Panoramic Radiography Important Notes
- The areas, which are not visible in O.P.G are:
- Mandibular canine area
- Coronoid process
- Anterior body of mandible
Panoramic radiography questions and answers
Panoramic Radiography Long Essays
Question 1. Describe the principle, indication, and limitations of panoramic radiographs.
Or
Describe the principles of panoramic radiography. Enumerate its indications and limitations
Answer.
Panoramic Radiographs Principle:
- This is based on the curvilinear variant of conventional tomography
- The movement of the tube head and the film produces an image through the process known as “tomography”
- Curvilinear tomography is also based on the principle of reciprocal movement of an X-ray source and an image receptor around a central point or plane called an image layer
Panoramic Radiographs Indications:
- As a substitute for full mouth intraoral periapical radiograph
- For evaluation of tooth development for children, the mixed dentition and also the aged
- To assist and assess the patient for and during orthodontic treatment
- To establish the site and size of lesions
- Prior to any surgical procedures
- Forthe detection of fractures
- For follow-up of treatment, progress of pathology or prostoperative bony healing
- Investigation of TMJ dysfunction
- To study the antrum
- For overall view of the alveolar bone levels
- Assessment of underlying bone diseases
- Evaluation of developmental anomalies
- Evaluation of bone level before inserting implants
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question and Answers
Panoramic Radiographs Limitations:
- Areas of diagnostic interest outside the focal through may be poorly visualized
- Poor diagnostic value in terms of magnification, distortion, loss of details
- There is overlapping of teeth in the bicuspid area of the maxilla and mandible
- In cases of pronounced inclination, the anterior teeth are poorly defined
- The density of spine causes lack of clarity in central portion of the film
- Formation of ghost images due to soft tissue shadows and air spaces
Panoramic Radiography Short Essays
Question 1. OPG.
Or
Note on panoramic imaging
Or
Panoramic radiography
Answer.
OPG Definition:
- It is a technique for producing a single tomographic image of the facial structures that induces both the maxillary and mandible dental arches and their supporting structures
OPG Principle:
- This is based on curvilinear variant of conventional tomography
- The movement of the tube head and the film produces an images through the process known as “tomography”
- Curvilinear tomography is also based on the principle of reciprocal movement of an X-ray source and an image receptor around a central point or plane called as image layer
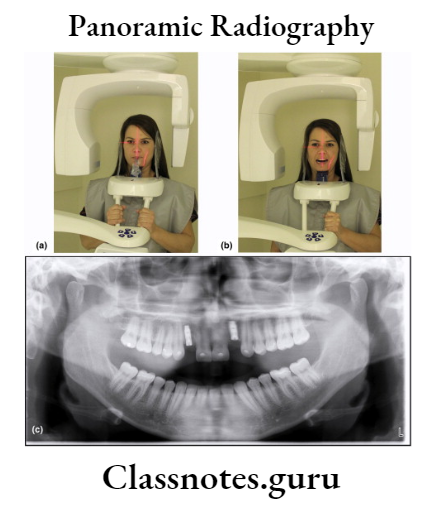
OPG Procedure:
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Make the patient to remove all the accessories that may interfere with the image
- Position the patient such that he is in the focal through
- Instruct the patient to look straight
- Patient is positioned such that dental arches are located in the middle of the focal through
- Occlusal plane is adjusted such that the Frankfort plane is parallel to the floor
- This is done by placing central incisor into a notched incisal device with lead marker
- Center the lower border of mandible on the chin rest and is equidistant
- Instruct the patient to position the tongue on the palate
- Exposure the film
- Process it as usual
OPG (orthopantomogram) questions for BDS
Question 2. Advantages and disadvantages of orthopantomograph
Answer.
Orthopantograph:
- It is a technique for producing a single tomographic image of the facial structures that induces both the maxillary and mandible dental arches and their supporting structures
Orthopantograph Advantages:
- Broad coverage of facial bones and teeth
- Low radiation dose
- Ease of apnoramic radiographic technique
- Can be used in patients with trismus or in patients who cannot tolerate intraoral radiography
- Quick and convenient technique
- Useful visual aid in patient education and case presentation
Orthopantograph Disadvantages:
- Resolution is very low
- Cannot be used in the diagnosis of caries
- Cannot be used in the evaluation of bone loss due to periodontal diseases
- Shows superimposition, especially in the premolar region
- Structures outside the image layer cannot be visualized
- Cannot be used as substitute to intraoral radiography
- Magnification across image is unequal
- Requires accurate patient positioning to avoid positioning errors and artifacts
- Difficult to image both jaws when patient have severe maxillomandibular discrepancy
Panoramic radiograph interpretation questions
Panoramic Radiography Short Answers
Question 1. Principle of panoramic imaging.
Answer.
Panoramic Imaging Principle:
- This is based on curvilinear variant of conventional tomography
- The movement of the tube head and the film produces an images through the process known as “tomography”
- Curvilinear tomography is also based on the principle of reciprocal movement of an X-ray source and an image receptor around a central point or plane called as image layer
Question 2. Advantages of OPG
Answer.
Advantages of OPG
- Broad coverage of facial bones and teeth
- Low radiation dose
- Ease of apnoramic radiographic technique
- Can be used in patients with trismus or in patients who cannot tolerate intraoral radiography
- Quick and convenient technique
- Useful visual aid in patient education and case presentation
Question 3. OPG – indications
Answer.
OPG – indications
- As a substitute for full mouth intraoral periapical radiograph
- For evaluation of tooth development for children, the mixed dentition and also the aged
- For assist and assess the patient for and during orthodontic treatment
- To establish the site and size of lesions
- Prior to any surgical procedures
- For detection of fractures
- For follow up of treatment, progress of pathology or prostoperative bony healing
- Investigation of TMJ dysfunction
- To study the antrum
- For overall view of the alveolar bone levels
- Assessment of underlying bone diseases
- Evaluation of developmental anomalies
- Evaluation of bone level before inserting implants
Panoramic radiography viva questions
Panoramic Radiography Viva Voce
- 3 centers of rotation are there in OPG
- Radiation exposure is less for panoramic radiography compared to CT scan. It is highest for arthography.
- In panoramic radiograph smiling or appearance of structures is seen if patients chin is tilted downward.
- Frowning appearance is seen if patient’s chin is tilted upwards
