Miscellaneous Short Essays
Question 1. Odds ratio.
Answer:
Odds Ratio Definition:
Odds Ratio is a measure of the strength of the association between risk factors and outcome
Odds Ratio It Is Based On:
- The disease being investigated must be relatively rare. Example: Chronic disease
- The cases must be representative of those with the disease
- The controls must be representative of those without the disease
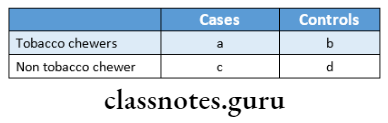
Odds Ratio Example:
If the odd’s ratio is 6.2- means the risk of oral cancer was 6.2 times greater in individuals in tobacco chewers than in non-chewers
Read And Learn More: Percentive Communitive Dentistry Question And Answers
Question 2. Tristan de Cunhan study.
Answer:
Tristan de Cunhan’s study
- It is a small remote island in the South Atlantic inhabited by people of European descent
- In the early 1960s volcanic eruption led to the evacuation of the entire community to England
- After a few years, an improvement occurred and the region became habitable
- Thus the people returned
- Modern industries developed and processed food became easily available
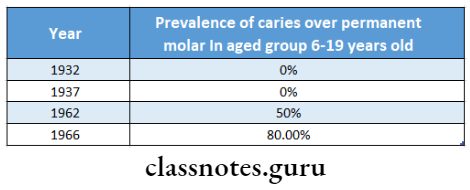
- Dental examination was carried out on an island in 1932, 1937 and 1953
- In England in 1962
- On an island in 1966
- Results obtained are
Question 3. Functional appliances.
Answer:
Functional Appliances Definition:
Functional Appliances is defined as loose fitting/ passive appliances that harness natural forces of oro-facial musculature that are transmitted to teeth and alveolar bone
Classification Of Functional Appliances:
- According to Tom Graber
- Group A: teeth supported
- Group B: teeth/ tissue supported
- Group C: vestibular positioned
- Based on use
- Removable
- Semi fixed
- Fixed
Functional Appliances Uses:
Intercept and treat jaw discrepancies
Functional Appliances Changes That Occur:
- Increase/ decrease jaw relationship
- Change spatial jaw relationship
- Changes direction of jaw growth
Accelerates desired growth
Community Dentistry Essay Questions
Question 4. Diet counseling.
Answer:
Diet Counseling
- Steps
- Introduce diet dairy
- 24-hour diet record is prepared
- A daily diet of dairy is advised
- Analyse complete records
- Isolating the sugar factors
- Patients education
- Consumption of sugar substitutes
Diet Counseling First Appointment:
- A diet diary of 6 consecutive days is prepared
- The form of particular food taken, its approximate amount along with snacks, candies, syrups, chewing gums consumption is recorded
- Identify the sugar-containing food items
- Mark such items with red Xs while others with blue Xs
- Explain to the patient the harmful effects of sugar-containing substances and explain to decrease the red Xs items while increasing the blue Xs items
- Teach him as a game
- Suggest sugar substitutes like peanuts
Diet Counseling Recall Visits:
- Recall appointments are carried out at regular intervals during the next months
- During these visits evaluate the patient’s progress and provide reinforcement
Question 5. Interceptive orthodontics.
Answer:
Interceptive Orthodontics Definition:
Interceptive Orthodontics is that phase of the science and art of orthodontics employed to recognize and eliminate potential irregularities and malpositions of the developing dentofacial complex
Interceptive Orthodontics Procedures:
- Serial Extraction
- Serial Extraction is the planned extraction of certain deciduous teeth and later specific permanent teeth in an orderly sequence and pre-determined pattern
- Developing anterior crossbite
- Treated to prevent minor orthodontic problems
- Interception Of Habits
- Habits that are intercepted are
- Thumb sucking
- Tongue thrusting
- Mouth breathing
- Habits that are intercepted are
- Space Regaining
- Space lost by the mesial movement of the molar can be regained by distal movement of 1st molar
- Muscular exercise
- It helps to improve aberrant muscle function
- Interception of skeletal Malrelation
- To reduce the severity of the disease
- Removal of soft tissues and bony barriers
Question 6. Exfoliative cytology.
Answer:
Exfoliative Cytology
Refers to the removal of surface cells for cytological examination
Exfoliative Cytology Uses:
Exfoliative Cytology For Diagnosis:
Routine screening of patients with oral lesions and recurrent carcinoma
Exfoliative Cytology The Stains Used Are:
Papanicolaon stain
Public Health Dentistry Questions And Answers
Question 7. Four-handed dentistry
Answer:
Four-Handed Dentistry
Four-handed dentistry is the term given to the art of seating both the dentist and the dental assistant in such a way that both are within easy reach of the patient’s mouth
Four-Handed Dentistry Process:
- The patient is in a fully supine position
- The assistant will hand the dentist the particular instrument he wants
- Assistant can also perform functions like retraction or aspiration
Four-Handed Dentistry Advantages:
- Dentists can completely keep their eyes on the field of operation
- Less fatigue
- Greater efficiency
- Training Period Of Assistant:
- One or two years
Question 8. Orofacial signs of sexual abuse.
Answer:
Orofacial Signs Of Sexual Abuse
- Contusion
- Laceration of
- Tongue
- Buccal mucosa
- Palate
- Alveolar mucosa
- Frenum
- Fractured, displaced, or avulsed teeth
- Facial bone and jaw fractures
- Burns
- Discolored teeth
- Pulpal necrosis
- Bruises
- Lichenification
- Scarring at the corners of the mouth
Dental Public Health Short And Long Questions
Question 9. Expert witness.
Answer:
Expert Witness
- An expert witness is a witness who by education, training, skill, or experience is believed to have expertise and specialized knowledge in a particular subject
- They are usually instructed to produce a joint statement detailing points of agreement and disagreement
- They charge a professional fee which is paid by the party
- They may be issued with a witness summon
- They must be qualified on the topic of testimony
- They may also deliver expert evidence
Expert Witness Expert Evidence:
- Fingerprints
- Blood analysis
- DNA fingerprinting
Question 10. Quarantine.
Answer:
Quarantine Definition:
A period of time during which a vehicle, person, or material suspected of carrying a contiguous disease is detained at a port of entry under enforced isolation to prevent the disease from entering a country
- It is used to separate and restrict the movement of good persons who may have been exposed to a communicable disease to see if they become ill
- It can apply to humans as well as animals
- Quarantine periods are very short
Quarantine Purpose:
- Prevent the spread of contamination
- To contain the contamination such that others are not put at risk
Question 11. Perjury.
Answer:
Perjury
A crime that occurs when an individual willfully makes a false statement during a judicial procedure after he/she has taken an oath to speak the truth
Perjury Basic Elements:
- A false statement is made under oath during a judicial proceeding
- The statement must be material or relevant to the proceeding
- The witness must have the specific intent to deceive
Perjury Punishment:
- Fine
- Imprisonment
- Both
Miscellaneous Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Positive health.
Answer:
Positive health
- Positive health is the group of subjective, biological, and functional that increase health and illness target
- Positive Health Indicator:
- Positive health is one or a collection of questions that assess the presence of one / several aspects of health as more than the absence of disease or symptoms
Question 2. Sporadic.
Answer:
Sporadic
- Sporadic means scattered about
- The cases occur irregularly, haphazardly from time to time, and generally infrequently
Community Dentistry Important Questions
Question 3. Gingival physiotherapy.
Answer:
- Gingival physiotherapy Device used
- Toothbrush
- Rubber tip stimulator
- Interdental cleaning device
- Gingival physiotherapy Effects
- Epithelial thickening
- Increased keratinization
- Increased mitotic activity
Question 4. Soil, Seed, and Sower.
Answer:
Soil, Seed and Sower
- Soil, Seed and Sower is one of the principles of health education
- According to it:
- The people are the soil
- Seeds: health facts- must be truthful
- Sower: transmitting media- should be attractive, palatable, and acceptable
Question 5. Co-insurance.
Answer:
Co-insurance
- Co-insurance is defined as ” an arrangement under which a carrier and the beneficiary are each liable for a share of the cost of the dental services provided”
- Co-insurance means that the patient pays a percentage of the total cost of the treatment
- V helps to keep the premium down
- Example: The patient has to pay 20% of the cost of the treatment, and the remaining 80% will be paid by the insurance company
Question 6. Folk medicine.
Answer:
Folk medicine Definition:
Folk medicine is the treatment of disease or injury based on tradition, especially on oral tradition, often utilizing Indigenous plants as remedies
- It refers to healing practices and ideas of body physiology and health preservation known to a limited segment of the population in a culture
- It often coexists with formalized education-based and institutionalized systems of healing
- Practices of folk medicine may be influenced by the formalized medical systems
Synonyms:
- Traditional medicine
- Alternative medicine
Question 7. Emporiatics.
Answer:
Emporiatics
- Emporiatics is the specialty of travel medicine dealing with diseases that travelers can acquire especially in the tropics
- Emporiatics deals with the prevention and management of health problems of international traveler
- Example: traveler’s diarrhea
- It comprises of
- Prevention
- Assistance
- Wilderness medicine
- Access to healthcare
Question 8. Standard of living.
Answer:
Standard of living
- Standard of living refers to the level of wealth, comfort, material goods, and necessities available to a certain socioeconomic class
- Standard of living is inherent subjective
Standard of living Factors Effecting:
- Income
- Quality and availability of employment
- Poverty rate
- Housing
- Hours of work
- Quality health care
- Quality of education
- Life expectancy
- Incidence of disease
- Cost of services
- Environmental Quality
Community Dentistry Exam Questions
Question 9. Mores.
Answer:
Mores
- They are norms or customs which express fundamental values of society
- They are derived from the established practices of a society rather than from written laws
- They consist of shared understandings about the kinds of behavior likely to evoke approval, disapproval, toleration, or sanction, within particular contexts
Question 10. Need for dental care.
Answer:
Need for dental care Types:
- Normative need
- Normative is the requirement for care as determined by expert opinion
- Felt need
- Felt is the requirement of care as determined by the patient or public
- Expressed need
- Expressed arises out of attempts by members of the public to seek attention for their perceived needs
Need for dental care Approaches to Estimate Need:
- Surveys of dental health status
- Surveys of need for dental care using a questionnaire
- Analyses of service or treatment records
Question 11. Accretion.
Answer:
Accretion
Accretion is a process where most of the fluoride is buried within the mineral crystallites during the period of crystal growth
Question 12. Census.
Answer:
Census
- Census is the collection of information from all the individuals in a population
- Census is the total process of collecting, completing and publishing demographic, economic and social data pertaining at a specified time or times to all persons in a community
Census Disadvantages:
- Expensive
- Time-consuming
- Less accurate
Community Dentistry Short And Long Questions
Question 13. Primordial prevention.
Answer:
Primordial prevention
- Primordial prevention is the prevention of the emergence or development of risk factors in countries or population groups in which they have not yet appeared
- Primordial prevention is receiving special attention in the prevention of chronic diseases
- In it, efforts are directed toward discouraging children from adopting harmful lifestyles
- The main intervention in primordial prevention is through individual and mass education
Question 14. Hidden caries.
Answer:
Hidden caries
- Hidden caries is a term used to describe occlusal dentin caries that is missed on visual examination but is large enough and demineralized enough to be detected radiographically
- The detection rate of such lesions will depend upon the prevalence of caries in the population
- Occlusal enamel appears sound or only minimally demineralized
- Hidden caries is difficult to diagnosed
Question 15. Clinical manifestation of AIDS.
Answer:
Clinical manifestation of AIDS
- Unexplained diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Malaise
- Loss of body weight
- Fever
- Night sweat
- Oral thrush
- Generalized lymphadenopathy
- Enlarged spleen
- Opportunistic infections
Question 16. Deductible.
Answer:
Deductible
- A deductibleis stipulated flat sum that the patient must pay towards the cost of treatment before the benefits of the program go into effect
- A deductibleis sometimes called” front-end-payment”
Question 17. Space maintainers.
Answer:
Space maintainers Definition:
A space maintainer is a device used to maintain the space created by the loss of deciduous teeth
Space Maintainer Requirements:
- Maintain the space created
- Restores function
- Prevent supra eruption of opposing teeth
- Simple to construct
- Withstand functional forces
- Do not exert excessive forces
- Maintain oral hygiene
- Allow growth of permanent teeth
- Should not interfere with oral function
Question 18. Geriatric dentistry.
Answer:
Geriatric dentistry
- Geriatric dentistry is the delivery of dental care to older adults involving the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of problems associated with normal aging and age-related disease as part of an interdisciplinary professionals
- In older individuals, dental disease is more common due to
- Decreased immunity
- Presence of systemic disease
Common Oral Problems Are:
- Periodontitis
- Attrition
- Root caries
- Early edentulism
Community Dentistry Miscellaneous Questions
Question 19. Epizootic.
Answer:
Epizootic
- An epidemic outbreak of the disease in an animal population often with the implication that it may extend to humans
- Epizootic can lead to an epidemic among humans who are exposed to disease animals
- Epizootic may be
- Restricted to a specific area/ local
- Genera
- Epizootic affects a large number of animals at the same time within a particular region
Question 20. Seasonal trends.
Answer:
Seasonal trends
- Seasonal trends is a prominent feature of infectious disease occurrence
- Example: Measles and varicella are usually found with their peak incidence during the early spring season
- Similarly, upper respiratory tract infections show an increase during the winter season and GIT infections have a seasonal rise during the summer months
- The seasonal variation in disease occurrence can be attributed to changes in environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, rainfall, overcrowding, etc.
Question 21. Critical pH.
Answer:
Critical pH
- Critical pH represents the demineralization-remineralization cycle
- At a critical pH of 5.5 or below
- Hydrogen ions (H+) react with the phosphate group present in the oral cavity
- Results in the formation of hypophosphate
- Due to this, hydroxyapatite crystals dissolve and are termed dimerization
- At neutral pH
- With adequate presence of calcium and phosphorous, dissolution is inhibited
Question 22. Newburgh Kingston study.
Answer:
Newburgh Kingston study
- On May 2nd, 1945, sodium fluoride was added to the drinking water of Newburg on the Hudson River
- Kingston town was the control
- After 10 years of fluoridation, Ast et al in 1956 reported that the DMF rate had fallen from 23.5% to 13.9%
- Newburgh Kingston thus confirmed the caries inhibitory property of fluoride in drinking water
Question 23. Prevalence of HIV.
Answer:
Prevalence of HIV
- Prevalence of HIV refers to the percentage of people ages 15-49 who are infected with HIV
- Prevalence of HIV is the number of persons living with HIV at a given time regardless of the time of infection, whether the person has received a diagnosis or the stage of HIV disease
- The HIV prevalence rate in India is less than in numerous other countries
- During the 1990s, HIV infection rates rose like an epidemic affecting every Indian society
- A rise of 0.1% of the population adds more than half a million HIV patients
- The north-east and south of India have high HIV rates
Community Oral Health Essay Topics
Question 24. Customs and habits.
Answer:
Customs:
- Customs refers to practices that have been repeated by a number of generations, practices that tend to be followed simply because they have been followed in the past
- They have a traditional, automatic, mass character
Customs Habits:
- Customs Habits is defined as the tendency towards an act that has become a repeated performance, relatively fixed, consistent and easy to perform by an individual
- Customs Habits is a purely personal affair, not entailing any obligation
- Example: Smoking a cigarette after dinner
Question 25. Blanket referral.
Answer:
Blanket referral
- Blanket referral is an effective program in many schools
- Blanket referral consists of the referral of all children to their family dentists
- In this program, all children are given referral cards to take home and subsequently to the dentist who signs the cards on completion of examination, treatment, or both
- The signed cards are then returned to the school nurse or classroom teacher
