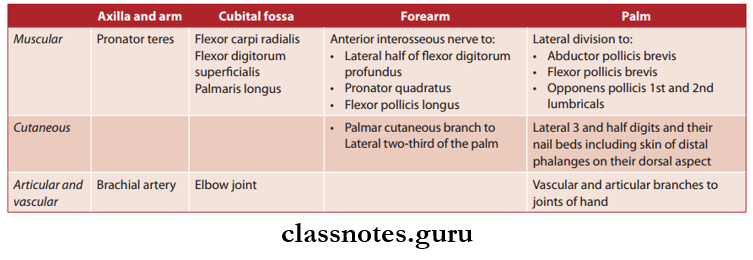
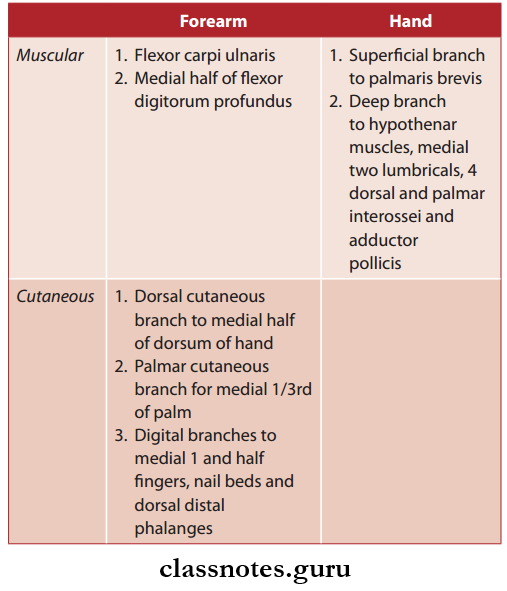
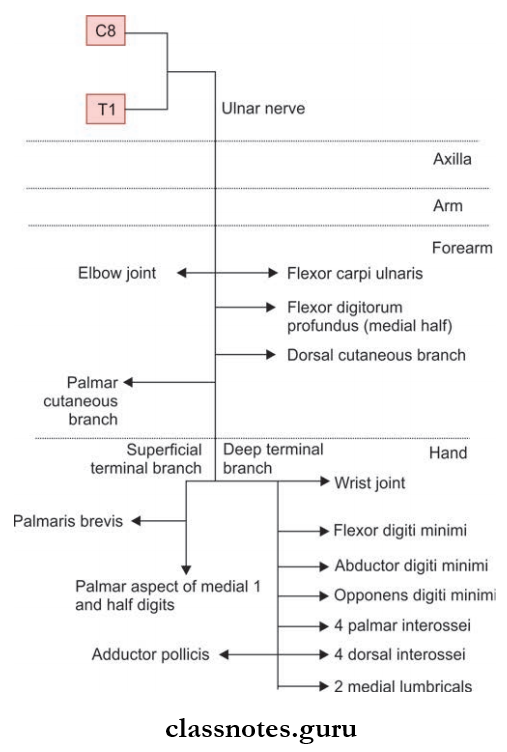
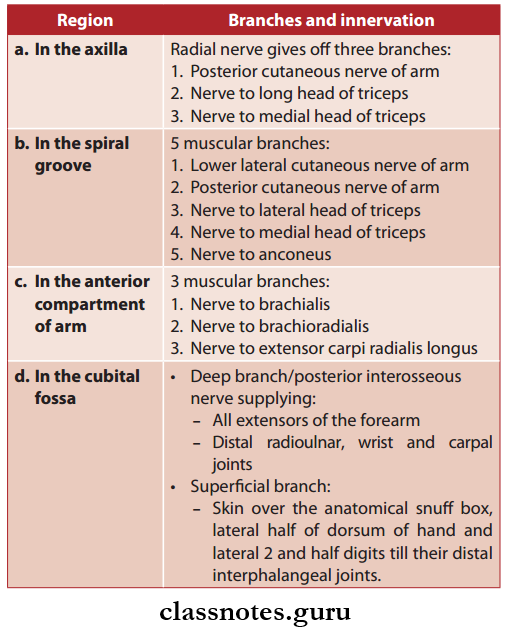
How Do Our Activities Affect The Environment?
Human beings are part ofthe environment. Our activities affect the environment. Changes in the environment affect us. Sahara and Thar deserts are the creation of excessive exploitation of resources by human beings.
By our activities, we are polluting air, water, and soil. Two of the major problems faced by humanity are ozone layer depletion and the disposal of waste we generate.
Ozone Layer And How Is It Getting Depleted?
How do our activities cause a depletion of the ozone layer?
Ozone (O3) is a triatomic molecule which is formed of 3 atoms of oxygen. Normal oxygen is diatomic (O2). It is essential for aerobic organisms. It is also essential for combustion or burning. However, ozone is a deadly poison. Luckily very little ozone is present in the lower part atmosphere or troposphere where we live.
A good quantity of ozone occurs in the upper part of the atmosphere called the stratosphere. Part of the stratosphere where ozone occurs in good quantity is called ozonosphere or ozone layer.
It lies at a height of 11-16 km above the poles and 23-25 km above the equator. As discovered by Molina (1992), ozone is formed in the stratosphere through the action of higher energy UV rays on oxygen.
Oxygen molecule splits up to form nascent or atomic oxygen [0]. Nascent or free oxygen atoms are highly reactive. They combine with diatomic normal oxygen molecules to form ozone molecules.
⇒ \(\begin{gathered}
\mathrm{O}_2 \xrightarrow{\mathrm{UV}}[\mathrm{O}]+[\mathrm{O}] \\
\mathrm{O}_2+[\mathrm{O}] \longrightarrow \mathrm{O}_3 \text { (ozone) }
\end{gathered}\)
Stratospheric ozone is highly protective. It filters out, rather than dissipates the energy of harmful UV radiations t 100 – 280 nm, UVB 280- 320 nm). UVA radiations (320- 390 nm) are allowed to pass down from the ozone layer an the earth.
They have some use in sun tanning and synthesis of vitamin D in the skin but excessive exposure is harmful to ozone Depletion. The amount of ozone present in the stratosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s.
A big 0 thinned ozone layer was discovered by Farman et al (1985) over Antarctica. By 2000, it covered an area of 28.3 million km2. Ozone has also thinned out in other areas. Some Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS).
They are substances that react with ozone and destroy the same, common ozone-depleting substances are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halon. Out of them, chlorofluorocarbon is used as refrigerants, coolants, foam-producing agents, solvents for cleaning, aerosol spray, propellants, tuning, etc. Halon is used as a fire extinguisher.
ODS rise from the surface of the earth and reach the stratosphere. By the action of UV radiations, chlorofluorocarbon splits up to release chlorine. Chlorine reacts with ozone to form chlorine monoxide and oxygen.
Class 10 Biology Effect of Human Activities on the Environment
Chlorine monoxide breaks to release oxygen and chlorine. The released chlorine reacts with fresh molecules of ozone. It is estimated that a single atom of chlorine can destroy one hundred thousand ozone molecules. It can persist in the stratosphere for upto 100 years.
⇒ \(\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{CCl}_2 \mathrm{~F}_2 & \longrightarrow \mathrm{CCIF}_2+\mathrm{Cl} \\
2 \mathrm{Cl}^2+\mathrm{O}_3 & \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{O}_2 \\
2 \mathrm{Cl}_2 \mathrm{O} & \longrightarrow 4 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{O}_2
\end{aligned}\)
It is estimated that a 1% reduction in the ozone layer increases the incidence of 2% more UV radiation reaching the earth.
Harmful Effects of Ozone Depletion.
- Skin Cancers. High-energy UV radiation reaching the earth will result in an increased number of skin cancers, skin aging, and herpes.
- Blinding. Cornea becomes swollen leading to what is called snow blindness. There will be an increased incidence of photobombing, dimming of eyesight, and cataracts.
- Immune System. It is weakened so that there is an increased incidence of diseases.
- Photosynthesis. It is reduced by 10-25%.
- Larval Deaths. They will increase especially in the aquatic animals.
- Mutations. The incidence of mutations shall increase. Most mutations are harmful.
International Efforts to Check Ozone Layer Damage
Montreal Protocol. In Montreal in 1987, UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) succeeded in getting an agreement from industrialized nations to limit the production of chlorofluorocarbons to the level of 1986.
Helsinki Declaration. In 1989, it was agreed to phase out the production of CFCs by the end of the 20th century.
Beijing Conference. In 1999, a fund was created with the help of UNEP, UNDP, and World Bank to help developing countries to phase out ozone-depleting substances.
Kigali (Rwanda) Conference (2016). All countries have given a time frame for phasing out ODS.
Effect of International Efforts
In 2004, the ozone hole over Antarctica was 28.3 million km2. It decreased to 27.5 million km2 in 2006, 25.0 million km2 in 2011, 21.0 million km2 in 2013 and 19.1 million km2 in 2017. The data indicates that the health of the ozone layer is improving every year.
Activity 5.6 Study of Ozone Layer Depletion.
With the help of the internet, newspapers, and libraries prepare a list of ozone-depleting chemicals.
What efforts have been made to control the emission ofthese chemicals? Have they been replaced or phased out? Have the efforts to reduce the damage to the ozone layer borne any fruit? The collected data shows that efforts at the international level to phase out ODS have borne fruit.
The ozone hole over Antarctica which was 28.3 million km2 in 2000 A.D., was reduced to 19.1 million km2 in 2017.
Chlorofluorocarbons are being replaced by hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCDFCs). They have shorter atmospheric life and deliver less active chlorine.
Managing the Garbage We Produce
What is Garbage? Suggest some measures to manage the garbage we produce. Garbage is solid waste from homes, vegetable markets, fruit markets, and food industries. Another source of garbage is disposables and packaging.
Disposables are used to check contamination. Decorative packagings are used to attract customers. Tourist spots are littered all around with such garbage.
It is estimated that an average Indian produces 0.5 kg of garbage per day while the higher group of individuals produces about 1.5 kg of waste. Garbage management is clean non-polluting and non-contaminating disposal of garbage.
It consists of collection, transport, and disposal of garbage. Stress is being laid to segregate the garbage into biodegradable (green bins) and nonbiodegradable (blue bins) waste. In some localities, even recyclable articles are also separated (in red bins).
- Pig and Cattle Feeding. Pigs and stray cattle feed on waste food particles and reduce the bulk of garbage.
- Rag Pickers. They pick up recyclable articles like polythene, plastic, glass, metallic waste, paper, cardboard, rags, and e-waste. The articles are sold to factories for recycling.
- Composting. Biodegradable waste is used in the preparation of manure and compost.
- Biogas. Farm and cattle waste is used to generate biogas and prepare manure.
- Incineration. Hazardous wastes (For example hospital wastes) are burnt in chambers fitted with devices to control gaseous and particulate emissions. Ash and unbumt matter are used in landfilling.
- Land Filling. Solid nonbiodegradable waste is dumped in a low-lying area. It is pulverized by machines and covered with soil, lime, or bleaching powder.
Activity 5.7 Waste Disposal
Watch the collection of your domestic waste. Which agency (Panchayat, Municipal Corporation, or some resident welfare Association) is involved in the collection, transport, and disposal of waste?
Does segregation of biodegradable (green bins) and nonbiodegradable (blue bins) occur in your house? If not where is the segregation carried out? Find out the sites and methods of their disposal (biodegradable by composting and nonbiodegradable by dumping or landfilling).
Class 10 Biology Notes on Environmental Impact of Human Activities
Activity 5.8 Amount of Waste
Daily weigh the garbage generated in your home for about two weeks. Make it a point to weigh the biodegradable mid-nonbiodegradable wastes separately. Calculate the waste generated per person. Similarly weigh tire waste generated by your class daily for about 15 days. Weigh the biodegradable and nonbiodegradable waste separately. Suggest some methods of their disposal, Biodegradable for compost formation. Nonbiodegradable tomunicipal vans for disposal.
Activity 5.9 Sewage and Industrial Waste
Sewage. Study the sewage treatment in your locality, town, city, and village. Is there a regular sewage treatment plant (STP)? Where is wastewater passed? How are waterbodies ofthe area protected from contamination by raw sewage?
Industrial Waste. Industries generate a lot of waste. Some of the wastes are recyclable. They are sent for recycling. Others are toxic and harmful to the environment. Find out modes of checking pollution by at least one industry. How are the soil and water bodies protected from pollution?
Disposable Cups
In older times tea was served in trains in reusable glasses. The problems of cleanliness and contamination are always there. They were solved with the introduction of disposable plastic cups. However, used cups could not be burnt as they would emit toxic fumes.
There is not enough space to bury millions of cups daily. The railway ministry then introduced burnt clay cups or hills as they could be broken and pulverized.
However, the manufacture of a very large number of kulaks and their transport posed a big problem. The use of fertile topsoil left many fields barren. The practice was, therefore, discontinued. Soon disposable paper cups became available.
They were the best option as used paper cups could be recycled, burnt down, and allowed to decompose. The present trend is now to use disposable plates, spoons, glasses, etc. at parties, religious functions, marriages, etc.
These functions also generate a lot of leftover food. Proper and hygienic disposal of these items causes a minimum adverse impact on the environment.
NCERT Class 10 Biology Human Impact on Environment
Activity 5.10 e-waste
e-waste is discarded electrical and electronic devices. Search the internet and library to prepare a list of commonly produced e-waste. Find out how these items are broken down to obtain useful articles.
Also find out the hazardous or toxic substances, a worker engaged in e-waste breakdown comes in contact with, for example, nickel, arsenic, cadmium, mercury, selenium, chromium, silicon, lead, beryllium, etc.
Plastic Recycling. Polythene and plastic can be recycled. However, the process of recycling involves the release of hydrocarbons and cancer-causing dioxin.








 `
`