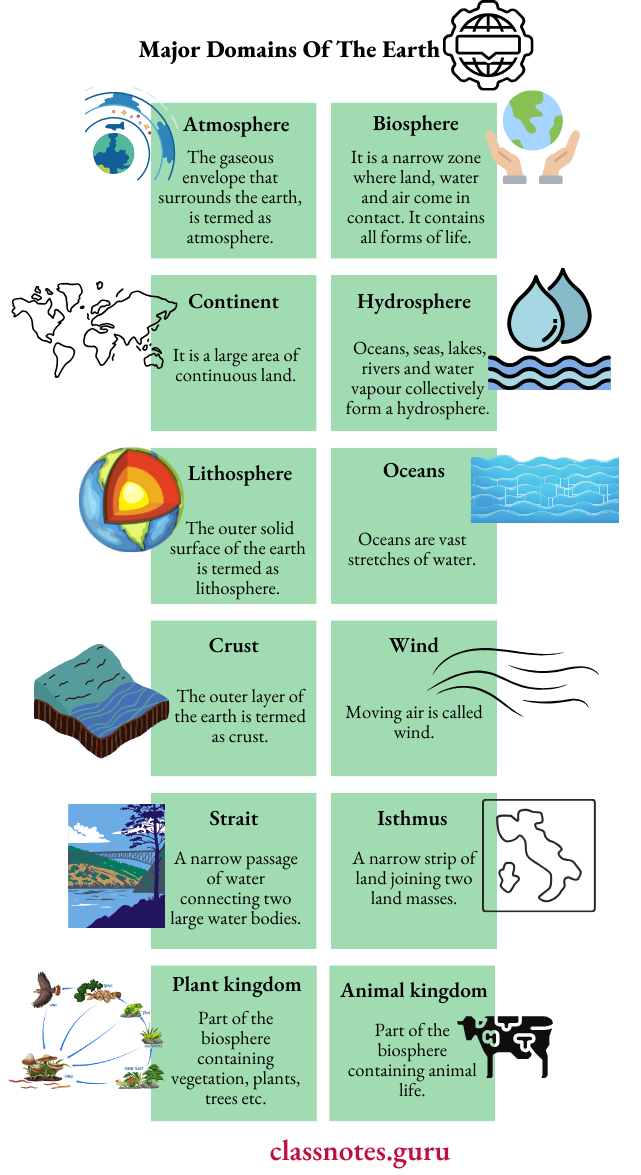
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering To Growing Food Exercises
Question 1. Complete the sentences
- Hunter-gatherers chose to live in caves and rock shelters because ________
- Grasslands developed around ______ years ago.
Answer:
- They provided shelter from the bad weather and wild animals.
- 12,000
Question 2. Why do people who grow crops have to stay in the same place for a long time?
Answer:
- People who grow crops have to stay in the same place for a long time to look after plants-protecting them from birds, and animals, and keep them, etc. so that they can grow crops or seeds could ripen safely.
- Settled life is useful and essential to lead a civilized life.
- People grow crops to meet their daily food and other needs.
From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
Read and Learn More NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science
Question 3. Why do archaeologists think that many people who lived in Mehrgarh were hunters to start with and that herding became more important later?Answer:
- Archaeologists who excavated the site of Mehrgarh found evidence of many kinds of animal bones from the earliest levels.
- Archaeologists included bones of wild animals such as deer and pigs.
- In later levels, they found more bones of sheep and goats.
- In still later levels, cattle bones are most common, suggesting that these were the animals that were kept generally by the people of Mehrgarh.
The people of Mehrgarh were hunters to start with and herding became more important later.

Question 4. Why did the hunter-gatherers travel from place to place? In what ways are these similar to/different from the reasons for which we travel today?
Answer:
- There were at least four to five reasons why hunter-gatherers moved from place to place.
- Animals moved from place to place—either in search of smaller prey or in the case of deer and wild cattle, in search of grass and leaves. That is why, those who hunted them had to follow their (i.e., animals) movements.
- Plants and trees bear fruit in different seasons. So, people might have moved from season to season in search of different types of fruits.
- People, plants, and animals need water to survive. Water is found in lakes, streams, and rivers. Many rivers and lakes are perennial (with water throughout the year) while others are seasonal. People living on seasonal river banks would have to go in search of water during the dry seasons (winter and summer).
- In the following ways, people move or travel differently from the regions nowadays.
- People nowadays travel from one place to another by bus, train, airplane, or car.
- Generally, they do not like to give up their place due to shortage of water or change of seasons. Rather they arrange water through the regular supply of water and they use electronic means (air-conditioners/fans/heaters etc.) according to seasons.
- People move from one place to another for better facilities for education, health, employment, business, tourism, etc.
Question 5. List three ways in which hunter-gatherers used fire. Would you use fire for any of these purposes today?
Answer:
- Hunter-gatherers used fire as a source of light.
- Hunter-gatherers used fire to cook meat or food,
- Hunter-gatherers used fire to scare away animals also.
- The fire kept them warm in winter.
Yes, fire is used as a source to cook food including meat.
We also use it to keep us warm. Some people use it for religious purposes like havans; and also to bum dead bodies.
Question 6. List three ways in which the lives of farmers and herders would have been different from those of hunter-gatherers.
Answer:
- The lives of farmers and herders had been different in the following ways:
- Farmers And Herders started leading a settled life instead of a nomadic life, like hunter-gatherers.
- Farmers And Herders became food producers instead of food gatherers. Domestication of plants and animals became part and parcel of the people of the Neolithic age.
- Different types of houses were built by farmers and herders. They used tools of different forms from the earlier Palaeolithic stage people. These include tools that were polished to give a fine cutting edge, and mortars and pestles used for grinding grain and other plant produce.
- Generally, farmers ate cooked and well-prepared foods, while on the other hand, hunter-gatherers ate uncooked food.
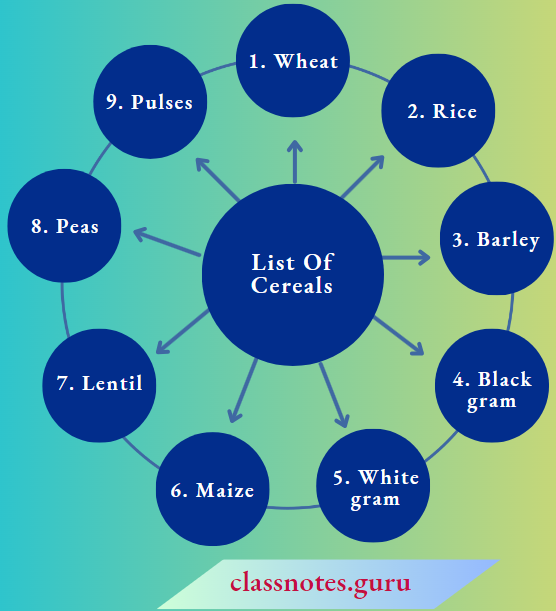
Question 7. List the cereals that you eat. Do you grow the cereals you eat? If yes, draw a chart to show the stages of growing them. If not, draw a chart to show how these cereals reach you from the farmers who grow them.
Answer:
List Of The Cereals:
Class 6 History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food Solutions
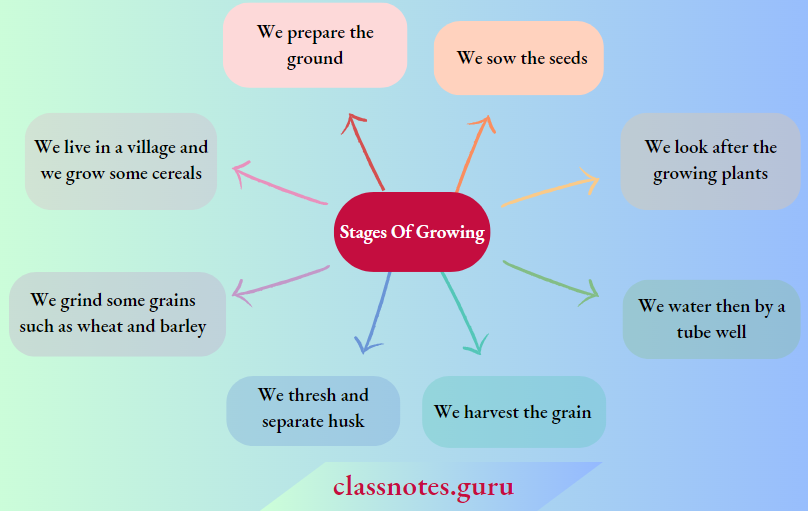
Yes, We Live In A Village And We Grow Some Of The Cereals. Chart Showing The Stages In Growing:
We Live In A Big City. We Do Not Grow Grain. We Get The Grains Indirectly From The Farmers.
- Farmers bring their produce to market.
- The grain traders buy cereals.
- We as customers go and purchase cereals from the traders.
Question 8. What do we use fire for today?
Answer:
Today fire is used for cooking, and keeping ourselves warm. In some communities, it is also used for religious purposes like having or burning the dead.
Question 9. Can you think of any reasons why the dog was perhaps the first animal to be tamed?
Answer:
The wild ancestor of the dog was the first animal to be tamed perhaps because it would have been relatively gentler than the rest and faithful to its owner.
Question 10. Do you think hunter-gatherers would have made and used pots? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
No, hunter-gatherers would not have made and used posts because
- Hunter-gatherers were not living a settled life and had no need for storage of food.
- Wheel or pottery making was not known till then.
Question 11. Apart from food, what are the other things that could have been obtained from animals? What are animals used for today?
Answer:
Apart from milk and meat as food, animals would have been used for
- Their hide, (skin)
- Protection, animals like dogs.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 2 Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering To Growing Food Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Do you know when trains were used first of all?
Answer:
Yes, I know that trains were first used about 200 years ago.
Question 2. When were the buses used first of all?
Answer:
People began using buses for about 90 days ago.
Question 3. Write the name given to the pre-historic age.
Answer:
Stone Age.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 2
Question 4. What is the Stone Age?
Or
Define Stone Age.
Answer:
In the pre-historic age or period when mainly tools, weapons, and implements made of stone were used, that period is known as the Stone Age.
Question 5. What do you mean by “Neolithic Age”?
Answer:
The word ‘Neo’ means ‘new’ and ‘Lithic’ means ‘stone’. We can say the meaning of “Neolithic Age” is “New Stone Age”.
Question 6. What is Flint?
Answer:
A flint is a hard grey stone that can produce a spark, whenever it is rubbed.
Question 7. Write the difference between seasonal and perennial water sources.
Answer:
Seasonal rivers, lakes, etc. have water only during the rainy season whereas the perennial sources have water throughout the year.
Question 8. What were the uses of wood in the past?
Answer:
In the past wood was used as firewood or to make shelters like huts. It was also used as a handle for tools and weapons.
Question 9. From where does most of our food come?
Answer:
Today, most of our food comes from plants that are grown and animals that are reared.
Question 10. Write the meaning of the word/term domestication of animal in brief.
Answer:
Domestication of animals means to tame animals.
Question 11. Name the first domesticated animal by the early man.
Answer:
Most probably “dog” was the first animal to be domesticated by early man.
Question 12. Write one of the characteristics of a village life.
Answer:
- One of the distinctive features (or characteristics) of village life is that most people who live there are engaged in food production (or farming).
- They also rear animals like cows, buffalo, goats, etc.
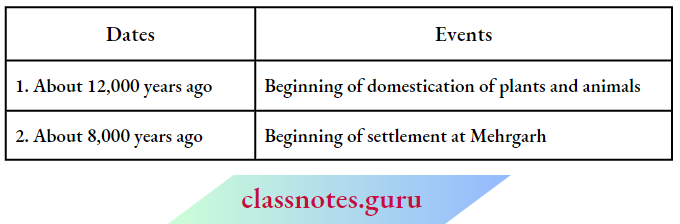
Question 13. Write important historical events against the following dates:
- About 12,000 years ago
- About 8,000 years ago
Answer:
Question 14. How was grain stored by the early settlers?
Answer:
Grain was stored in clay pots, woven baskets, or in the pits dug in the ground.
Question 15. Why were people buried with goats after death?
Answer:
People were buried with goats as it was believed that it would serve as food after death.
From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food: NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 2 Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering To Growing Food Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1 Who were the earliest people of the Indian subcontinent? Write a few lines about them.
Answer:
- The earliest people who lived in the Indian subcontinent as early as two million years ago were hunter-gatherers.
- The earliest people’s name comes from the way in which they got their food, by hunting wild animals, catching fish and birds, and by gathering fruits, roots, nuts, seeds, leaves, stalks, and eggs.
Question 2. Discuss in short the art of Rock Paintings done by the people of the early Stone Age.
Answer:
- Many of the caves in which the early people lived in the Palaeolithic and Mesolithic periods have paintings on the walls.
- Some of the best examples are from Madhya Pradesh and southern Uttar Pradesh.
- These paintings show wild animals, drawn with great accuracy and skill.
Question 3. What were the skills required by the hunter-gatherers?
Answer:
- Hunter-gatherers had to be faster and stronger than the animals they hunted.
- Hunter-gatherers had to be quick, alert, and fast at the time of hunting.
Question 4. How do we know that the early man was familiar with the use of fire?
Answer:
Traces of ash in the Kurnool caves indicate that the use of fire was known to the early man. Fire could have been used for warming, cooking or scaring animals.
Question 5. Discuss in short ‘the Beginning of Farming’.
Answer:
- The climate of the world was changing and so were plants that people used as food.
- People probably noticed several things:
- Where edible plants were found.
- How seeds broke off stalks.
- Fell on the ground and new plants sprouted from them, and so on.
Question 6. How did cultivation give a new way of life to the people or settled life?
Answer:
New Way of Life and Process of Farming
- When people began growing plants it meant that they had to stay in the same place for a long time looking after the plants, watering, weeding, and driving away animals and birds till the grain ripened. And then, the grain had to be used carefully.
- As grain had to be stored for both food and seed, people had to think of ways of storing it. In many years, they began making large clay pots, woven baskets, or dug pits into the ground.
- They also began to construct houses for storing grains and for living purposes.
Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food NCERT Class 6
Question 7. Discuss in brief the settled life of the earliest people of Burzahom (Kashmir) in the New Stone Age.
Or
Write a short note on “Towards a Settled Life in Burzahom”.
Answer:
Towards a Settled Life in Burzahom (Kashmir).
- Archaeologists have found traces of huts or houses at some sites. For example, in Burzahom (Kashmir) people built pit houses, which were dug into the ground, with steps leading into them. These might have provided shelter in cold weather.
- Archaeologists have also found fireplaces both inside and outside the huts which suggests that, depending on the weather people could cook food either indoors or outdoors.
Question 8. What do the scientists look for to decide whether a settlement is of farmers or herders?
Answer:
- Scientists study evidence of remains of plants and animals’ bones to decide whether a settlement is of farmers or herders.
- Findings of various types of burnt grains indicate that many crops were grown in different parts. So that indicates that the settlement is of farmers.
- Bones of different animals have been found at different levels (Mehrgarh) indicating which animals were kept by people. So, that settlement may be of herders.
Question 9. What do we mean by “rearing” animals?
Answer:
Animals multiply naturally and provide milk which is a source of food and meat. This means that animals that are reared can be used as food.
Question 10. Describe the changes that came with settled life.
Answer:
Many kinds of earthen pots have been found.
- Settled life were decorated and were used for storing or cooking food like rice, and lentils.
- Settled life weaving of cloth began using different materials such as cotton; cotton was being grown now.
- Hunting and gathering still continued along with herding and farming.
NCERT History Class 6 Chapter 2
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 2 Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering To Growing Food Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. How do we know about hunter-gatherers? Write about their tools.
Answer:
- Archaeologists have found some of the things that hunter-gatherers made and used. It is likely that people used tools of stone and bone, of which stone tools have survived best.
- Some of stone tools were used for cutting wood, which was used as firewood. Wood was also used to make huts and tools.
- Other stone tools were used to cut meat and bone, scrape bark and hides, and chop fruit and roots. Some may have been used attached to handle bone or wood, to make spears and arrows for hunting.
Question 2. What were the main effects of the changing environment on the rearing of animals and other activities?
Answer:
- Around 12,000 years ago, there were major climatic changes with a shift to relatively warm conditions.
- In many areas, this led to the development of grasslands, and animals that depended on grass, such as deer, antelope, goat, sheep, and cattle flourished.
- Those who hunted animals now followed them, learning about their food habits and their breeding seasons.
- It is likely that this helped people to start thinking about herding and rearing some animals themselves.
- Fishing also became an important activity of the people.
- This was also a time when several grain-bearing grasses, including wheat, barley, and rice, grew naturally in different parts of the subcontinent.
- Men, women, and children probably collected these grains as food, and learned where they grew, and when they ripened.
- This may have led them to think about growing plants on their own.
Question 3. Discuss in brief ‘The Beginning of Herding’.
Answer:
- The Beginning of Herding
- The climate of the world was changing and so were animals that people used as food.
- People could also attract and tame animals (after the beginning of farming) by leaving food for them near their shelters.
- The first animal to be tamed was the wild ancestor of the dog.
- Later, people encouraged animals that were relatively gentle, lived in herds, and ate grass, such as sheep, goats, cattle, and also pigs, to come near the camps where they lived.
- Often, they protected these animals from attacks by other wild animals.
Question 4. What do you understand by the term? What is the general effect of this process on plants and animals? What points were kept in mind before/during this process?
Answer:
- Meaning Of Domestication Domestication was the name given to the process in which people grew plants looked after animals and left them at a popular place.
- Effect Very often, animals that were tended by people become different from wild animals.
- This was because people selected plants and animals for domestication.
- Precautions Or Points Kept In Mind For Domestication
- People selected those plants and animals that are not prone to diseases.
- They also selected plants that yielded large grains and had strong stems, capable of bearing the weight of the ripe grain.
- Seeds from selected plants would preserved and sown to ensure that new plants (and seeds) will have the same qualities.
- Amongst animals, those that were relatively gentle were selected for breeding.
History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food Summary
Question 5. Discuss in brief the stone tools used by the people in the Neolithic age.
Answer:
- Stone Tools of the Neolithic Age
- Stone has been found on many sites related to the New Stone Age. Many of these are different from the earlier Palaeolithic tools.
- Stone tools of this stage of the Stone Age include tools that were polished to give a fine cutting edge, and mortars and pestles used for grinding grain and other plant produce.
- At the same time, tools of the Palaeolithic types continued to be made and used. Some tools were also made of bone.
Question 6. What were tribes? What is their importance?
Answer:
Many of the farmers and hunters lived in groups called tribes.
- Usually, two or three generations live together.
- Farmers And Hunters followed occupations like hunting, gathering, farming, herding, and fishing.
- Agricultural work was done by the women and children.
- Thrashing, husking grinding, etc. was also done by the women.
- Animals were looked after by the men.
- Both men and women did weaving and made tools, huts, etc.
- Farmers And Hunters took part in dancing and singing.
- Farmers And Hunters decorated their houses and articles.
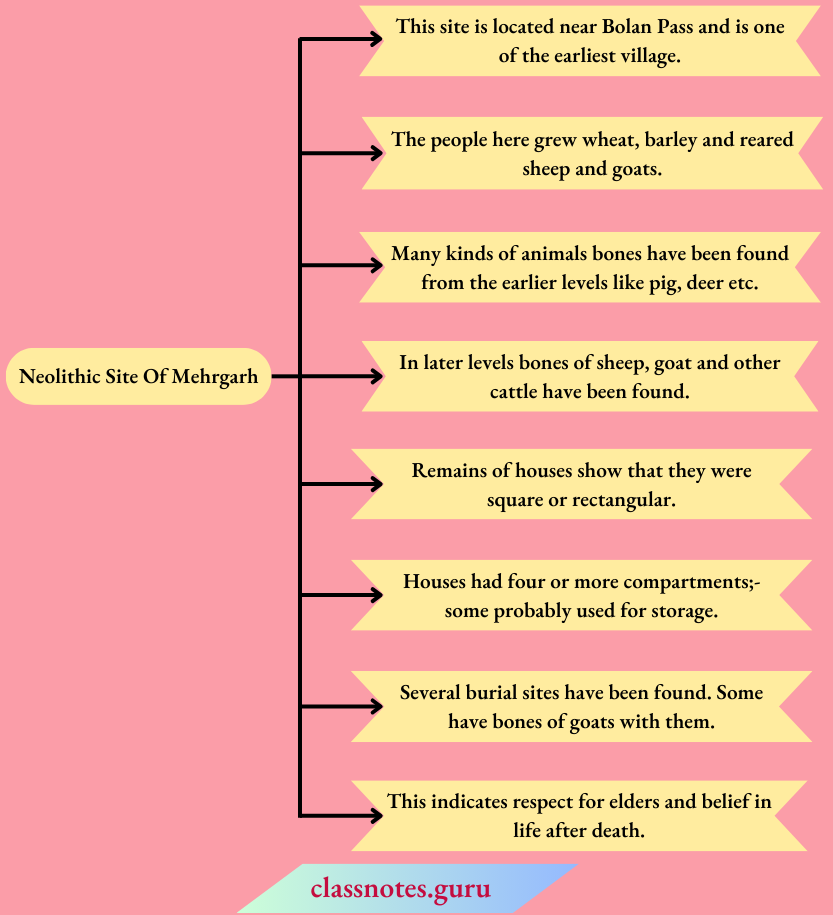
Question 7. Describe the Neolithic site of Mehrgarh.
Answer:
This site is located near Bolan Pass and is one of the earliest villages.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 2 Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering To Growing Food Multiple Choice Questions
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1. When were the trains used first in the world?
- 200 years ago
- 250 years ago
- 150 years ago
- 300 years ago
Answer: 3. 150 years ago
Question 2. Why do hunter-gatherers move from place to place?
- In search of food
- In search of water
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 3. How did the ancient people travel?
- By buses
- By trains
- By ships
- On foot
Answer: 4. On foot
From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food History Chapter 2 Study Material
Question 4. Who had found the things which were made and used by the hunters?
- Astrologists
- Archaeologists
- Psychologists
- None of these
Answer: 2. Archaeologists
Question 5. In ancient times tools were made up of which material?
- Stone
- Wood
- Bone
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 6. For what purpose were the stone tools used?
- To cut meat and bone
- To chop fruits and roots
- To make spears and arrow
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 7. When did the domestication begin?
- About 12,000 years ago
- About 8,000 years ago
- About 6,000 years ago
- About 4,000 years ago
Answer: 1. About 12,000 years ago
Question 8. What is indicated by traces of ash?
- Use of water
- Use of tools
- Use of fire
- All of these
Answer: 3. Use of fire
Question 9. For what purpose did the men, women, and children collect the grains?
- For food
- For growing crops
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Question 10. What was the Mesolithic period?
- 6000-7000 years ago
- 7000-8000 years ago
- 8000-9000 years ago
- 12,000-10,000 years ago
Answer: 4. 12,000-10,000 years ago
Question 11. What type of food do we get from plants?
- Milk
- Meat
- Fruits, vegetables, and grains
- None of these
Answer: 3. Fruits, vegetables, and grains
Question 12. Name the animal that gives us milk.
- Cow
- Goat
- Sheep
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 13. Select the animal that was the first to be domesticated.
- Lion
- Bear
- Dog
- Elephant
Answer: 3. Dog
Question 14. Where is the evidence of wheat, barley, sheep, goat, and cattle found?
- Koldihwa (UP)
- Gulf Krai (Kashmir)
- Mehrgarh (Pakistan)
- Hallur (Andhra Pradesh)
Answer: 3. Mehrgarh (Pakistan)
Question 15. Which of the following is an important source of milk and meat?
- Tiger
- Dog
- Goat
- Cat
Answer: 3. Goat
Question 16. Where is Mehrgarh located today?
- Uttar Pradesh
- Andhra Pradesh
- Pakistan
- China
Answer: 3. Pakistan
Question 17. In ancient times dead persons were buried with goats which means:
- To serve as food in the next life
- To serve as food in the present life
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 1. To serve as food in the next life
Class 6 History Chapter 2 NCERT Solutions: Key Points
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 2 Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering To Growing Food Objective Type Questions
Question 1. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1. ______ was used to make tools and huts.
Answer: Wood
2. Grain bearing grasses like _____, rice and ________ grew in different parts of the subcontinent.
Answer: Wheat, barley
3. Grasslands led to an increase in a number of ______ that survived on grass.
Answer: Animals
4. Bhimbetka is located in the present-day state of _______
Answer: Madhya Pradesh
5. _____ and _______ were considered gentler animals.
Answer: Sheep, goat, pig, or cattle (any two)
6. Dead people in Mehrgarh were buried with ________
Answer: Goat
7. Houses in Mehrgarh were ________ or ________ in shape.
Answer: Square, rectangular
Question 2. State whether the given statements are true or false.
1. Grasslands developed around 12,000 years ago.
Answer: True
2. Some of the best examples of rock paintings are from Madhya Pradesh.
Answer: True
3. Palaeolithic site Hunsgi is in Karnataka.
Answer: True
4. The climate of the world changed to colder conditions around 12,000 years ago.
Answer: True
5. The Palaeolithic age was immediately followed by the Neolithic age.
Answer: False
6. Pit houses were found in Burzahom.
Answer: True
NCERT Solutions Class 6 History Chapter 2 From Hunting Gathering to Growing Food
7. The first animal to be tamed was a goat.
Answer: False
8. Grain was stored in jute bags.
Answer: False
9. Palaeolithic tools were still made and used in the Neolithic period.
Answer: True
10. Bones from different levels in Mehrgarh indicate herding came after hunting.
Answer: True
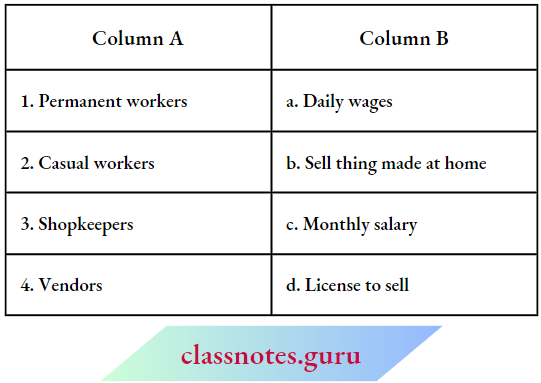
Question 3. Match the content of Column A with that of Column B
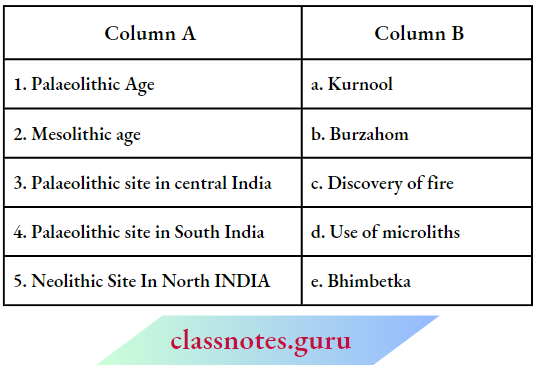
Answer: 1-(c), 2-(d), 3-(e), 4-(a), 5-(b)