Oral Pathology Miscellaneous Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Autoclave
Answer:
Autoclave
Autoclave is the process of sterilization by saturated steam under high pressure above 100 degrees C temperature
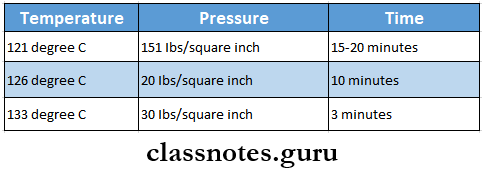
Autoclave Sterilization Conditions:
Autoclave Uses:
- Articles Sterilised In Autoclave Are:
- Culture media
- Rubber articles like tubes, gloves, etc
- Syringes and surgical instruments
- OT gowns, dressing materials
- Endodontic instruments
- Hand instruments
Question 2. Odontalgia
Answer:
Odontalgia
- Odontalgia refers to chronic tooth pain
- Odontalgia is throbbing and constant toothache
- The intensity of pain varies from very mild to very severe
- Odontalgia occurs without any cause
- Pain may be associated with a dental procedure
- Odontalgia is not relieved by any dental procedure
- Odontalgia is not aggravated by hot or cold food or drinks or chewing or biting
- Odontalgia is diagnosed by clinical history and radiographic examination
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Questions and Answers
Question 3. Gram staining
Answer:
Gram Staining
Gram staining is an essential procedure used in the identification of bacteria and is frequently the only method required to study their morphology
Gram Staining Method:
- Primary staining with pararosanilinc dye for 1 minute
- Application of Gram’s iodine over slide for 1 minute
- Decolonization with organic solvent for 10-30 seconds
- Counterstaining with the dye of contrasting color for 30 seconds
Question 4. Histopathology of dentin
Answer:
Histopathology Of Dentin Consists Of:
- Dentinal Tubules
- Dentinal Tubules extend through the entire thickness of the dentin from the dentin enamel junction to the pulp
- Dentinal Tubules follow an S-shaped path
- Peritubular Dentin
- Peritubular Dentin is the dentin that immediately surrounds the dentinal tubules
- Peritubular Dentin is hyper mineralized structure
- Intertubular Dentin
- Intertubular Dentin is dentin located between dentinal tubules
- Intertubular Dentin forms main body of dentin
- Presenting
- Presenting is first formed dentin
- Presenting lines pulpal portion of the tooth
- Presenting consists of collagen and non-collagenous components
- Odontoblast Process
- Odontoblast Process are cytoplasmic extensions of the odontoblasts
- Odontoblast Process extends into dentinal tubules
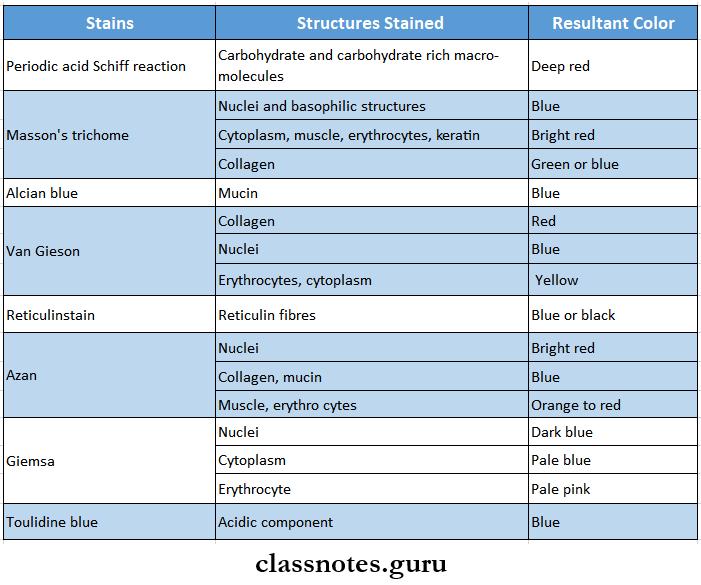
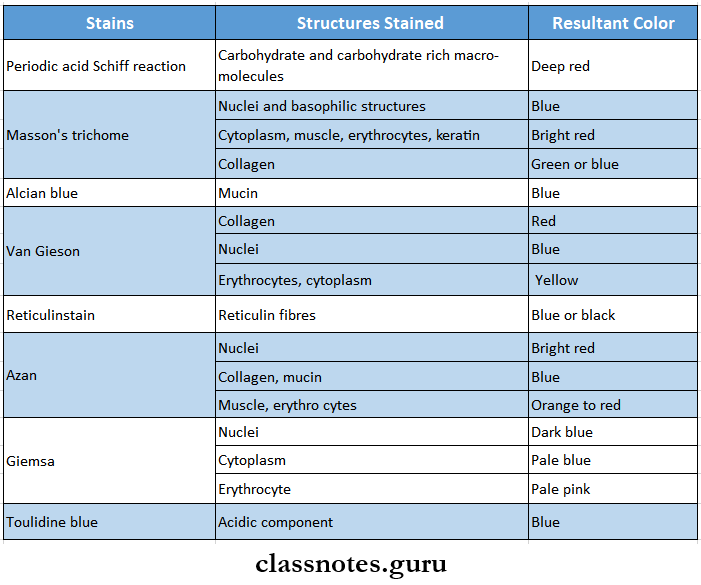
Question 5. Common and special stains used
(or)
Histopathological diagnosis of the lesions
Answer:
Common And Special Stains Used
Question 6. Haemotoxylin and eosin staining
Answer:
Haemotoxylin And Eosin Staining
- Haemotoxylin and eosin are routine staining methods
- Haemotoxylin is a basic dye with an affinity for nucleic acid
- Haemotoxylin stains either regressive or progressive
- With regressive stain, the slides are left in the solution for a set period of time
- With progressive stain, the slide is dipped in solution until the desired intensity of staining is achieved
- Eosin is an acidic dye for cytoplasmic components of cell
Question 7. Barodontalgia or Aerodontalgia
Answer:
Barodontalgia Or Aerodontalgia
Barodontalgia Or Aerodontalgia is an unusual type of dental pain that occurs as an effect of a change in the pressure
Barodontalgia Or Aerodontalgia Clinical Features:
- Barodontalgia Or Aerodontalgia affects some persons who experience pain in the tooth during high altitude flight or during deep sea diving
- At ground levels, the tooth is completely asymptomatic
- Pain occurs a few hours or days later
- Barodontalgia Or Aerodontalgia occurs in an endodontically treated tooth with improper obturation of canals
- The entrapped air in the improperly obturated root canals may expand during flight or during diving which creates pressure in the periapical nerve budles and produces pain
Question 8. Dead tracts of Fish
Answer:
Dead Tracts Of Fish
- Dentinal tubules are emptied by complete retraction of the odontoblast process from the tubule or through the death of the odontoblast
- The dentinal tubules become sealed off so that in-ground section air-filled tubules appear by transmitted light as black dead tracts
- Dead Tracts Of Fish are most often seen in coronal dentin
- Frequently bound by bands of sclerotic dentin
- Dead Tracts Of Fish areas demonstrate decreased sensitivity
- Dead Tracts Of Fish are the initial step in the formation of sclerotic dentin
Question 9. The isomorphic phenomenon at Kolnwr
Answer:
The Isomorphic Phenomenon At Kolnwr
- If the feature of lichen planus
- Isomorphic Phenomenon At Kolnwr refers to the development of skin lesions of lichen planus
- The Isomorphic Phenomenon At Kolnwr extends along the areas of Injury or irritation
- Isomorphic Phenomenon At Kolnwr sometimes exhibits periods of regression and recurrence
Question 10. Culture media for Candida albicans and Tubercle bacilli
Answer:
Culture Media For Candida Albicans:
- Sabouraud’s Dextrose Dgar Media
- Media is inoculated and incubated at 25-37 degrees C for 24 hours
- Cream-colored smooth pasty colonies appear
- On grain staining, it shows gram-positive budding yeast cells
Culture Media For Tubercle Bacilli:
- Lowenstein-Jensen Media
- Results in dry, rough, buff-coloured colonies which get raised with a wrinkled surface
- Liquid Media
- Bacilli grow over it as surface pellicle
Question 11. Fixatives
Answer:
Fixatives
Question 12. ELISA
Answer:
ELISA
ELISA Is color reaction test
ELISA Method:
- A serum containing antibodies Is developed from the patient’s blood sample
- ELISA is added to die ELISA plate
- Wash off the inactive antibodies
- A second layer of antibodies, called a conjugate is added
- Excess antibodies are again washed off
- A substrate (chromogen) is added to it.
ELISA Result:
- Color becomes a darker positive test
- No color change – Negative lest
Question 13. Microtome
Answer:
Microtome
- Microtome is a tool used to cut sections for study under a microscope
- Microtome Types
- Sledge
- Rotary
- Cryomicrotome
- Ultramicrotome
- Vibrating microtome
- Laser microtome
- Saw
- Microtome Knives Used With It Are
- Steel
- Glass
- Diamond
- Microtome Uses
- Histological examination
- Frozen section
- Electron microscopy
- Spectroscopy
Question 14. Foam Cells
Answer:
Foam Cells
- Foam Cells are a type of cell containing cholesterol
- Contains low-density lipoprotein
- Foam Cells Present in
- Chlamydia
- Toxoplasma
- Tuberculosis
- Foam cells are formed when circulating monocyte-derived cells are migrated to the atherosclerotic site or fat deposits in blood vessel walls
- Foam Cells can lead to atherosclerosis
Question 15. Reiter’s syndrome
Answer:
Reiter’s Syndrome
- There Is A Tetrad Of Manifestations
- Urethritis – urethral discharge associated with burning sensation and itching
- Arthritis – bilateral, symmetrical, and polyarticular
- Conjunctivitis – mild
- Mucocutaneous lesions – red or yellow keratotic macules or papules
Question 16. Decalcifying Agents
Answer:
Decalcifying Agents
- They are acidic substances that combine with lime forming water-soluble compounds that easily can be removed
- Decalcifying Agents Types
- Chelating Agents
- Take up the calcium ions
- Example: EDTA
- Acids
- Help to produce of solution of calcium ions
- Example:
- Weak acid – acetic acid, formic acid
- Strong acid – nitric acid, hydrochloric acid
- Chelating Agents
Question 17. Technique of exfoliative cytology
Answer:
Technique Of Exfoliative Cytology

The Technique Of Exfoliative Cytology Results:
- Class 1: Normal
- Class 2: atypical
- Class 3: Intermediate
- Class 4: Suggestive of cancer
- Class 5: Positive for cancer
