Arm Introduction
- Arm extends from the shoulder joint to the elbow joint.
- Humerus is the one and only bone present in the arm.
- Apart from the humerus, the arm consists of neurovascular bundles located medially and muscles arranged in compartments.
Arm Question And Answers
Question 1. Briefly explain the fascial compartments of arm.
Answer:
- The deep fascia covers the arm like a sleeve.
- Lateral and medial intermuscular septa extend inwards from this fascial sleeve and attach to the humerus dividing the arm into anterior and posterior compartments.
- The anterior compartment consists of muscles involved in flexion action, hence called as flexor compartment.
- Posterior compartment consists of the triceps muscle involved in extension action, hence this compartment is called the extensor compartment.
- Two additional septa, the transverse and anteroposterior septa divide flexor compartment into three.
Question 2. What are the contents of the anterior compartment of arm?
Answer:
The contents of the anterior compartment of arm It consists of:
- Three muscles
- Biceps brachii
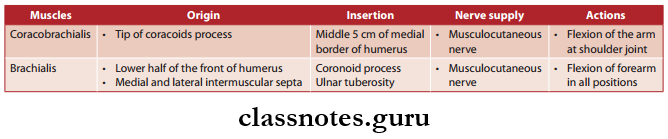
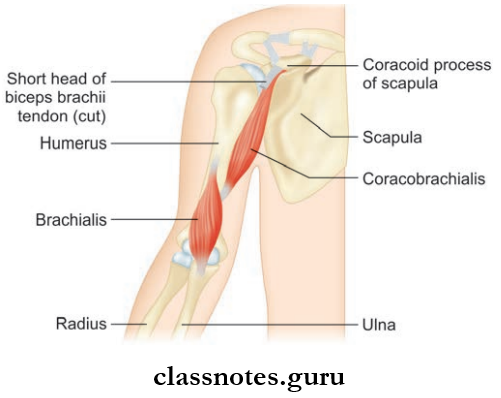
- Coracobrachialis
- Brachialis
- Nerves
- Musculocutaneous nerve
- Median nerve
- Radial nerve Nerves passing through the arm
- Ulnar nerve
- Brachial artery.
Question 3. Write a note on the biceps brachii.
Answer:
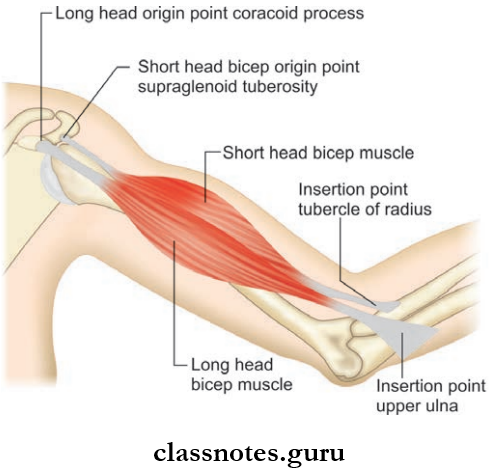
Biceps Brachii Origin:It has two heads of origin:
- Short head from the coracoids process along with coracobrachialis.
- Long head from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula and glenoid labrum.
Biceps Brachii Insertion
- The main tendon to posterior rough part of the radial tuberosity
- Bicipital aponeurosis to the skin
Read And Learn More: Anatomy Question And Answers
Biceps Brachii Nerve Supply
- Musculocutaneous nerve
Biceps Brachii Actions
- Flexion of the elbow
- Powerful supinator when the forearm is flexed
- All screwing actions
- Short head flexes the arm
- Long head prevents the upward displacement of the head of humerus
Biceps Brachii Clinical Anatomy
The biceps reflex is routinely tested in CNS examination to assess the integrity of the musculocutaneous nerve and C5, and C6 spinal segments.
Question 4. Write about the origin, insertion, nerve supply, and actions of coracobrachialis and brachialis.
Answer:
Mnemonic
- Elbow: muscles that flex it
- Three Bs Bend the elbow:
- Brachialis
- Biceps
- Brachioradialis.
Question 5. What are the anatomical peculiarities of the insertion of the coracobrachialis muscle?
Answer:
- Brachial artery comes to the anterior aspect from its medial position in the arm.
- Median nerve crosses from the lateral to the medial side in front of brachial artery.
- Below this level, the circular shaft of the humerus becomes triangular.
- The basilic vein pierces the deep fascia.
- The nutrient artery enters to the humerus.
- The medial cutaneous nerve of the arm and forearm pierces the deep fascia.
- Radial nerve pierces deep lateral intermuscular septum and goes from posterior compartment to anterior compartment.
- Ulnar nerve pierces medial intermuscular septum and goes to the posterior compartment.
Question 6. Write a note on cubital fossa mentioning its boundaries and contents.
Answer:
- It is a triangular hollow present in front of the elbow.
- It is homologous with the popliteal fossa in the lower limb.
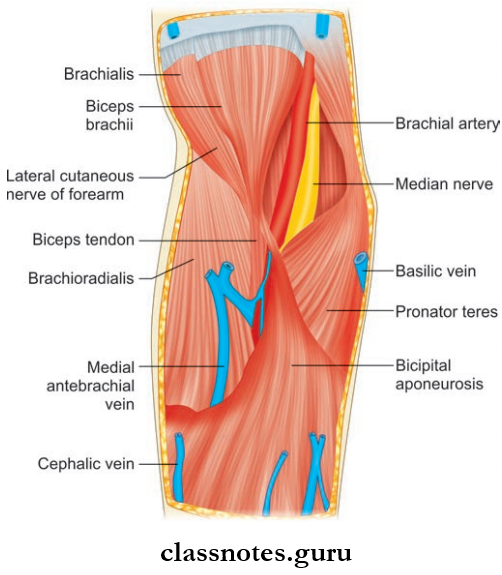
Cubital fossa Boundaries
- Lateral Medial border of the brachioradialis muscle
- Medial Lateral border of pronator teres muscle
- Base Directed upwards, represented by an imaginary line joining the front of the lateral and medial epicondyles of humerus
- Apex Directed downwards, meeting point of lateral and medial border
- Roof From superficial to deep:
- Skin
- Superficial fascia containing median cubital vein, medial and lateral cutaneous nerves of forearm
- Deep fascia with bicipital aponeurosis
Cubital fossa Content: From medial to the lateral side are:
- Median nerve
- Brachial artery
- Tendon of biceps brachii.
Cubital fossa Clinical Anatomy
- A medial cubital vein in the cubital fossa is the vein of choice for intravenous injection.
- When blood pressure is recorded, BP cuff is wind around the arm to exert external pressure over the brachial artery.
- Supracondylar fracture of humerus can lead to injury to brachial artery and median nerve. In such cases knowledge of cubital fossa is essential to reduce the fracture.
Question 7. What are the contents of posterior compartment of the arm?
Answer:
The contents of posterior compartment of the arm Its contents are:
- 1 muscle: Triceps brachii
- 1 nerve: Radial nerve
- 1 artery: Profunda brachii artery.
Question 8. Write a note on the triceps brachii muscle.
Answer:
Triceps brachii muscle Origin It has three heads:
- Long head from the infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
- Lateral head from the oblique ridge present on the upper part of the posterior surface of the humerus
- Medial head from the large triangular area on the posterior surface of humerus below the radial groove and the medial and lateral intermuscular septa
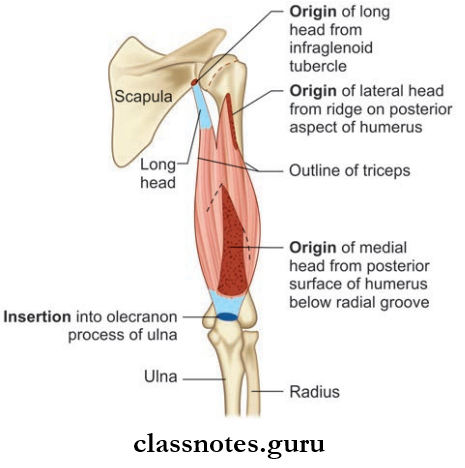
Triceps brachii muscle Insertion
- Posterior part of the superior surface of the olecranon process
Triceps brachii muscle Nerve Supply
- Radial nerve
Triceps brachii muscle Actions
- Powerful extensor of the elbow
Triceps brachii muscle Clinical Anatomy
If radial nerve is injured in the radial groove, an extension of the elbow and triceps reflex is not lost because the triceps muscle is innervated by the radial nerve in the axilla.
Question 9. Cross-section at the level of middle of the arm.
Answer:
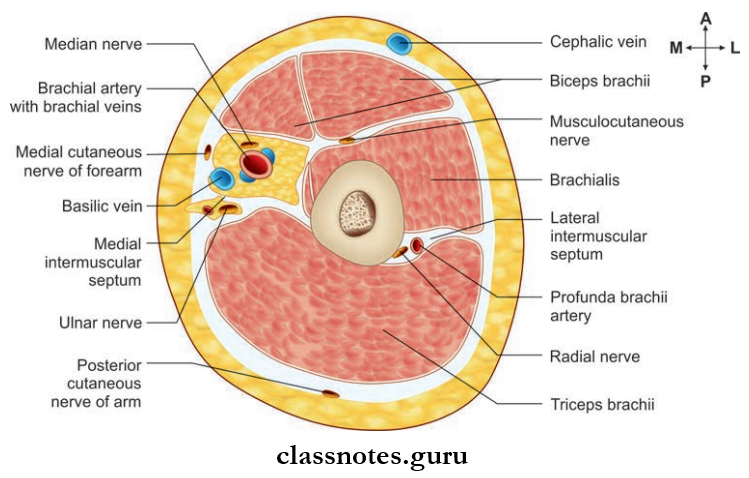
Arm Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which is the nerve of anterior compartment of arm?
- Axillary nerve
- Radial nerve
- Ulnar nerve
- Musculocutaneous nerve
Answer: 4. Musculocutaneous nerve
Question 2. Which muscle does not belongs to anterior compartment of arm?
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Biceps brachii
- Coracobrachialis
Answer: 2. Brachioradialis
Question 3. Which among these are considered as powerful supinator?
- Biceps brachii
- Triceps brachii
- Coracobrachialis
- Deltoid muscle
Answer: 1. Biceps brachii
Question 4. Where is triceps brachii inserted?
- Medial epicondyle of humerus
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus
- Olecranon process
- Radial tuberosity
Answer: 3. Olecranon process
Question 5. Bicipital aponeurosis is inserted into where?
- Radial tuberosity
- Skin
- Ulnar tuberosity
- Medial lateral epicondyle of humerus
Answer: 2. Skin
