Clinical Diagnostic Methods Important Notes
- Clinical Diagnostic Methods Grades of mobility
- Grade 1 – noticeable/barely discernable movement of the teeth within the sockets
- Grade 2 – lateral/horizontal mobility within a range of 1mm or less
- Grade 3 – movement greater than 1 mm or when the tooth can be depressed into the sockets
- Clinical Diagnostic Methods Thermal tests
- According to Grossman, a response to cold reflects a vital pulp regardless of whether it is normal or abnormal
- A heat test does not confirm vitality
- An abnormal response to a heat test however indicates the presence of a pulpal or periapical disorder requiring endodontic treatment
- Thermal test should be first performed on the teeth to be used as controls
- The tests are performed by placing the stimuli on the incisor-labial or the occlusal-buccal surface
- According to Cohen, the temperature for performing heat tests is 65.5°C or 150F
- The temperature of dry ice used in the cold test is -78°Clinical
- The painful response which subsides when the stimuli are removed from the tooth indicates reversible pulpitis
- Painful response which doesn’t subside on removal of stimuli indicates irreversible pulpitis
- Clinical Diagnostic Methods Clinical Diagnostic Methods Electric pulp testing
- The electrolytes applied to it are Nicholas-colloidal graphite, Grossman toothpaste
- The best localization or placement of electrolytes during this test are incisal 2/3rd of labial surfaces of maxillary premolars and molars
- During EPT gives should not be used
- To eliminate biased decisions, EPT is performed first on the control tooth
- EPT cannot be used on patients having a cardiac pacemaker
- EPT is not useful for recently erupted teeth with immature apex
- EPT does not test the vitality of the pulp as it depends on the nerve supply to the pulp whereas pulp vitality depends on the blood supply
- The two main varieties of pulp tester available are bi-polar and mono-polar
- Clinical Diagnostic Methods Xeroradiography
- It uses a rigid aluminium/selenium-coated photoreceptor plate
- The plate is electrically charged placed in a waterproof electric cassette positioned in the mouth and exposed to X-rays at a lower level of radiation
- Advantages:
- Produces sharper, clearer and finer details of the image
- Reduces patient radiation dose
- Pronounced edge enhancement effect
- Clinical Diagnostic Methods Pulse oximetry
- It is a non-invasive oxygen saturation monitor
- Detects pulp vitality by testing the integrity of blood supply to pulp
- It uses red and infrared wavelengths
- Clinical Diagnostic Methods Clinical Diagnostic Methods Laser Doppler flowmetry
- A non-invasive method to measure the blood flow
- A better and more reliable method for determining the pulp vitality the electric pulp testing method
- Radiovisiography
- It contains 3 components
- Radio – consists of a hypersensitive intra=oral sensor and a conventional x-ray unit
- Visio – consists of a video monitor and display processing unit
- Graphy – It is high-resolution video printer that instantly provides a hard copy of the screen image
Pulp Vitality Tests In Endodontics
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Long Essays
Question 1. Discuss various diagnostic methods in Endodontics
Answer:
Endodontics Diagnosis:
- It is defined as the utilization of scientific knowledge to identify a diseased process and differentiate it from another disease process.
Read And Learn More: Endodontics Question and Answers
Diagnostic Process In Endodontics :
Consists of 4 steps
Step 1:
- Chief Complaint:
- Reason for which patient has come to the dentist
- Recorded inpatient’s own words
- Medical/Dental History:
- To know the patient’s attitude towards treatment:
Diagnostic Tests In Endodontics
Endodontics Investigation:
Step 2:
- Provisional Diagnosis:
- Based on the patient’s chief complaint
Step 3:
Differential Diagnosis In Endodontics:
- Having similar signs and symptoms
Endodontic Diagnosis
Step 4:
Final Diagnosis In Endodontics
Examination:
- Extraoral:
- Physical appearance
- Examination of swelling
- Palpation of salivary glands
- Palpation of TMJ
- Palpation of lymph nodes
- Intraoral:
- Soft tissue examination
- Hard tissue examination
- Radiograph:
- Features seen in periapical lesions
- Loss of lamina dura
- Aetiology of necrosis
- Interpretations
- Black/Grey area
- Decay, pulp, Abscess, Cyst
- White area
- Enamel, restoration
- While line
- Lamina dura
- Features seen in periapical lesions
Clinical Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics Uses:
- For diagnosis
- For examining the extent of caries
- For calcification, necrosis, obstruction
- For periodontal lesions
- For examining perforation
- For determining the working length
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics – Vitality Test:
- Thermal test:
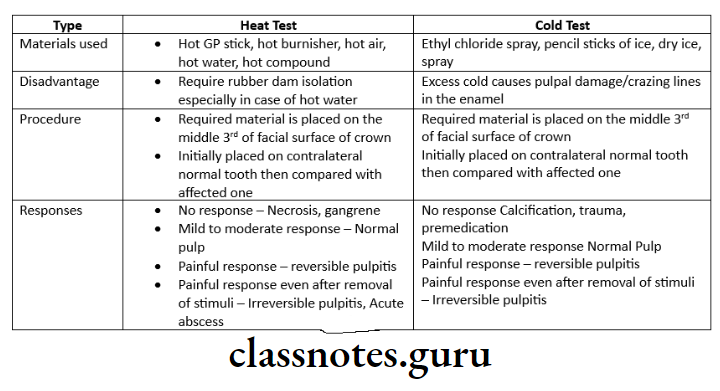
- Electrical Pulp Testing:
Use: To suggest the vitality of tooth
Limitation: Does not give any information about the vascular supply:- Instrument Used:
- Battery operated
- Graduation form 0-10
- Deliver direct current of high-frequency
- Technique:
- Instrument Used:

- Precaution:
- Recording should be compared with normal adjacent and contralateral tooth
- Precaution:
- Test Cavity:
- It is done only when other methods fail.
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics Procedure:

- Anaesthesia Testing:
- Useful when the patient is unable to localized pain.
- Procedure:
- Anaesthesia is the most posterior tooth in the suspected quadrant
- Bite Test:
- Useful if the patient complaints of pain on occlusion
- Causes Of Pain:
- Endo-period lesion
- Crack in tooth
- Material Used:
- Cotton swab
- Toothpick
- Orangewood stick
- Tooth sloth.
Procedure:

Endodontic Diagnosis Techniques
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Short Essays
Question 1. RVG [Radio-Visiography].
Answer.
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics – Radio:
- Sensitive intraoral sensor
- It transmits information via a fiberoptic bundle to CCD
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics – Visio:
- Video monitor
- Display processing unit
- It magnifies the images
- It is memorised by the computer
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics – Graphy:
- Consists of a high-resolution video printer.
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics Advantages:
- Reduction of radiation
- Production of instantaneous images
- Control of contrast
- Elimination of film
- Magnifies images
- Storage of information
- Infection control
- Time saver
Endodontic Diagnosis
Diagnostic Methods In Endodontics Disadvantages:
- Expensive
- Soft tissue imaging is not possible
- Bulky
Question 3. Xero Radiography.
Answer.
Xero Radiography
- Does not require films/dark rooms
- Imaging was recorded on an aluminium plate coated with selenium.
Xero Radiography Procedure:

Xero Radiography Advantages:
- Edge enhancement
- Improves visualization
- Both positive and negative images are possible
Xero Radiography Disadvantages:
- Discomfort to patient
- Variation in exposure time
- Development must be done within 15 minutes
Diagnostic Tools In Endodontics
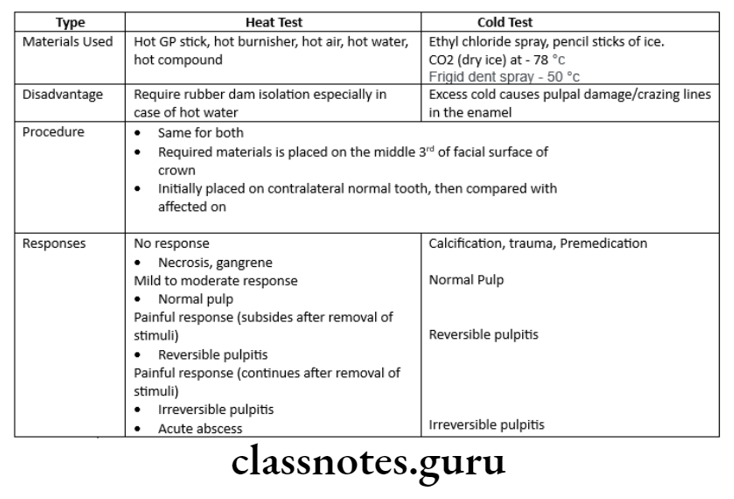
Question 4. Thermal Test/Cold Test.
Answer.
Thermal Test/Cold Test
Question 5. Electric pulp Tester.
Answer.
Electric Pulp Tester Use – To suggest the vitality of the tooth
Electric Pulp Tester Limitation:
- Does not give any information about the vascular supply
Electric Pulp Tester Instrument Used:
- Battery operated
- Graduation from 0 – 10
- Deliver direct current of high-frequency
Electric Pulp Tester Precaution:
Recording should be compared with normal adjacent and contralateral tooth
Electric Pulp Tester Various Tester:
- Burton vitallometer [But not battery operated]
- Dialogue
- Pelton crame compact
- Neotest ADP
Electric Pulp Tester Interpretation:
- Slight response – Inflamed pulp
- No response – Pulpal necrosis
Endodontic Diagnosis
Electric pulp Tester False Responses:
- Acute alveolar abscess
- Contact with gingival tissue
- In multirooted tooth
- Recently traumatized tooth
- Recently erupted tooth
- Patients with high pain threshold
- Calcified canal
- Partial necrosis of pulp
- Premedication
- Poor battery
- Extensive restoration

Question 6. Pulp Vitality Test.
Answer.
Pulp Vitality Test
- Thermal test:

- Electrical Pulp Testing:
Use: To suggest the vitality of the tooth
Limitation: Does not give any information about the vascular supply- Instrument Used:
- Battery operated
- Graduation from 0 – 10
- Deliver direct current of high-frequency
- Precaution:
- Recording should be compared with normal adjacent and contralateral tooth
- Instrument Used:
Question 7. Diagnostic aids in endodontics
Answer.
Diagnostic Aids In Endodontics – Examination:
- Extraoral:
- Physical appearance
- Examination of swelling
- Palpation of salivary glands
- Palpation of TMJ
- Palpation of lymphnodes
- Intraoral:
- Soft tissue examination
- Hard tissue examination
- Radiograph:
- Features seen in periapical lesions
- Loss of lamina dura
- Aetiology of necrosis
- Interpretations
- Black/Grey area
- Decay, Pulp, Abscess, Cyst
- White area
- Enamel, restoration
- White line
- Lamina dura
- Features seen in periapical lesions
Diagnostic Aids In Endodontics Uses:
- For diagnosis
- For examining, necrosis, obstruction
- For calcification, necrosis, obstruction
- For periodontal lesion
- For examining perforation
- For determining the working length
Endodontic Diagnostic Procedures
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Short Answers
Question 1. Test Cavity.
Answer.
Test Cavity
It is done only when other methods fail.
Question 2. Anaesthesia testing.
Answer.
Anaesthesia Testing
Useful when the patient is unable to localized pain.
Anaesthesia Testing Procedure:
- Anaesthesia is the most posterior tooth in the suspected quadrant.
Clinical Diagnostic Methods Viva Voce
- Tenderness on percussion of a tooth indicates extension of pulpal disease or infection into the periapical area
- Electric pulp testers most frequently employ low-frequency current
- Electric pulp testing measures the sensory nerve response to irritants of electricity
- The mobility test is the ability to move a tooth between two fingers
- Electric pulp testing is done to differentiate between vital and non-vital pulp
- A violent response to heat and instant relief to cold is indicative of reversible pulpitis
- Percussion tests evaluate the status of the periodontium surrounding teeth
