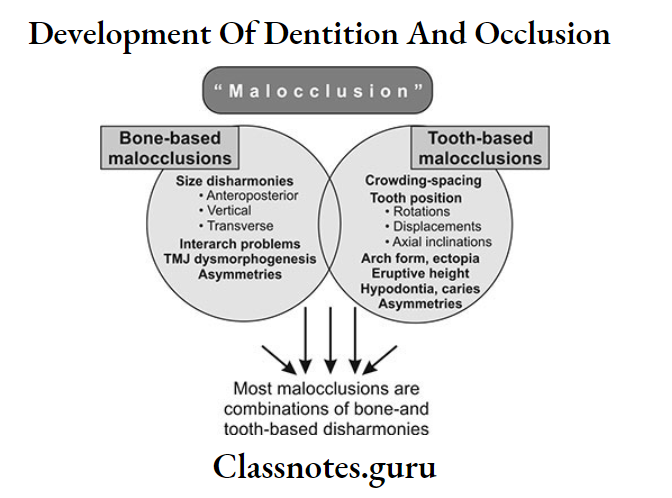
Etiology Of Malocclusion Important Notes
Causes of malocclusion:
- General Factors:
- Hereditary
- Congenital
- Environment – Prenatal, Postnatal
- Metabolic
- Nutritional
- Habits
- Posture
- Trauma and accidents
- Local Factors:
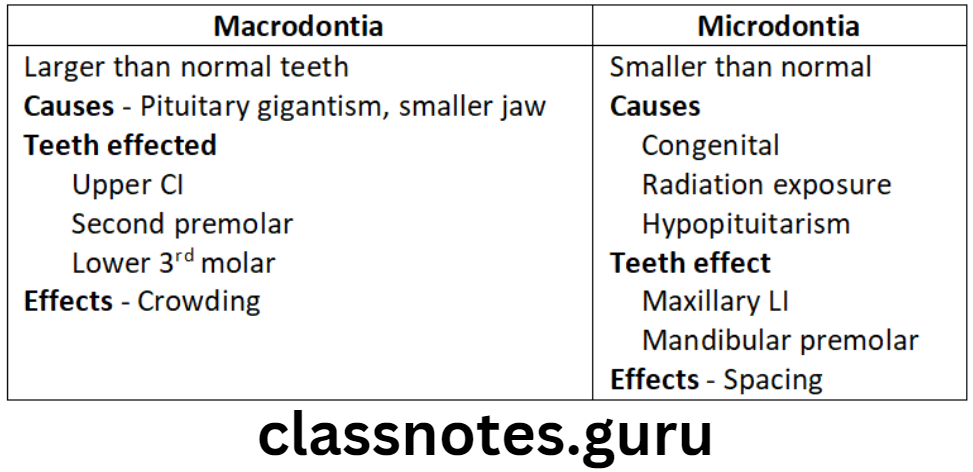
- Anomalies of number
- Anomalies of tooth size
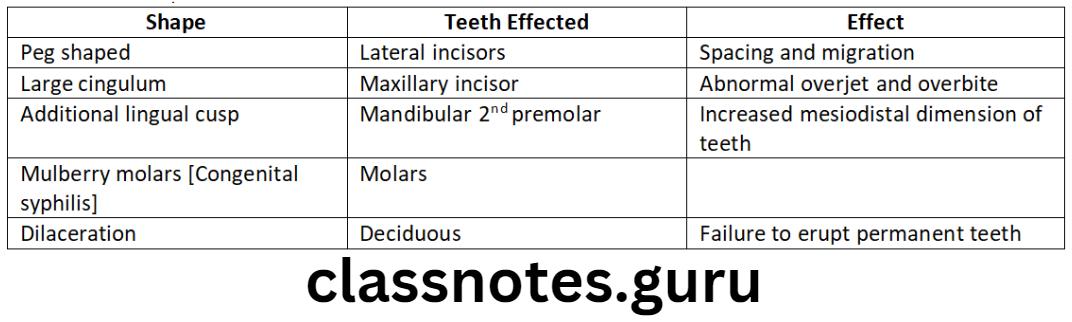
- Anomalies of tooth shape
- Abnormal labial frenum
- Abnormal eruptive path
- Premature loss of deciduous
- Prolonged retention of deciduous
- Delayed eruption of permanent teeth
- Ankylosis
- Dental caries
- Improper dental restoration
- Acromegaly features
- Accelerated development of mandible
- Hypercementosis
- Macroglossia
- Early eruption of dentition
Etiology Of Malocclusion Long Essays
Question 1. Classify various factors in etiology of malocclusion. Elaborate on endocrinal factors.
Answer.
Classification Of Etiology of Malocclusion: Graber’s classification
General Factors:
- Hereditary
- Congenital
- Environment – Prenatal, Postnatal
- Metabolic
- Nutritional
- Habits
- Posture
- Trauma and accidents
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Local Factors:
- Anomalies of number
- Anomalies of tooth size
- Anomalies of tooth shape
- Abnormal labial frenum
- Premature loss of deciduous
- Prolonged retention of deciduous
- Delayed eruption of permanent teeth
- Ankylosis
- Dental caries
- Improper dental restoration
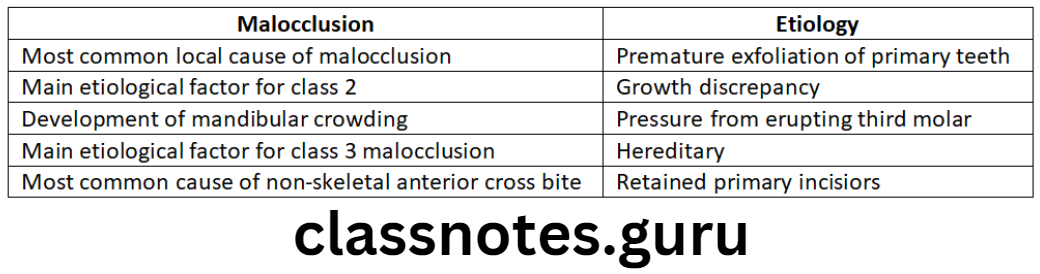
Endocrinal Imbalance Causing Malocclusion:
Disorders and their features:
Question 2. Discuss local of malocclusion./Discuss the environmental or local causes of malocclusion in detail.
Answer.
Local Causes:
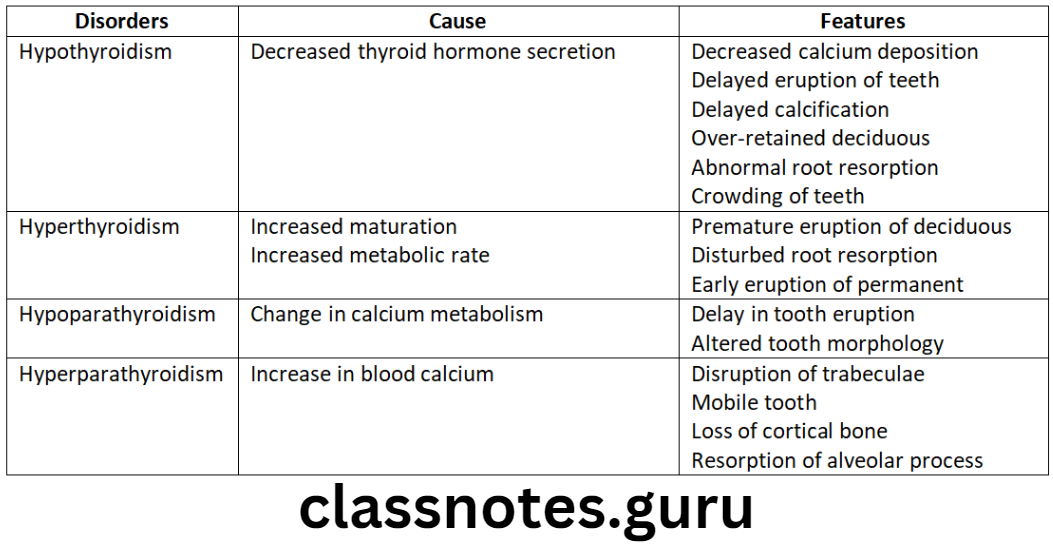
Anomalies in number of teeth:
- Normal no. of teeth should be present
- Extra/missing teeth creates malocclusion
- Anomalies of Tooth size: For normal occlusion harmony between tooth size and arch length must be present
- Anomalies of Tooth shape:
- Abnormal labial frenum: High frenal attachment of maxillary labial frenum causes midline diastema
- Premature loss of deciduous:
- Effects: Migration of adjacent teeth
- Prevent eruption of permanent successor
- May lead to impaction
- Effects: Migration of adjacent teeth
- Prolonged retention of deciduous teeth:
- Effects: Prevent eruption of permanent
- Abnormal eruptive path
- Effects: Prevent eruption of permanent
- Delayed Eruption of Permanent:
- Causes:
- Congenital
- Supernumerary teeth
- Mucosal barrier
- Premature loss of deciduous
- Endocrinal disorder
- Root fragments of deciduous
- Causes:
- Abnormal Eruptive path:
- Causes:
- Supernumerary teeth
- Impacted teeth
- Retained deciduous
- Bony barrier
- Causes:
- Ankylosis:
- Root surface is directly fused to bone
- Absence of PDL
- Causes:
- Trauma
- Infections
- Congenital
- Endocrinal disorders
- Effects:
- Causes submerge of teeth
- Migration of adjacent teeth
- Dental Caries:
- Effects:
- Premature loss of deciduous
- Migration of adjacent
- Decrease in arch length
- Effects:
- Abnormal axial inclination
- Supra-eruption of opposing teeth
- Improper Dental Restoration:
- Over contoured
- Effects:
- Functional shift of mandible
- Effects:
- Under-contoured
- Effects:
- Supra-eruption of opposing teeth
- Loss of arch length
- Food lodgement
- Periodontal weakening of teeth
- Effects:
- Over contoured
Etiology Of Malocclusion Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Ankylosis.
Answer.
- Root surface is directly fused to bone
- Absence of PDL
Causes Of Ankylosis:
- Trauma
- Infections
- Congenital
- Endocrinal disorders
Effects Of Ankylosis:
- Causes submerge of teeth
- Migration of adjacent teeth
Question 2. Abnormal labial frenum.
Answer.
- Abnormalities of maxillary labial frenum are quite often associated with maxillary midline spacing
- Rarely a heavy fibrous frenum is found attached to the interdental papilla region
- This can prevent the two maxillary central incisors
- Diagnosed by positive blanch test
- A midline IOPA or occlusal radiograph exhibits notching of the interdental alveolar crest
Question 3. Supernumerary teeth.
Answer.
Morphology: Different or resemble normal tooth (supplemental)
Size: Common in males
Site: Common in maxilla
Syndrome: Associated
- Cleidocranial dysplasia
- Gardener syndrome
Types Of Supernumeraty teeth:
- Mesiodens: Between central incisors
- Result: Midline spacing
- Distomolar: Beyond 3rdmolar
- Paramolar: In region of molar
Causes Of Supernumerary teeth:
- Non-eruption of adjacent teeth
- Deflect eruption
- Crowding
- Risk of cyst formation
Question 4. Prolonged retention of deciduous teeth.
Answer.
- Prolonged retention of anterior teeth
- Results in lingual or palatal eruption of their permanent successors
- Prolonged retention of posterior teeth
- Results in eruption of permanent teeth either bucally or lingually or remain impacted
Question 5. Premature loss of deciduous teeth.
Answer.
- It refers to loss of a tooth before its permanent successor is sufficiently advanced in development and eruption to occupy its place
- It can cause migration of adjacent teeth into the place and can therefore prevent the eruption of the permanent successor
- Severity of malocclusion depends on
- Premature loss of deciduous molars leading to shifting of adjacent teeth into space
- Early extraction of deciduous teeth
- Person with arch length deficiency and crowdling
Question 6. Prenatal causes of malocclusion.
Answer.
Prenatal causes of malocclusion:
- Abnormal fetal posture during gestation
- Maternal fibroids
- Amniotic lesions
- Maternal diet
- Maternal metabolism
- Maternal infections like German measles
- Teratogenic drugs
Question 7. Blanch Test.
Answer.
Use Of Blanch Test: For detection of high frenal attachment
Steps:
- Step 1: Upper lip is stretched
- Step 2: Upper lip is pulled outward and forward
- Step 3: Blanching seen beside the papilla
- Step 4: IOPA is taken i.r.t. 11 & 21
Etiology Of Malocclusion Viva Voce
- Early loss of deciduous teeth can cause migration of adjacent teeth into the space and thus prevent the eruption of permanent succesor
- Extra teeth in relation to the normal teeth is called supernumerary teeth
- Mesiodens are supernumerary teeth present between two central maxillary incisors
- Mesiodens are most common type of supernumerary teeth
- Supernumerary teeth present distal to the last molar is called distomolar
- Anamalous structure projecting from cingulum of maxillary permanent incisors is called Talon’s cusp
- Fusion occurs through union of two normally separated tooth gem
- Germination arises from division of single tooth germ
- Concrescence is fusion of teeth after completion of root formation
- Presence of notching and positive blanch test is diagnostic of abnormal thick labial frenum.