Scapular region consist of the muscles, intermuscular spaces, nerves, vessels, and anastomosis around the scapula.
Scapular Region Question And Answers
Question 1. Enumerate the muscles around the scapula.
Answer:
- They are originating from the scapula and inserted into the humerus, hence called scapulohumeral muscles.
- They are also called intrinsic shoulder muscles.
- They act on the glenohumeral joint.
- They are:
- Deltoid
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Teres major
- Teres minor
- Subscapularis.
Question 2. Write a note on deltoid muscle.
Answer:
Deltoid Muscle
- It is a thick, powerful, and curved triangular muscle covering the shoulder joint contributing to its rounded contour.
- It resembles the inverted Greek letter delta, hence the name
- Structurally it is divided into 3 parts:
- Clavicular part (unipennate)
- Acromion part (multipennate)
- Spinous part (unipennate)
Deltoid Muscle Origin
- Clavicular part (unipennate): Anterior part of lateral 1/3rd of clavicle
- Acromion part (multipennate): Lateral border of acromion
- Spinous part (unipennate): Lower lip spine of scapula
Deltoid Muscle Insertion
- Deltoid tuberosity of humerus
- Nerve Supply
- Accessory nerve
Read And Learn More: Anatomy Question And Answers
Deltoid Muscle Actions
- Anterior fibers: Flexion and medial rotation
- Middle fibers: Abduction of the arm
- Posterior fibers: Extension and medial rotation of arm

Deltoid Muscle Clinical Anatomy
- Intramuscular injections are given commonly in the lower half of the muscle to avoid injury to the axillary nerve which winds around the neck of the humerus under the muscle.
- In the shoulder region, injury to the supraspinatus tendon is common and the patient feels difficulty in the initiation of abduction of the shoulder joint.
- The tendon of supraspinatus may undergo degeneration and subsequent calcification as advances and results in rupture of tendon.
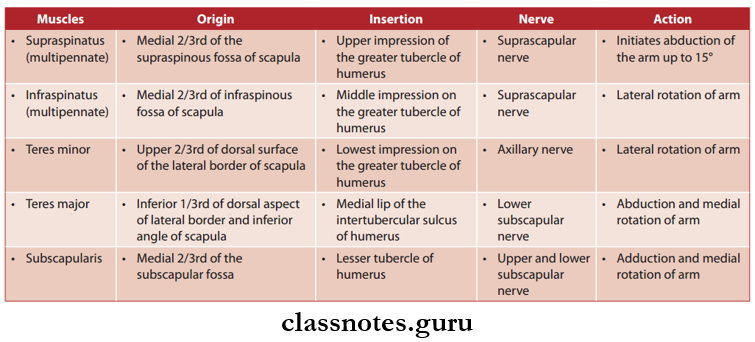
Question 3. Write about the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of the muscles around the scapula.
Answer:
Question 4. What is the rotator cuff or musculocutaneous cuff of the shoulder joint? Write about its formation and functions.
Answer:
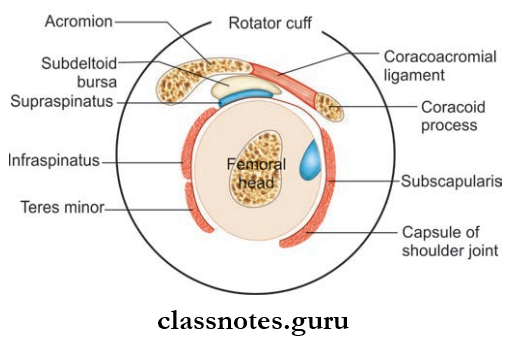
- It is a firous sheath formed by the flattened tendons of four scapulohumeral muscles.
- They are:
- Supraspinatus fusing superiorly
- Infraspinatus fusing posteriorly
- Tere minor fusing posteriorly
- Subscapularis fusing anteriorly
- It is blended with the capsule of shoulder joint.
Rotator cuff or Musculocutaneous cuff Functions
- It gives strength to the shoulder joint.
- It grasps and holds the relatively larger head of the humerus
- against smaller and shallower glenoid cavities.
Rotator cuff or Musculocutaneous cuff Clinical Anatomy
- The cuff is deficient inferiorly through which inferior dislocation of the humerus from the joint can take place more easily.
Mnemonic Rotator cuff muscles
- The SITS muscles:
- Clockwise from top:
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Teres minor
- Subscapularis
- A pro baseball pitcher has injured his rotator cuf muscles.
- As a result, he SITS out for the rest of the game and then gets sent to the minor leagues.
Question 5. Write a short note on subacromial bursa.
Answer:
- It is the largest bursa of the body.
- It is situated below the coracoacromial arch and the deltoid muscle.
- Under the bursa there are:
- Tendon of supraspinatus
- Greater trochanter of humerus.
Subacromial bursa Functions
- It protects supraspinatus tendons against friction with the acromion process.
- It facilitates the movements of the greater tubercle of the humerus under the acromion during overhead abduction.
Subacromial bursa Clinical Anatomy
- Subacromial bursitis commonly appears after inflammation of the supraspinatus tendon. It causes pain when pressure is applied just below the acromion.
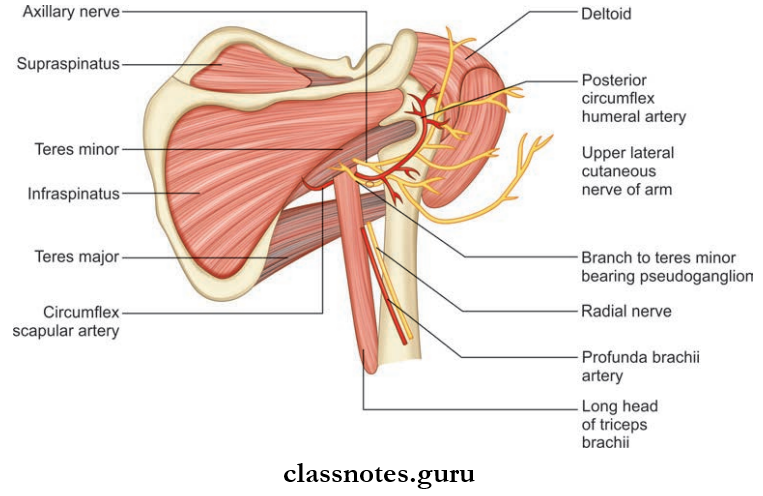
Question 6. List the intermuscular spaces with their boundaries and contents.
Answer:
- There are two triangular and one quadrangular space formed by the muscles in the scapular region.
- They are seen clearly from behind after reflecting the posterior part of the deltoid.
- They are:
Quadrangular Space Boundaries:
- Superior:
- Teres minor posteriorly
- Subscapularis anteriorly
- The capsule of the shoulder joint between the above two muscles
- Inferior: Teres major
- Medial: Long head of triceps
- Lateral: Surgical neck of humerus.
Structures passing through quadrangular space:
- Axillary nerve
- Posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein.
Upper Triangular Space Boundaries
- Superior: Teres minor
- Lateral: Long head of triceps
- Inferior: Teres major
Structures passing through upper triangular space:
- Circumflx scapular artery.
Lower Triangular Space Boundaries:
- Medial: Long head of triceps
- Lateral: Shaft of humerus
- Superior: Teres major.
Structures passing through lower triangular space:
- Radial nerve
- Profunda brachii artery and vein.
Scapular Region
Question 1. The following part of scapula forms the lateral most palpable landmark on the shoulder:
- Superior angle
- Glenoid cavity
- Coracoid process
- Acromion
Answer: 4. Acromion
Question 2. Subacromial bursa separates coracoacromial arch from the tendon of:
- Subscapularis
- Teres minor
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
Answer: 3. Supraspinatus
Question 3. Which of the following has actions similar to that of teres minor?
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Subscapularis
- Teres major
Answer: 2. Infraspinatus
Question 4. Which muscle does NOT substantially contribute to the stability of the shoulder joint?
- Subscapularis
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Teres minor
Answer: 1. Subscapularis
Question 5. Which is NOT a boundary of the quadrangular space?
- Teres major
- Teres minor
- Long head of triceps
- Latissimus dorsi
Answer: 4. Latissimus dorsi
