Skeletal Maturity Indicators Important Notes
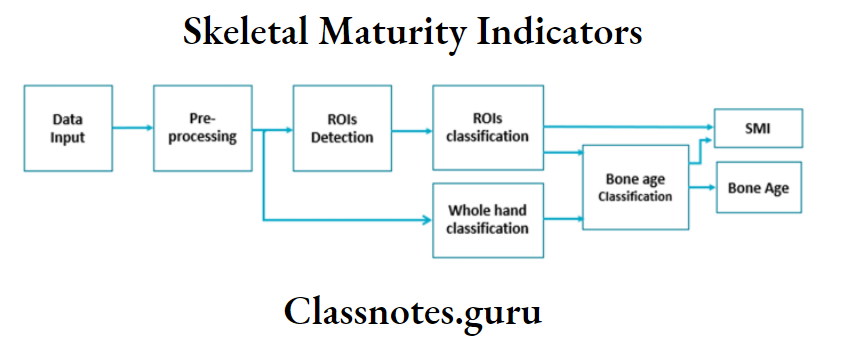
- Skeletal maturity indicators
- Hand wrist radiographs
- Skeletal maturation using cervical vertebrae
- Clinical and radiographic examination of stages of tooth development
- Fishman’s skeletal maturity indicator
- It evaluates hand-wrist radiographs making use of anatomical sites located on the thumb, third finger, fifth finger, and radius
- 11 skeletal maturity indicators were described covering the entire period of adolescent development
- Interpretation uses four stages of bone maturation
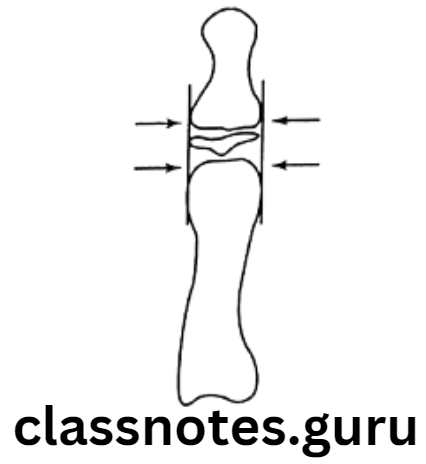
- Epiphysis equal in width to diaphysis
- Appearance of abductor sesamoid of the thumb
- Capping of epiphysis
- Fusion of epiphysis
Skeletal Maturity Indicators Short Essays
Question 1. Hand Wrist Radiograph.
Answer.
It is one of the skeletal maturity indicators
Significance Of Hand Wrist Radiograph:
- Describes ossification and union of small bones of hand and wrist
- Determines skeletal age of patients
Indications Of Hand Wrist Radiograph:
- In the discrepancy between dental and chronological age
- Determines the skeletal age of the patient
- Determines skeletal malocclusion
- Predict future skeletal growth
- Predict pubertal growth spurt
- Aid in research
- Assess the growth status of individual
Methods Of Hand Wrist Radiograph:
- Atlas method by Greulich and Pyle
- Bjork, Grave, and Brown’s method
- Fishman’s skeletal maturity indicator
- Hagg and Taranger’s method
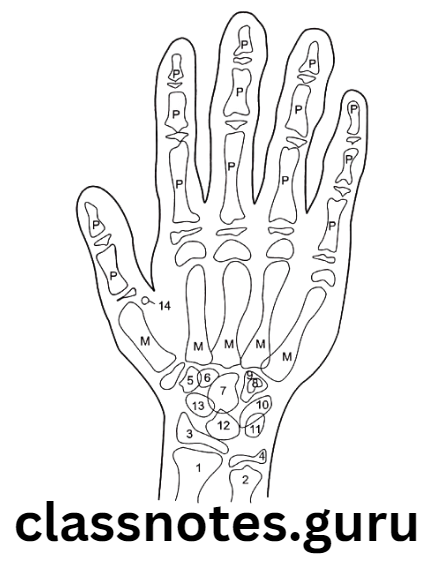
Anatomy Of Hand Wrist:
Consist of:
- Distal ends of long bones of the forearm
- Carpals
- Metacarpals
- Phalanges
Question 2. Maturity Indicators.
Answer.
Importance Of Maturity Indicators:
- Determine the stage of maturity
- Assess skeletal growth
- Decides the treatment planning
- Helps in objective diagnosis
- Assess different ossification centers
Methods Of Maturity Indicators:
- Hand wrist Radiograph
- Cervical vertebrae
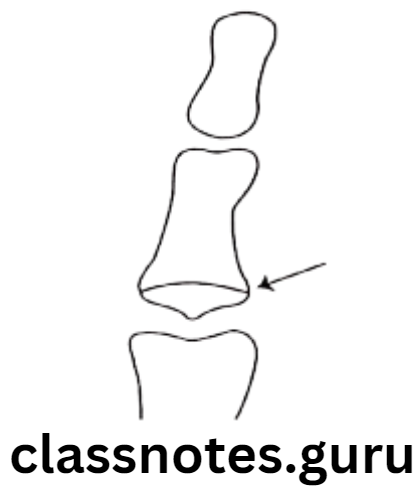
- By Hassel and Farman
- Shapes of cervical vertebrae determine stages of development
- Shapes of C3 and C4 are compared
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
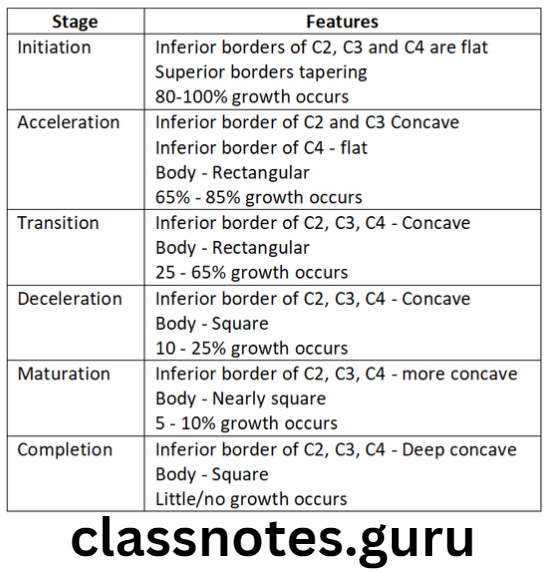
- Inferior vertebral borders were examined
- Flat – when immature
- Concave – when matured
- Six stages in vertebral development are viewed
- Inferior vertebral borders were examined
- Tooth Mineralization
- Selected teeth – lower canine
- Calcification patterns and stages of mineralization are examined
- Maxillary sinus
- Frontal sinus
Question 3. Fishman’s Skeletal Maturity Indicators.
Answer.
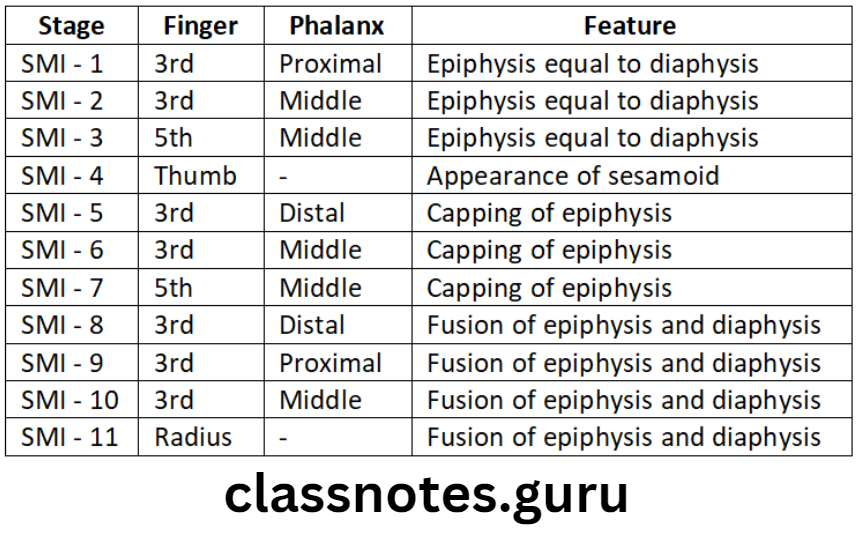
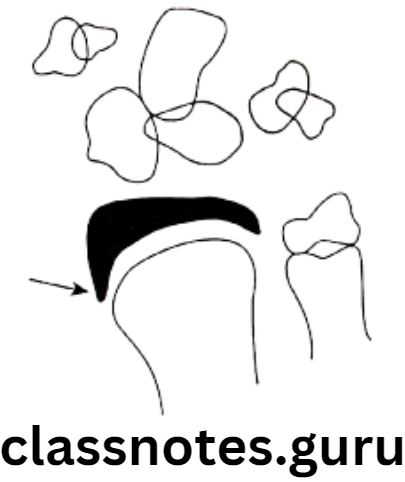
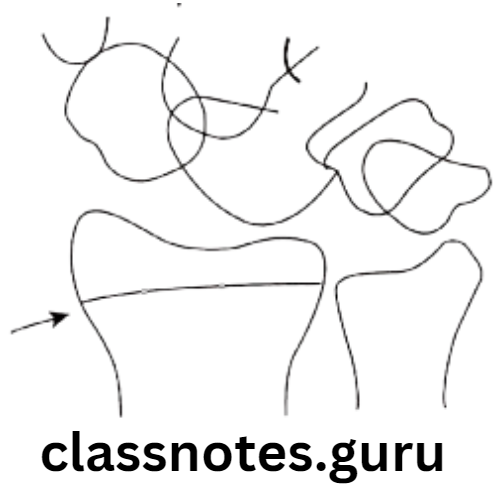
Skeletal Maturity Indicators Short Questions And Answers
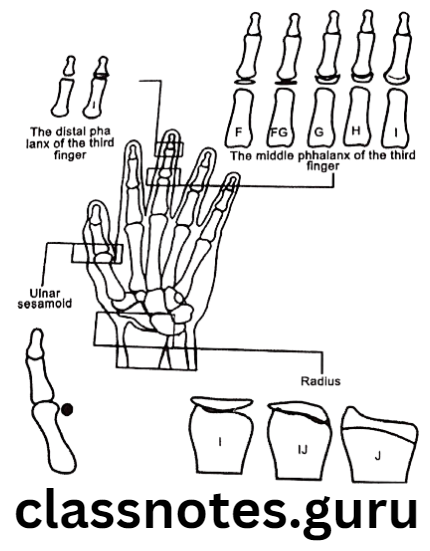
Question 1. MP 3.
Answer.
- Used in maturation assessment by Hagg and Taranger
- Describes changes in third finger middle phalanx

Question 2. Stages of Maturation using Cervical Vertebrae.
Answer.
Question 3. Carpal index.
Answer.
- One of the skeletal maturity indicator
- Used as a part of hand wrist
- Carpals – consist of eight small bones arranged in
- Proximal Row
- Scaphoid
- Lunate
- Triquetral
- Pisiform
- Distal row
- Trapezium
- Trapezoid
- Capitate
- Hamate
- These bones show specific patterns of appearance, ossification, and union
- These are compared with standards
- Proximal Row
Skeletal Maturity Indicators Viva Voce
- Skeletal age is useful throughout the post-natal growth period
- Dental age as a maturity indicator is useful from birth to early adolescence
- Morphological age as a maturity indicator is useful from late infancy to early adulthood
- 29 bones are included in the hand-wrist region
- The radius and ulna are long bones of the hawristist region there are 8 carpal bones in the hand wrist
- There are 5 metacarpal bones in the hand wrist
- Each digit of the hand has proximal middle and distal phalanges
- Sesamoid is small nodular bone
- There are 1 primary ossification center and one secondary ossification center for each metacarpal bone
