Types Of Immunity
- Innate immunity
- Acquired immunity
- Types
- Active immunity
- Natural active
- Artificial active
- Passive immunity
- Natural passive
- Artificial passive
- Active immunity
- Types
Immunity essay questions and answers
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question and Answers
Antigens
- Heterophile Antigen
- These are the same or closely related antigens present in different tissues of more than one species
- Haptens
- These are substances unable to induce antibody formation on its own but can be immunogenic when linked to carrier proteins
- Haptens is a partial/incomplete antigen
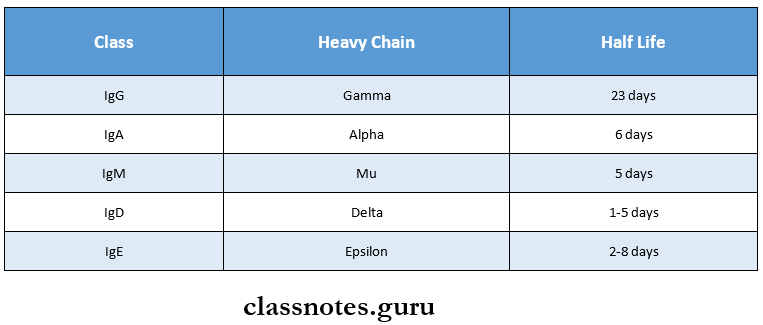
Immunoglobulin
- These are substances which are formed in serum in response to an antigen
- Immunoglobulin consists of two heavy chains and two light chains held together by disulphide bonds
Immunoglobulin Classes
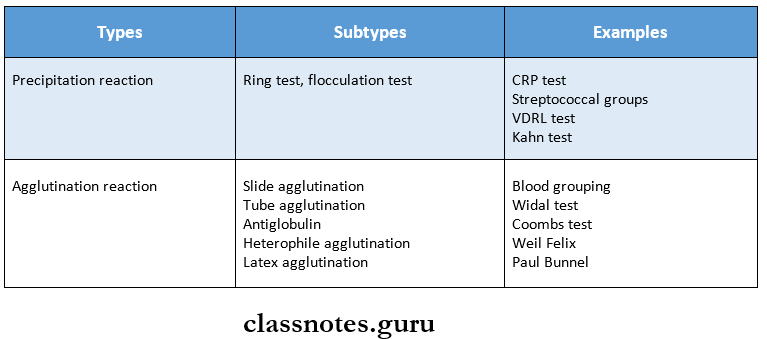
Types Of Antigen-Antibody Reactions
5. Complement
- Complement refers to a system of factors which occurs in normal serum and are activated by antigen-antibody reaction
- Complement is triggered by two parallel pathway
- Classical pathway
- Alternate pathway
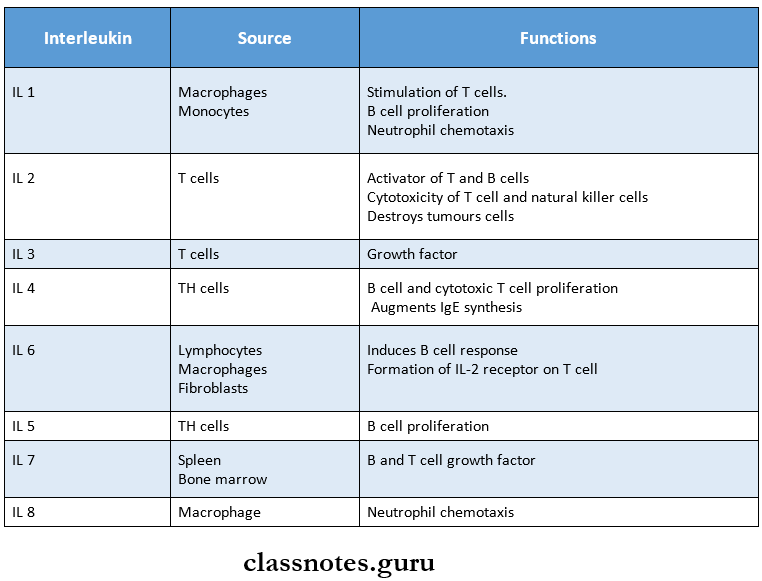
6. Interleukins (IL)
Immunity short and long answer questions
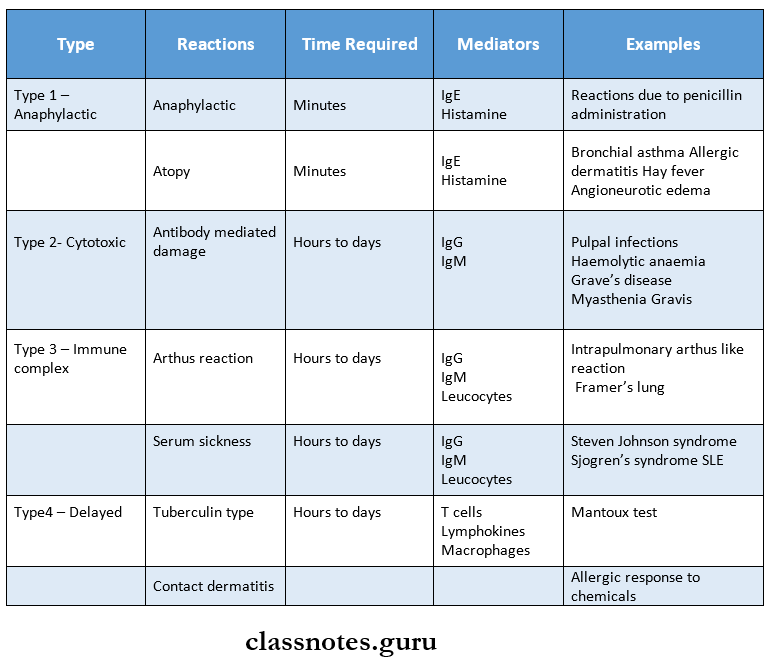
Hypersensitivity Reactions
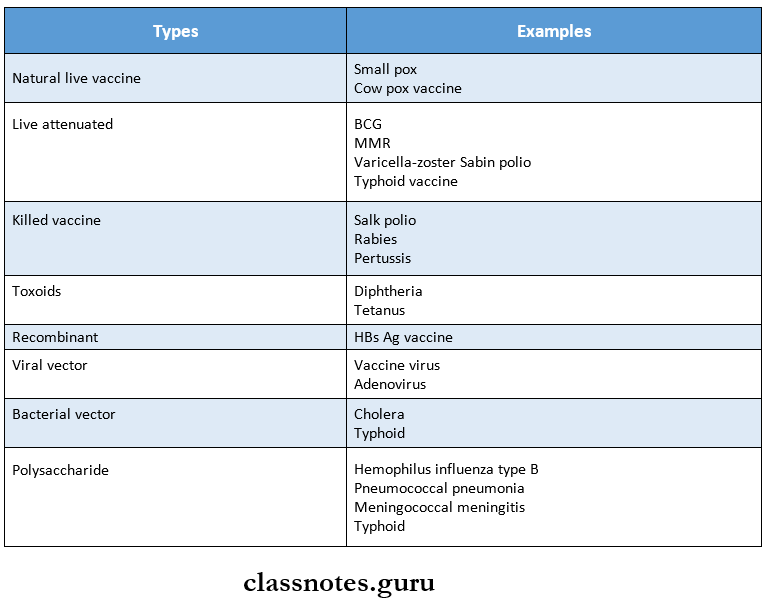
8. Vaccines
Types of immunity explained
Immunity
Question 1. Define and classify immunity. Discuss acquired immunity.
Answer:
Immunity Definition
1. Immunity:
- Immunity is defined as resistance exhibited by the host against any foreign antigen including micro-organisms.
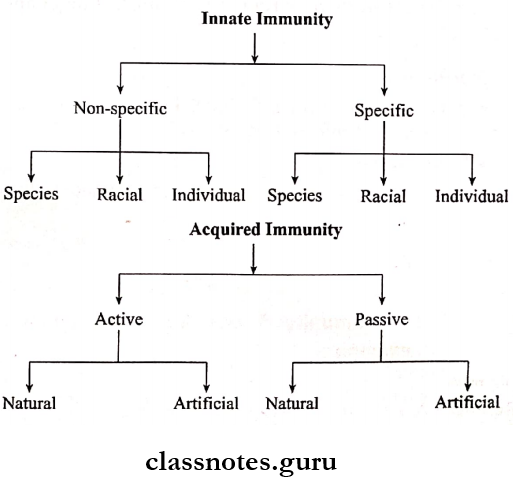
Immunity Classification
- Immunity may be classified into different types as follows.
Acquired immunity Definition
- Acquired immunity is the resistance acquired by an individual during life.
Acquired immunity Types:
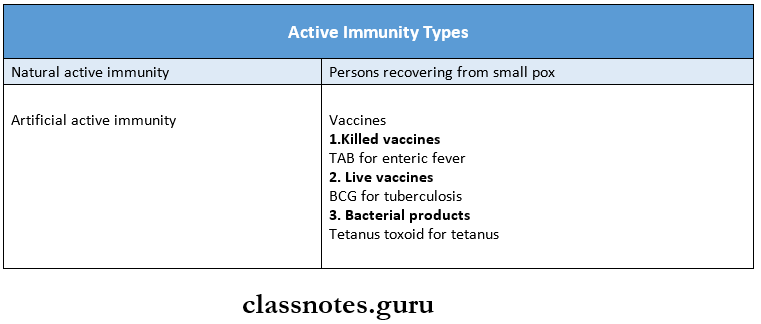
1. Active Immunity:
- Active Immunity is subdivided into two types.
- Natural Active Immunity.
- Acquired by natural subclinical or clinical infections.
- It is long-lasting.
- Example: A person recovering from smallpox develop natural active immunity.
- Artificial Active Immunity.
- Induced by vaccination.
- Natural Active Immunity.
Active Immunity Mechanism
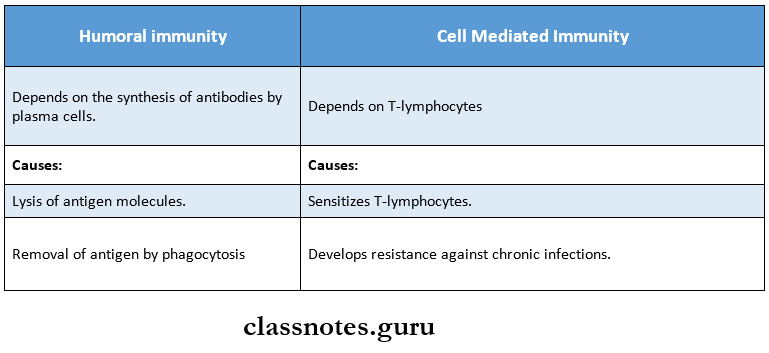
- Active immunity stimulates both humoral and cell-mediated immunity.
Innate and acquired immunity essay
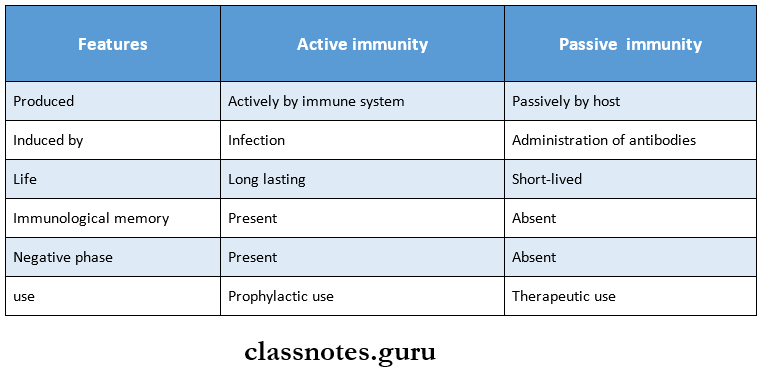
Passive Immunity
- Passive Immunity is subdivided into two types:
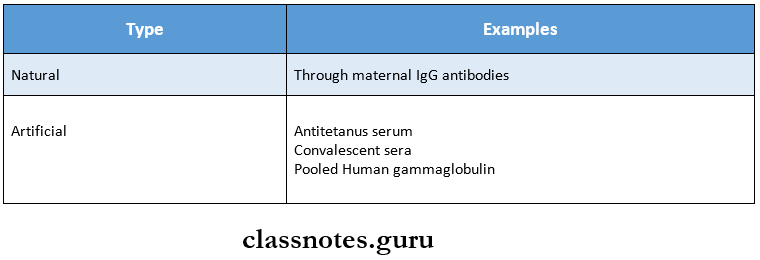
- Natural
- Immunity is transferred from mother to fetus transplacentally.
- Artificial
- Occurs through the parenteral administration of antibodies.
- Natural
Passive Immunity Mechanism
- Passive Immunity is induced in an individual by preformed vaccines against infective agents.
- Passive Immunity is short-lasting.
- Passive Immunity is used when immunity is required immediately.
Passive Immunity Uses
- To provide immediate short-term protection
- For suppression of active immunity.
- For treatment of serious infection
Innate immunity
Innate immunity Definition:
- Innate immunity is the resistance that individual possesses by birth.
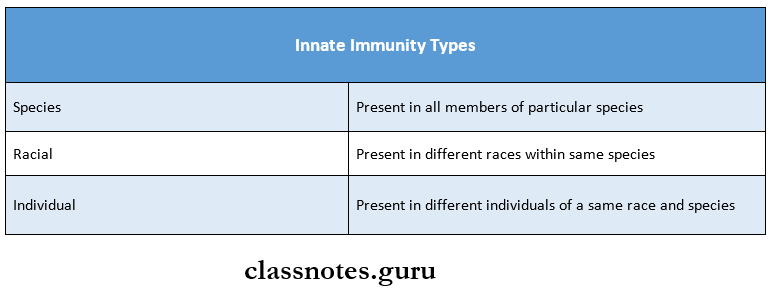
Innate Immunity Types:
- Factors influencing it:
1. Age:
- Infants have immature immunity, while during old age there is gradual decreases in immunity.
- This increases susceptibility to infections.
2. Hormones:
- Hormonal disorders may lead to increased susceptibility to infections.
3. Nutrition:
- Malnutrition predisposes to infections.
Innate Immunity Mechanism
1. Epithelial Surfaces:
- Skin.
- Act as a mechanical barrier to micro-organisms
- Provides bacteriocidal secretions.
- The resident bacterial flora prevents colonization by pathogens.
- Respiratory Tract.
- Nasal passages arrest the inhaled particles.
- The mucous secretions of the respiratory tract act as a trapping mechanism.
- Cilia help to propel the particles toward the pharynx.
- Intestinal Tract.
- Mouth – inhibits micro-organisms.
- Acidic gastric pH – destroys bacteria.
- Intestine – prevents colonization of bacteria,
- Conjunctiva.
- Tears flushes away bacteria and dust particles.
- Lysozyme present in tears has bacteriocidal actions.
- Genitourinary Tract.
- Urine eliminates bacteria.
- Vaginal secretions destroy pathogens.
- Semen contains antibacterial substances.
Antibacterial Substances
- Antibacterial Substances include properdin, complement, lysozyme, beta-lysin, basic polypeptides, and interferons.
3. Cellular Factors:
- Phagocytic cells ingest pathogenic organisms and de¬stroy them.
4. Inflammation:
- Inflammation is a non-specific defense mechanism.
- Inflammation phagocytoses and destroys micro-organisms.
5. Fever:
- Stimulates production of interferon
6. Acute Phase Proteins:
- Activate alternate pathways of complement.
Immunity BSc nursing notes
Types Of Active Immunity With Examples
Difference Between Active And Passive Immunity
Difference between innate and adaptive immunity
Two Examples Of Passive Immunity
Humoral and cell-mediated immunity essay
Antigen Definition
- The antigen is a substance which, when introduced into a body evokes an immune response to produce a specific antibody with which it reacts in an observable manner.
Antigen Types
1. Complete Antigen.
- These can induce antibody formation by themselves.
2. Complete Antigen.
- These can induce antibody formation by themselves.
3. Incomplete Antigen/Haptens.
- These are unable to induce antibody formation on their own.
- But can become immunogenic when they are covalently linked to carrier proteins.
