Submandibular Region Question And Answers
Question 1. Write a short note on suprahyoid muscles.
Answer:
Suprahyoid Muscles
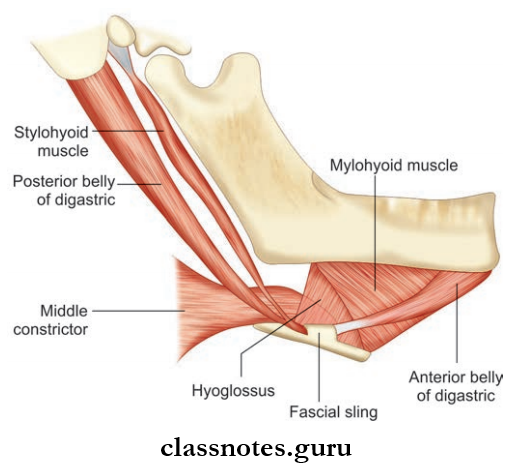
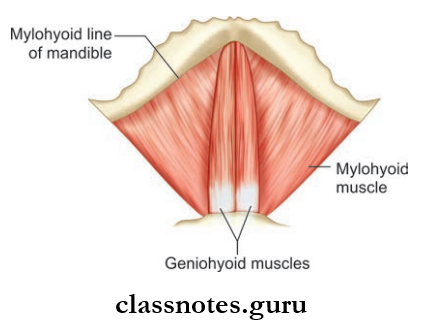
These include the digastric, the stylohyoid, the mylohyoid, and the geniohyoid.
Digastric Muscle: It has 2 bellies united by a tendon.
- Digastric Muscle Origin
- Anterior Belly: From digastric fossa of mandible
- Posterior Belly: Mastoid notch of the temporal bone.
- Digastric Muscle Insertion: Both heads are united by the intermediate tendon which pierces stylohyoid muscle and is held by a fibrous pulley to hyoid bone.
- Digastric Muscle Nerve supply
- Anterior Belly: Nerve to mylohyoid
- Posterior Belly: Facial nerve.
- Digastric Muscle Action
- Depresses mandible
- Elevates hyoid bone.
Styloid Muscle
- Styloid Muscle Origin: Posterior surface of the styloid process
- Styloid Muscle Insertion: Junction of body and greater cornua of the hyoid bone
- Styloid Muscle Nerve supply: Facial nerve
- Styloid Muscle Action
- Fixing of hyoid bone
- Pulls hyoid bone upwards and backward.
Mylohyoid Muscle
- Mylohyoid Muscle Origin: Mylohyoid line of mandible
- Mylohyoid Muscle Insertion
- Posterior fibers to the body of hyoid bone
- Anterior and middle fingers to the median raphe between the mandible and hyoid bone
- Mylohyoid Muscle Nerve supply: Nerve to mylohyoid
- Mylohyoid Muscle Action
- Elevates the floor of the mouth during deglutition
- Helps in the depression of the mandible and elevation of the hyoid bone.
Geniohyoid Muscle
- Geniohyoid Muscle Origin: Inferior mental spine/genial tubercle
- Geniohyoid Muscle Insertion: Anterior surface of body of hyoid bone
- Geniohyoid Muscle Nerve supply: C1 through hypoglossal nerve
- Geniohyoid Muscle Action: Elevates hyoid bone.
Hyoglossus Muscle
- Hyoglossus Muscle Origin: Whole length of greater cornua and lateral part of body of hyoid bone
- Hyoglossus Muscle Insertion: Side of the tongue between Styloglossus and inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue
- Hyoglossus Muscle Nerve supply: Hypoglossal nerve
- Hyoglossus Muscle Action
- Depresses tongue
- Retracts protruded tongue and makes dorsum convex.
Question 2. Write a note on the submandibular salivary gland.
Answer:
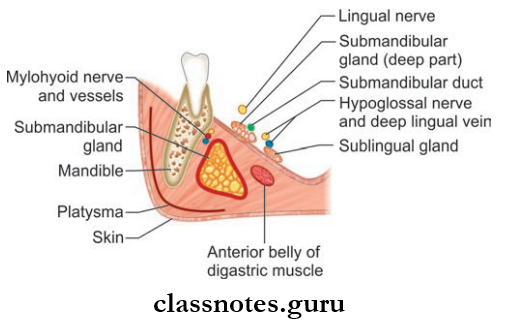
Submandibular Salivary Gland
- It is a J-shaped gland present in the anterior part of the digastric triangle
- It is indented by the posterior border of the mylohyoid which divides the gland to superficial and deep parts.
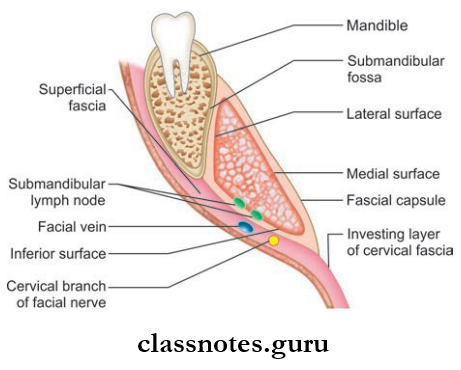
Superficial Part (Larger Part)
- It extends upwards deep to the mandible up to the mylohyoid line
- It consists of 3 surfaces: Inferior, lateral, and medial
- It is partially enclosed by the layers of deep cervical fascia
- The inferior surface is covered by the superficial layer and the medial surface is covered by the deep fascial layer.
Superficial Part Relations
- Inferior Surface:
- Skin
- Platysma
- Cervical branch of the facial nerve
- Deep fascia
- Facial vein
- Submandibular lymph nodes
- Lateral Surface:
- Submandibular fossa on mandible
- Insertion of the medial pterygoid
- Facial artery
- MedialSurface: Mylohyoid, hyoglossus, styloglossus muscles.
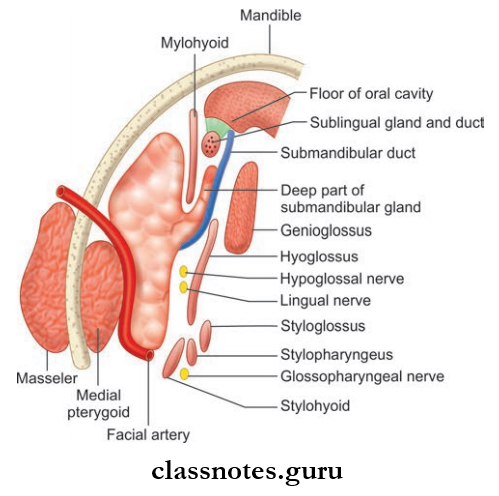
Deep Part (Smaller Part)
- Lies deep to mylohyoid and superficial to hyoglossus and styloglossus
- Posteriorly, it is continuous with superficial part
- Anteriorly, it extends up to the posterior end of the sublingual gland.
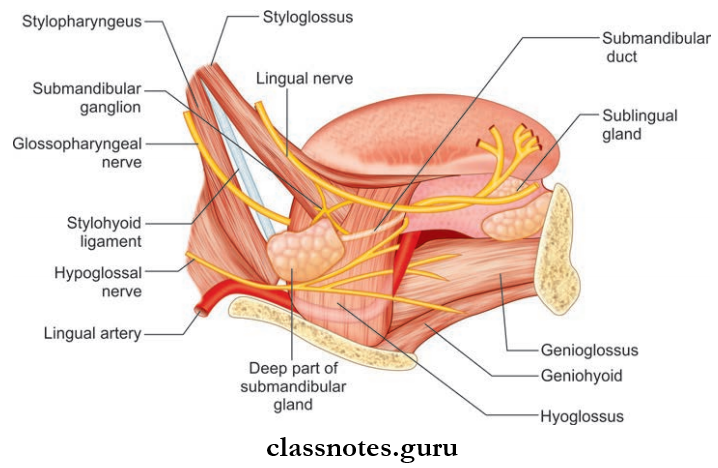
Submandibular Duct/Wharton’s Duct
- It is a 5 cm-long thin-walled structure
- It emerges at the anterior end of the deep part of gland
- It then runs forwards on the hyoglossus muscle between the hypoglossal and lingual nerves
- The duct is crossed by a lingual nerve at the anterior border of the hyoglossus muscle
- It opens on the floor of mouth on the summit of sublingual papillae at the sides of the frenulum of the tongue.
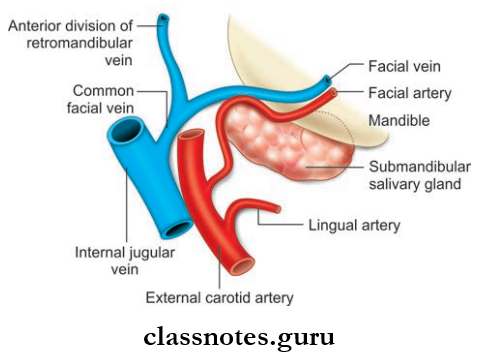
Salivary Gland Blood Supply
- Arterial: By facial artery
- Venous drainage: Drain into common facial/lingual vein.
Submandibular Salivary Gland Lymphatic Drainage: Drains into submandibular lymph nodes.
Submandibular Salivary Gland Nerve Supply
- Sensory fibers from the lingual nerve
- Vasomotor sympathetic fibers from the plexus on the facial artery
- Secretomotor fiers from the superior salivatory nucleus and through chorda tympani and lingual nerve.
Submandibular Salivary Gland Applied
- The salivary calculi in the submandibular duct occur due to stasis of secretion. The gland swells during eating when a stone blocks the duct.
- Excision of the submandibular gland for calculus or tumor is done by an incision below the angle of jaw.
- Since the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve passes posteroinferior to angle of the jaw, the incision is placed 4 cm below the angle to preserve the nerve.
Question 3. Write a short note on the sublingual gland.
Answer:
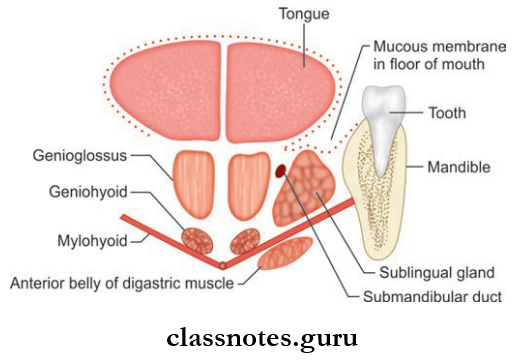
The Sublingual Gland
- Smallest of the three salivary glands
- Almond-shaped and weighs 3–4 g
Sublingual Gland Location: Lies above the mylohyoid muscle below the mucosa of the floor of the mouth, medial to the sublingual fossa of the mandible, and lateral to the genioglossus.
Sublingual Gland Features
- About 15 ducts arise from the gland
- The majority of the ducts open into the floor of mouth on the summit of the sublingual fold
- Few of the ducts join the submandibular duct.
Sublingual Gland Blood Supply
- Arterial supply from lingual and submental arteries
- Venous drainage by lingual vein.
Sublingual Gland Nerve Supply: By the branches from the submandibular ganglion.
Sublingual Gland Lymphatic Drainage: Drains into submandibular lymph nodes.
Sublingual Gland Applied: Ranula is the cystic swelling of the sublingual gland. It is soft and bluish in color and projects in the floor of the mouth.
Submandibular Region Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. The superficial relation of hyoglossus muscle includes all except:
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Lingual artery
- Lingual nerve
- Deep part of sublingual gland
Answer: 2. Lingual artery
Question 2. Select the incorrect statement about the submandibular gland:
- It develops from endoderm
- It consists of superficial and deep parts
- Its ducts open into the vestibule of the oral cavity
- It is grooved by the facial artery
Answer: 3. Its ducts open into the vestibule of the oral cavity
Question 3. Which of the following nerves crosses the submandibular gland?
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Lingual nerve
- Chorda tympani nerve
Answer: 3. Lingual nerve
Question 4. All of the following pass deeper to hyoglossus except:
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Stylohyoid ligament
- Lingual artery
Answer: 2. Stylohyoid muscle
Question 5. A correct statement about the submandibular ganglion is:
- It is functionally related to facial nerve
- It is situated in the inner surface of hyoglossus muscle
- It lies above lingual nerve
- It supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to submandibular and sublingual glands.
Answer: 1. It is functionally related to the facial nerve
