Red And White Lesions
Question 1. TNM staging
Answer:
TNM Staging
TNM Staging is the staging of malignancy which measures 3 major parameters of cancer
- T- The Size Of The Tumor
- N- lymph node involvement
- M-distant metastasis
- T- Primary Tumor
- The tx-primary tumor cannot be assessed
- To-No evidence of primary tumor
- This- carcinoma in situ o Ti- Tumour size- 2 cm or less in diameter
- T2– Tumour size- 2-4 cm in diameter
- T3– Tumour size- more than 4 cm in diameter
- T4– Tumour invades adjacent structures
- N- Regional Lymph Node
- Nx – Regional lymph node cannot be assessed
- N0-No regional lymph node metastasis
- N1– Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in dimension
- N2– Metastasis in the single ipsilateral lymph node, more than 3 cm but less than 6 cm
- N2a– Metastasis in the single ipsilateral lymph node, 3-6 cm in dimension
- N2b – Metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, not more than 6 cm
- N2c– Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, not more than 6 cm
- N3 – Metastasis in the lymph node, more than 6 cm in dimension
- M- Distant Metastasis
- Mx – The presence of distant metastasis cannot be assessed
- M0 – No distant metastasis Mi – Presence of metastasis
- M1– Presence of metastasis
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question and Answers
Question 2. Treatment of cancer
Answer:
Aims Of Cancer Treatment:
- Cure of the patient
- Palliation
- Preservation of function
- Cosmetic function
- Treatment of lymph node
- Treatment of advanced tumors
Role Of Chemotherapy:
- Cisplatin is the most effective drug
- In advanced cases, chemotherapy is given before surgery or radiotherapy
- This is called induction chemotherapy
Radiotherapy:
- Radiotherapy preserves anatomical parts and functions
- 6500-7500 cGy units are required to eradicate cancer
Role Of Surgery:
- It may be in the form of wide excision or wide excision with removal of the bone
- Radical neck dissection is done in case of lymph node involvement
Question 3. Lichenoid reactions
Answer:
Lichenoid Reactions
Lichenoid Reactions has a clinical picture similar to lichen planus
Lichenoid Reactions Etiology:
- Disorders: lichen planus
- Drugs:
- Antimicrobial: tetracycline
- Anti par asltit thlornquine
- Antihypertensive methyl dopa
- Anti ills gold
Lichenoid Reactions Clinical Features:
- Lichenoid mm positive over oral mucosa
- Lichenoid dermatitis: over the skin
- Lichenoid gingivitis.: over gingiva
Lichenoid reactions Management: discontinuation of the drug
Question 4. Erythroplakia.
Answer:
Erythroplakia
Erythroplakia is a red patch or plaque in the oral mucosa which cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other condition and which has no apparent cause
Etiology:
- Use of tobacco
- Alcohol
- Candida infection
- Idiopathic
Erythroplakia Clinical Features:
- Age: a fifth-seventh decade of life
- Sex: both sexes are equally affected
- Site
- The floor of the mouth
- Retromolar area
- Buccal mucosa
- Gingiva
- Tongue
- Soft palate
- Presentation
- It appears as a small or extensive reel lesion
- It has well-defined borders
Erythroplakia Types:
- Homogeneous
- Has uniform red patches all over
- Erythroplakia with interspersed patches of leukoplakia
- Has a few white leukoplakic patches along with a red patch
- Speckled leukoplakia
- It is characterized by the presence of soft irregular, raised, erythematous areas with a granular surface
Erythroplakia Differential Diagnosis:
- Candidiasis: Lesson can be rubbed off
- Denture Stomatitis: The commonly involved site is the palate
- Tuberculosis: Present of tubercular ulcers
- Histoplasmosis: It is common in farmers
Erythroplakia Management
- Elimination of the causative agent
- Mucosal stripping of the lesion
- Laser ablation
- Electrocoagulation
- Cryotherocoagulation
- Maintenance by periodic recall visits every 3 months
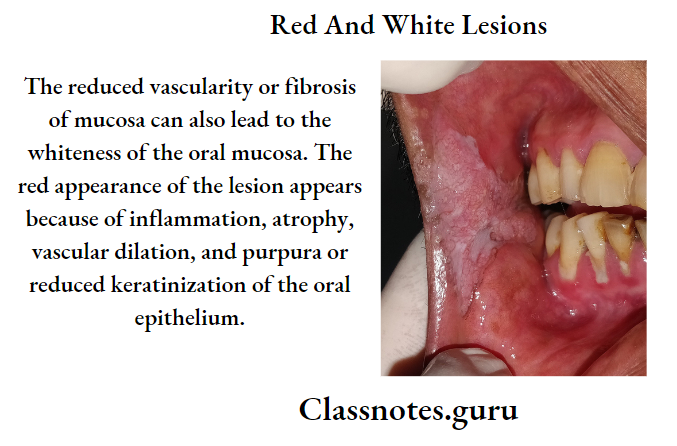
Question 5. Diagnosis of oral lichen planus.
Answer:
Diagnosis Of Oral Lichen Planus
- Clinical
- The presence of bilateral interlacing white striae
- Presence of Wickham striae and Koebner phenomenon
- Laboratory Diagnosis
- Hyperorthokeratosis
- Hyperparakeratosis
- Acanthosis with intercellular edema
- Civatte bodies
- The sawtooth appearance of the rete pegs
- Immunofluorescence
- Positive reactions with IgA, IgM, and IgG antisera
- Presence of subepithelial deposits of fibrinogen and antigenically related substances
Question 6. Atrophic candidiasis.
Answer:
Atrophic Candidiasis Synonym: Antibiotic sore mouth
Atrophic Candidiasis Clinical Features:
- Site: tongue, tissue underlying the prosthesis
- Presentation
- The lesion appears red or erythematous
- Patients usually have vague pain or a burning sensation
- Lesion reveals a lew white thickened foci, that are rubbed off leaving a painful surface
- It closely resembles erosive lichen planus and erythroplakia
Atrophic Candidiasis Differential Diagnosis:
- Chemical Burn: History of chemicals
- Drug Reaction: Diminished host response
- Syphilitic Mucous Patch– Skin lesion is also present
- NecroticUlcer And Gangrenous Stomatitis: Ulcer is deeper
- Traumatic Ulcer: History of trauma present
Atrophic Candidiasis Management:
- Elimination Of Causative Agent:
- Replacement of denture
- Relining of denture
- The denture must be cleaned thoroughly and regularly
- It should be left out of out of the mouth at night in a hypochlorite solution
- Topical application
- Clotrimazole:
- It is an effective topical treatment when dissolved in the mouth for five minutes daily
- Nystatin Preparation:
- Dissolves only in the mouth for 5 minutes a day.
- Amphotericin B:
- 5-10 ml of oral solution was used as a rinse.
Question 7. Erosive lichen planus.
Answer:
Erosive Lichen Planus
- It clinically exhibits a mixture of erythematous, ulcerated, and white pseudomembranous areas
- A faint white zone resembling radiating striae is frequently seen at the junction where the erosive area meets the normal epithelium
- Most of the lesions develop on the buccal mucosa and the vestibule
- Patients often complain of severe pain and burning sensation at the time of taking hot and spicy food
- Patients may restrict themselves to only the bland liquid diet
- Palpation of the affected mucosa often elicits pain and bleeding
- The areas of mucosa where the lesion has already healed up exhibit melanotic hyperpigmentation.
