Diseases Of The Respiratory System Important Notes
- Sputum And Its Associated Pathology
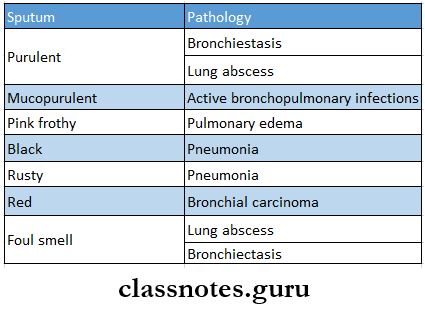
- Pleural Effusion
- Pleural Effusion is excess fluid that accumulates in the pleural cavity that surrounds the lungs
- Pleural Effusion can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs during ventilation
- Pleural Effusion is uncommon in children
- Transudative seen in
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Cirrhosis
- Heart, liver, and renal failure
- Exudative is seen in
- Pneumonia
- TB
- Malignant disease
- Rheumatoid disease
- SALE
- Transudate v/s Exudate
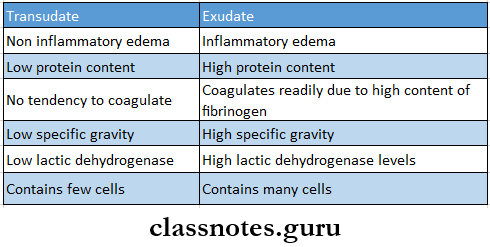
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Primary tuberculous comprises of
- Ghon’s focus
- Hilar lymphadenopathy
- Primary tuberculous comprises of
- DOTS
- It is directly observed treatment short course
- In this anti-tubercular drugs are administered under the direct supervision of peripheral health staff or through voluntary workers
- Category
- Category 1 – new patients
- Category 2 – previously treated patients
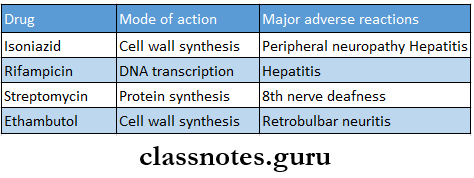
- Drugs Used For Tuberculosis
- Asthma
- Asthma is a disorder characterized by chronic airway obstruction and increased airway responsiveness
- Features
- Wheeze
- Breathlessness
- Cough
- The sensation of chest tightness
- Features of status asthmaticus
- Silent chest
- Bradycardia
- Pulsus paradoxes
- Exhaustion
- Confusion
- Reduced conscious level
- Diseases Of The Respiratory Tract
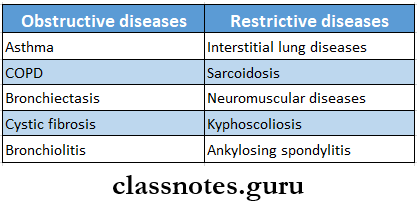
- Lung Abscess
- Lung Abscess is a collection of purulent material in a localized necrotic area of lung parenchyma
- Lung Abscess Clinical features
- Fever with chills
- Pleuritic chest pain
- Dry cough
- The presence of copious purulent discharge
- Hemoptysis
- Weight loss
- Anorexia
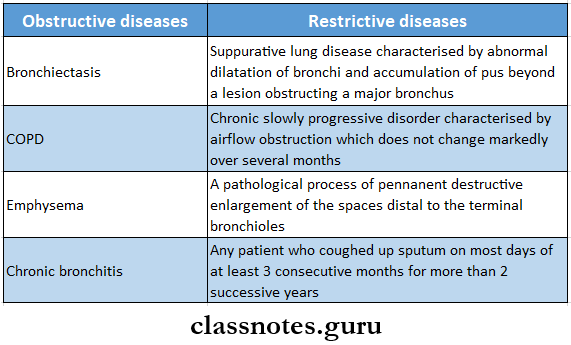
- Emphysema
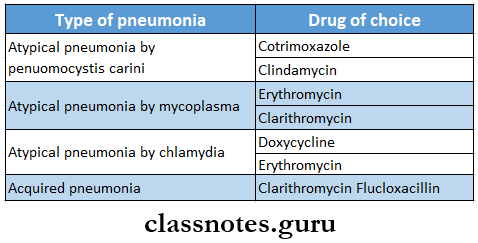
- Drug Of Choice In Different Pneumonia
Respiratory diseases notes for medical students
Diseases Of The Respiratory System Short Answers
Question 1. Clubbing
Answer:
Clubbing
- Clubbing is an enlargement of the distal segment of fingers and toes due to an increase in soft tissues
Grades:
- Grade 1- Softening of nail bed due to hypertrophy of the tissue at that site
- Grade 2- In addition to grade 1 changes, there is the obliteration of the angle between the nail base and the adjacent skin of the finger
- Grade 3- In addition to grade 2 changes, the nail itself loses its longitudinal ridges, becomes convex from above downwards as well as from side to side
- The nails assume the shape of a “parrot’s beak” or the terminal segment may become bulbous like a “drumstick”
- Grade 4- Tire finger changes are associated with hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy
Question 2. Bronchiectasis
Answer:
Bronchiectasis
- Bronchiectasis is defined as an abnormal and irreversible dilatation of bronchi
Etiology:
- Infective causes
- Bacterial- H. influenzae, staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, Tuberculosis, mycoplasma
- Viral- measles, adenovirus, influenza virus
- Fungal
- Obstructive causes
- Endobronchial benign neoplasm
- Foreign body aspiration
- Chronic bronchitis
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Noninfective causes
- Allergic
- Cystic fibrosis
- Clinical Features:
- Chronic cough with massive expectations
- Haemoptysis
- Recurrent pulmonary infection
- Dyspnoea
- hover, weight loss, anemia, and weakness
- Oedema
- Sepsis
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Question 3. Aspiration pneumonia
Answer:
Aspiration Pneumonia
- Aspiration Pneumonia is a consolidation of the lung in which there is the continued destruction of parenchyma by the inflammatory cells leading to the formation of microabscesses
Aspiration Pneumonia Clinical Features:
- High intermittent fever
- Cough
- Dyspnoea
- Tachycardia
- Restlessness
- Perspiration
- Weight loss
- Digital clubbing
Short answer questions on respiratory diseases
Question 4. Two causes of dull notes on percussion of the chest
Answer:
Causes Of Dull Note On Percussion Of The Chest
- Thickened pleura
- Pleural effusion
- Presence of solid growth
Question 5. Chronic obstructive lung disease
Answer:
Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is characterized by irreversible obstruction to the airflow throughout the lungs
Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Clinical Features:
- Age- common above 40 years of age
- Cough with small amounts of mucoid sputum
- Presence of pitting edema
- Types- pink puffers and blue bloaters
Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Investigations:
- Chest radiograph B Blood test
- Measurement of lung volumes
- Exercise test
Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Management:
- Smoking cessation
- Bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Oxygen therapy
Question 6. Drug resistance in tuberculosis
Answer:
Drug Resistance In Tuberculosis Develops Due To
- Slow division of mycobacterium
- Inadequate regimen
- Incomplete duration or dosage
- Presence of spontaneous point mutation
- The ability of mycobacterium to remain as persisted for years
- Intracellular location of bacilli
- Poor patient compliance
- Presence of caseous material
Question 7. Complication of chronic bronchitis
Answer:
Complication Of Chronic Bronchitis
- Type 1 and 2 respiratory failure
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension and corpulmonale
- Secondary infection
- Secondary polycythemia
Important short questions on respiratory diseases
Question 8. Hoarseness of voice
Answer:
Hoarseness Of Voice
Abnormal changes in the voice are called hoarseness
Causes
- Acute laryngitis
- Voice misuse
- Benign vocal cord lesions
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease
- Smoking
- Neurological diseases
- Thyroid problems
- Allergies
- Trauma to the voice box
- Laryngeal cancer
Question 9. Tracheal foreign body
Answer:
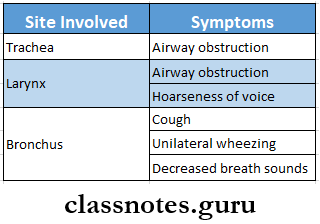
Tracheal Foreign Body
- Tracheal Foreign Body is common in children
- Common sites involved are
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchus
- Symptoms depend upon the site where the foreign body is settled
- Symptoms occur are:
Tracheal Foreign Body Investigations:
- Anteroposterior and lateral radiograph
- Biplane fluoroscopy
- Chest auscultations
Respiratory system disorders short notes
Question 10. DOTS on tuberculosis
Answer:
DOTS On Tuberculosis
- DOTS is Directly Observed Treatment Short course
- DOTS On Tuberculosis was recommended by WHO in 1995
- DOTS On Tuberculosis is found to be effective
- DOTS On Tuberculosis involves providing the most effective medicine and confirming that it is taken
- Anti-tubercular drugs during the intensive phase are administered under the direct supervision of peripheral health staff or through voluntary workers
- DOTS On Tuberculosis ensures a high cure rate through its following components
- Appropriate medical treatment
- Supervision and motivation by health and non-health workers
- Monitoring of disease status by health services
DOTS On Tuberculosis Category:
- According to DOTS, patients are grouped into two categories
- Category-1- New patients
- New sputum smear positive
- New sputum smear-negative
- New extrapulmonary
- New others
- Category 2- previously treated patients
- Smear positive relapse
- Smear positive failure
- Smear positive treatment after default
Pulmonary diseases short questions with answers
Question 11. CT scan
Answer:
CT Scan Uses:
- Evaluation of hilar and paratracheal lymph nodes
- Differentiate localized collection of fluid from a tumor
- Determine the position and size of pulmonary nodule
- Assess the spread of lung cancer
- Differentiate vascular mediastinal lesions
- Used to mark the site for pleural aspiration
Question 12. Causes of hemoptysis
Answer:
Causes Of Hemoptysis
- Inflammatory lung disease
- Bronchitis
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Lung abscess
- Bronchiectasis
- Neoplasms of lung
- Bronchial adenoma
- Bronchial carcinoma
- Cardiovascular
- Mitral stenosis
- Left ventricular failure
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Miscellaneous
- Pulmonary vasculitis
- Anticoagulant therapy
- Trauma to the lungs
Question 13. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
Answer:
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnoea
- Dyspnoea is abnormal and uncomfortable breathing which makes the patient aware of it
- Dyspnoea that occurs at night and awakens the patient is called paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
- It indicates left heart failure
- It gets precipitated by recumbent posture at night
Short notes on pneumonia and tuberculosis
Question 14. Bronchiectasis- three complications
Answer:
Bronchiectasis- Three Complications
- Recurrent pneumonia
- Corpulmonale
- Secondary amyloidosis
- Bacteraemia and septicemia
- Meningitis or brain abscess
- Massive hemoptysis
Question 15. Respiratory failure
Answer:
Respiratory Failure
- Failure of the respiratory system to maintain normal partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood is called respiratory failure
Respiratory Failure Types:
- Depending on the arterial blood gas analysis, it is classified into the following types
- Type 1 respiratory failure- hypoxemia
- Acute
- There is an acute alteration in blood gas concentration with hypoxemia and normal or hypocapnia
- Chronic
- There is a chronic alteration in blood gases due to the slow diffusion of carbon dioxide
- Acute
- Type 2- respiratory failure- Hypercapnia
- Acute- low PaO2 and pH but high PaO2
- There is hypercapnia and acute respiratory acidosis
- Chronic- low PaO2 high PaCO2 but low or normal pH
Question 16. Pleural effusion
(or)
Pulmonary effusion
Answer:
Pulmonary Effusion
- The collection of fluid in the pleural cavity irrespective of the nature of the fluid is called pleural effusion
Pulmonary Effusion Causes:
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Tuberculosis
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Pulmonary infarction
- Lymphomas
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Pancreatitis
Pulmonary Effusion Clinical Features:
- Fever
- Pleuritic pain
- Pyrexia
- Dyspnoea
- Treatment:
- Aspiration of pleural effusion
- Removal of the etiological agent
Respiratory infections short notes
Question 17. Pulmonary embolism
Answer:
Pulmonary Embolism Causes:
- Thrombotic
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Congestive heart failure
- Right-sided endocarditis
- Atrial fibrillation
- Nonthrombotic
- Fat embolism
- Amniotic fluid embolism
- Tumor embolism
- Parasitic embolism
- Air embolism
pulmonary Embolism Clinical Features:
- Acute dyspnoea
- Tachypnoea
- Tachycardia
- Haemoptysis
- Chest pain
- Pleuritic pain
- Wheezing
- Weakness, fatigue
- Syncope
- Hepatomegaly
Question 18. Anti-tubercular drugs
Answer:
Anti-tubercular Drugs
- According to the clinical utility, the anti-tubercular drugs are divided into
- First line drugs
- They have high antitubercular efficacy
- Have low toxicity
- They are:
- Isoniazid (H)
- Rifampicin (R)
- Pyrazinamide (Z)
- Ethambutol (E)
- Streptomycin (S)
- Second line drugs
- They have low antitubercular efficacy
- Have high toxicity
- They are:
- Thiacetone (Tzn)
- Para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS)
- Ethionamide (Etm)
- Kanamycin (Kmc)
- Amikacin (Am)
- Newer drugs are
- Ciprofloxacin
- Ofloxacin
- Clarithromycin
- Azithromycin
Pneumonia clinical features short answer
Question 19. Indications of oxygen therapy
Answer:
Indications Of Oxygen Therapy
- Type 1 respiratory failure
- Type 2 respiratory failure
- Shock
- Asphyxia
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Cardiac tamponade
- Acute severe asthma
- Acute pulmonary edema
- Tension pneumothorax
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
Pulmonary tuberculosis short note
Question 20. Lung cancer- three extra pulmonary manifestations
Answer:
Lung Cancer- Three Extra Pulmonary Manifestations
- Dyspnoea
- Haemoptysis
- Chronic coughing
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Cachexia
- Dysphonia
- Dysphagia
VIVA VOCE
- A decreased expiratory flow rate is the hallmark of obstructive lung disease
- Klibessela pneumonia is characterized by red current jelly sputum
- Legionella pneumonia is frequently associated with diarrhea
- Pneumonia alba is due to Treponema palladium
- Bronchopneumonia in measles is due to immunosuppression
- Plasma cell pneumonia is caused by pneuma- cystitis carnie
- Nosocomial pneumonia is hospital-induced pneumonia
- Koch’s phenomenon is seen in tuberculosis
- Most common cause of hemoptysis is bronchitis
- Pigeon chest is seen in severe asthma
- Barrel shaped chest is seen in COPD
