Radiographic Film Processing Long Essays
Question 1. Write about the composition of X-ray film. Describe the mechanism of image formation. Write a note on the composition of developing and fixing solution and their functions.
Answer.
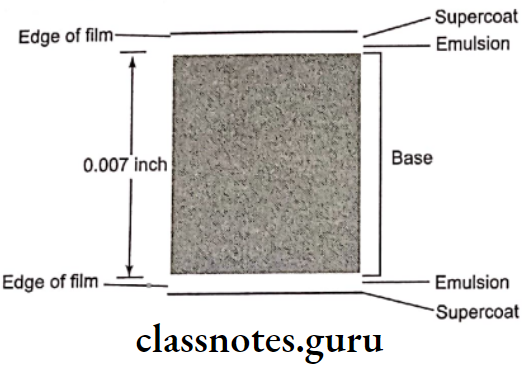
Composition Of Film:
Emulsion:
- It is sensitive to X-rays and visible light
- It records the image
- It consists of:
- Silver halide crystals
- They are composed of mainly silver bromide and lesser content of silver iodide which are photosensitive
- Each silver grain diameter is 1.8μm
- Gold may be added to improve its sensitivity
- Gelatin matrix
- It suspends silver halide crystals evenly in the gel made from cattle bone
- It absorbs the processing solution
- This allows the chemicals to react with silver halide crystals
Base:
- It is made up of Polyethylene terephthalate (polyester)
- Its diameter is 0.18mm
- The function of the base is to support the light-sensitive silver halide crystals
- The base is a slightly blue-tinted to enhance the image quality
- Its translucency cast no patterns on the resultant radiograph
- It withstands exposure during processing without distortion
- It is flexible for proper handling
- Adhesive layer
- It is applied to the base before the emulsion is applied for proper adaptation
Radiographic film processing long essay
Formation Of Image:
- The film emulsion is made up of silver bromide crystals and silver iodide crystals that are precipitated in gelatin
- When the silver halide crystals are irradiated by X-ray photons it will result in the release of electrons usually by the bromide ions
- This leads to the conversion of bromide ions to bromine atoms by removing electrons
- This recoil electron thus produced has sufficient kinetic energy with which it moves in the crystal and strikes the image site
- This imparts a negative charge to that region
- The free positively charged interstitial silver ions are attracted to the negative latent image site
- This neutralizes the image site with the result that an atom of metallic silver is deposited at the site
- After exposure of a film to radiation, the aggregate of silver atoms at the latent image sites comprises the latent image
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question and Answers
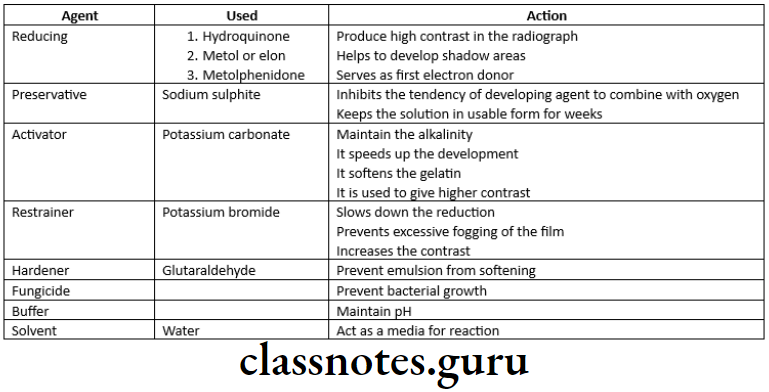
Composition Of Developer:
Film processing in radiology essay
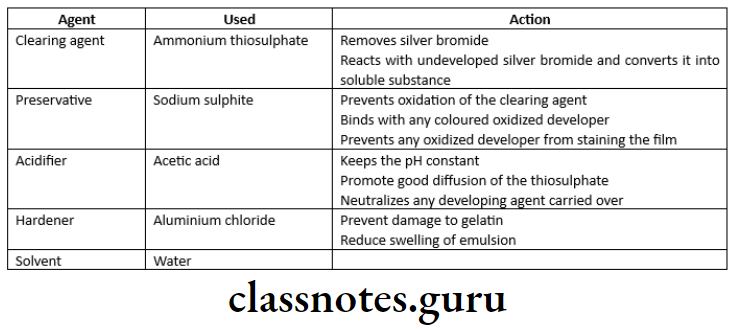
Fixing Solution
Question 2. Write in detail about the processing of X-ray film.
Or
Enumerate various film processing techniques. Describe in detail the manual procession.
Answer.
x-ray film Types:
- Manual method:
- Time-temperature
- Visual method
- Rapid processing method
- Automatic method:
- Monobath method
- Daylight method
- Digitalized processing method
- Self-developing films
Time Temperature Method:
- Initially replenish the developer & fixer solutions
- Set the temperature of the developer
- Unwrap the film
- Hold the film along the sides, & clip it to the hanger
- Agitate the film
- Keep it for the predetermined time
- After that place it in the circulating water
- Agitate for 20 – 30 seconds to remove excess solution
- According to the time & temperature of the developer, set that of the fixer
- Immerse the film in The Fixer
- Agitate for 5 of every 30 seconds
- After it, allow to drain the excess fixer solution
- Place it in circulating water for at least 20 minutes
- Dry the film
Visual Method:
- Place the film in the developer
- View them from time to time
- Look for the degree of darkness in the safelight
x-ray film Advantages:
- Developing to desired darkness is possible
- Fewer chances of errors
x-ray film Disadvantages:
- Individually processing required
- Thus, time-consuming
Automatic Film Processing
- This method uses equipment that automates all the processing steps
Automatic Film Processing Advantages:
- Rapid process
- Uniformity of the results is obtained
- Less space required
- The density and contrast of the film are consistent
Automatic Film Processing Disadvantages:
- Low quality as compared to that processed manually
- High cost of equipment
Automatic Film Processing Mechanism:
- The apparatus consists of a transport mechanism
- This picks up the unwrapped films which are passed through the developer, fixer, and drying sections
- The system uses a series of rollers driven by a constant-speed motor that operates through gears, belts, or chains
- The rollers consist of assemblies of multiple rollers
- It is so designed that the film crosses over from one roller to the next
- The operator may also be able to remove them independently for soaking, cleaning, and repairing
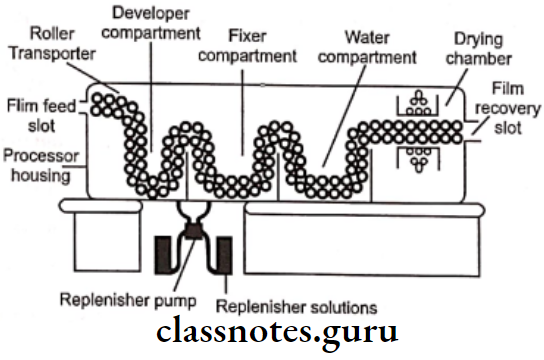
Radiographic film processing short essay
Question 3. Formation of latent image. Add a note about a fixer and developer solution
Answer.
Formation Of Image:
- The film emulsion is made up of silver bromide crystals and silver iodide crystals that are precipitated in gelatin
- When the silver halide crystals are irradiated by X-ray photons it will result in the release of electrons usually by the bromide ions
- This leads to the conversion of bromide ions to bromine atoms by removing an electron
- This recoil electron thus produced has sufficient kinetic energy with which it moves in the crystal and strikes the image site
- This imparts a negative charge to that region
- The free positively charged interstitial silver ions are attracted to the negative latent image site
- This neutralizes the image site with the result that an atom of metallic silver is deposited at the site
- After exposure of a film to radiation, the aggregate of silver atoms at the latent image site comprises the latent image
Fixing Solution:

Composition Of Developer

Radiographic Film Processing Short Essays
Question 1. Developer and fixing solution.
Answer.
Composition Of Developer:

Steps of radiographic film processing
Fixing Solution:

Question 2. Formation of latent image.
Answer.
Formation of the latent image
- The film emulsion is made up of silver bromide crystals and silver iodide crystals that are precipitated in gelatin
- When the silver halide crystals are irradiated by X-ray photons it will result in the release of electrons usually by the bromide ions
- This leads to the conversion of bromide ions to bromine atoms by removing an electron
- This recoil electron thus produced has sufficient kinetic energy with which it moves in the crystal and strikes the image site
- This imparts a negative charge to that region
- The free positively charged interstitial silver ions are attracted to the negative latent image site
- This neutralizes the image site with the result that an atom of metallic silver is deposited at the site
- After exposure of a film to radiation, the aggregate of silver atoms at the latent image site comprises the latent image
Question 3. Film processing.
Answer.
Film Processing Types:
- Manual method:
- Time-temperature
- Visual method
- Rapid processing method
- Automatic method:
- Monobath method
- Daylight method
- Digitalized processing method
- Self-developing films
Time Temperature Method:
- Initially replenish the developer & fixer solutions
- Set the temperature of the developer
- Unwrap the film
- Hold the film along the sides, & clip it to the hanger
- Agitate the film
- Keep it for the predetermined time
- After that place it in the circulating water
- Agitate for 20 – 30 seconds to remove excess solution
- According to the time & temperature of the developer, set that of the fixer
- Immerse the film in The Fixer
- Agitate for 5 of every 30 seconds
- After it, allow to drain the excess fixer solution
- Place it in circulating water for at least 20 minutes
- Dry the film
Manual film processing in radiography
Film Processing Visual Method:
- Place the film in the developer
- View them from time to time
- Look for the degree of darkness in the safelight
Film processing Advantages:
- Developing to desired darkness is possible
- Fewer chances of errors
Film processing Disadvantages:
- Individually processing required
- Thus, time-consuming
Question 4. Manual film processing.
Answer.
Time Temperature Method:
- Initially replenish the developer & fixer solutions
- Set the temperature of the developer
- Unwrap the film
- Hold the film along the sides, & clip it to the hanger
- Agitate the film
- Keep it for the predetermined time
- After that place it in the circulating water
- Agitate for 20 – 30 seconds to remove excess solution
- According to the time & temperature of the developer, set that of the fixer
- Immerse the film in The Fixer
- Agitate for 5 of every 30 seconds
- After it, allow to drain the excess fixer solution
- Place it in circulating water for at least 20 minutes
- Dry the film
Manual Film Processing Visual Method:
- Place the film in a developer
- View them from time to time
- Look for the degree of darkness in the safelight
Manual Film Processing Advantages:
- Developing to desired darkness is possible
- Fewer chances of errors
Manual Film Processing Disadvantages:
- Individually processing required
- Thus, time-consuming
Question 5. Automatic Film Processing.
Answer.
Automatic Film Processing
- This method uses equipment that automates all the processing steps
Automatic Film Processing Advantages:
- Rapid process
- Uniformity of the results is obtained
- Less space required
- The density and contrast of the film are consistent
Automatic Film Processing Disadvantages:
- Low quality as compared to that processed manually
- High cost of equipment
Automatic Film Processing Mechanism:
- The apparatus consists of a transport mechanism
- This picks up the unwrapped films which are passed through the developer, fixer, and drying sections
- The system uses a series of rollers driven by a constant-speed motor that operates through gears, belts, or chains
- The rollers consist of assemblies of multiple rollers
- It is so designed that the film crosses over from one roller to the next
- The operator may also be able to remove them independently for soaking, cleaning, and repairing
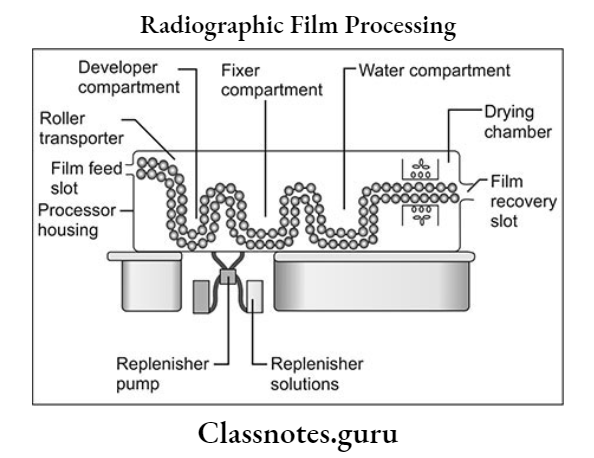
Automatic film processing radiology essay
Question 6. Coin test.
Answer.
Coin test AIM:
- To evaluate safelight requirements
Coin test Method:
- Shut all the lights
- Put on the safe light
- Open the film packet
- Place the film over the unwrapped surface
- Place a coin over it
- Leave it for approximately the time required for unwrapping the full-mouth radiograph which is about 5 minutes
- Develop the film
Coin test Result:
- If the image of the coin can be seen on the resultant film, the room is not light-safe
Radiographic Film Processing Short Answers
Question 1. Latent image.
Answer.
Latent image
- When the radiographic film is exposed to the information-carrying beam of photons exiting an object, the photosensitive silver halide crystals in the film emulsion interact with these photons and are chemically changed
- These chemically altered crystals constitute the latent image of the film
- This increases the liability of crystals to the chemical action of the developing process that converts the latent image into a visible image
Question 2. Composition of developer
Answer.
Composition Of Developer:

Essay on X-ray film processing
Question 3. Fixing solution
Answer.
Fixing Solution:

Radiographic darkroom procedure essay
Question 4. Darkroom requirements.
Answer.
Size:
- 3 feet x 3 feet for an individual dentist
- 16 – 20 square feet for group practice
- Should have sufficient space to accommodate the processing tanks
- It must include an adequate working area where the films are unwrapped
- It must contain a storage space
- It should be well-ventilated
- Room temperature must be 70 degrees
- Humidity levels must be between 50-70%
- The room must include both hot & cold running water
- Wastebasket for disposal of all film wrappings
- Safe light mounted on the wall or ceiling
- It should be at least 4 feet from the work surface
Film development and fixing short notes
Radiographic Film Processing Viva Voce
- The height of safe light from the working area should be 1.22m [4 feet]
- The temperature of X-ray processing tanks should be between 60-75°F
- In developer, sodium sulfite acts as a preservative
- Hydroquinone in developer is added to increase the contrast of the image
