NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 6 New Questions And Ideas
Question 1. Describe the ways in which the Buddha tried to spread his message to the people.
Answer:
- Buddha taught the people in Prakrit, which was the language of the ordinary people, so that everybody could understand his message without any difficulty.
- Buddha also encouraged people to think for themselves rather to simply accept what he said.
- Buddha, himself set an example by leading a simple life.
- Gautam Buddha moved from place to place to give his message to all people.
Question 2. Write whether true or false:
1. The Buddha encouraged animal sacrifices.
Answer: False
Read and Learn More NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science
2. Sarnath is important because it was the place where the Buddha taught for the first time.
Answer: True
3. The Buddha taught that karma has no effect on our lives.
Answer: False
4. The Buddha attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya.
Answer: True
NCERT Solutions Class 6 History Chapter 6 New Questions and Ideas
5. Upanishadic thinkers believed that the Atman and Brahman were ultimately one.
Answer: True.

Question 3. What were the questions that Upanishadic thinkers wanted to answer?
Answer:
Some of them wanted to know about life after death, others wanted to know why sacrifices should be performed.
Many Upanishadic thinkers felt that there was something permanent in the world, something that would last even after death. They described this as the atman or the individual soul and the brahman or the universal soul. They believed that ultimately, both the atman and the Brahman were one.
NCERT Books 6 Class
Question 4. What were the main teachings of the Mahavira?
Answer:
The Main Teachings Of Mahavira Are:
- He taught a simple doctrine, men and women who wished to know the truth must leave their homes.
- They must follow the rules of ahimsa, which means not hurting or killing living beings, even unintentionally. For example, they had to cover their mouth and nose with cloth. This was to ensure that they did not (even by mistake) kill small insects by the hot steam of their breath.
- Not to steal and lead a simple life.
- Mahavira was against the caste system. He questioned the superiority of Brahmins.
- Mahavira laid stress on Triratna or the three jewels of life
- Right Conduct,
- Right Belief
- Right Knowledge.
Question 5. Why do you think Anaglia’s mother wanted her to know the story of the Buddha?
Answer:
We think that Anagha’s mother wanted her to know the story of the Buddha. The story of the Buddha would tell her about Buddha’s life as well as about his teachings and ideas.
Question 6. Do you think it would have been easy for slaves to join them? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Yes, I think it would have been easy for slaves to join the sangha. Because Buddha favored and stressed the equality of human beings. Moreover, some slaves were very good in their work and performed many useful services for the people of Sanghas.
Question 7. Discuss the reasons why the Chinese pilgrims came to India.
Answer:
The Chinese pilgrims came to India to visit places associated with the life and teachings of the Buddha as well as famous monasteries. They procured Buddhist religious books also. They carried some books back with them.
Question 8. What is the true meaning of life?
Answer:
- It is very important even today to know the true meaning of life. Because this idea will make us truthful.
- We will lead a simple life. A simple way of life takes us towards honesty and makes us peaceful.
- This way of life also takes us nearer to God or Brahma.
New Questions and Ideas Class 6 History NCERT Solutions
Question 9. Why life is full of suffering and unhappiness?
Answer:
- Gautam, the Buddha taught us that worldly life is full of suffering and unhappiness.
- This is caused because we have cravings and desires (which generally cannot be fulfilled). Sometimes, even if we get what we desire, we are not satisfied and want even more (or other things).
- This is tanha or trishna or thirst.
- This carving could be removed by following moderation in everything.
Question 10. What is Ahimsa or Non-violence? Why is it important even today?
Answer:
Ahimsa or a Non-violence word meaning is not killing any other living person, creature, cattle, or insect. Ahimsa is useful even today. It makes us kind; and teaches us to respect the lives of others, including animals.
Question 11. Find out more about men and women who renounce the world today. Where do they live, what kinds of clothes do they wear, what do they eat? Why do they renounce the world?
Answer:
- Religious saints, monks, nuns, philosophers, jain-munnies (men as well as women), men and women who have joined the — Sangha renounce the world even today.
- They live in ashrams, vihars, sangha, dargahas, churches, or lonely places for meditation or worship. Some of them even live in remote forests or near0 some permanent rivers or in the high mountains. They meditate for the most of the time.
- They wear very simple clothes and clothes of a particular color (white, saffron, or green) and design.
- Generally, they eat vegetarian food, simple rice or chapattis along with milk, fruits, vegetables, and pulses.
- They renounce the world because they feel that only those who leave their homes can gain true knowledge and nirvana.
Question 12. What was the language used to compose the Vedas?
Answer:
The language used to compose Vedas was Vedic Sanskrit.
Question 13. What was the Buddha trying to teach the sorrowing mother?
Answer:
Buddha was trying to teach the sorrowing mother that no one is immortal. That one who has come to this world has to go back or die.
Question 14. How did the beggar convince the sages to share their food with him?
Answer:
The beggar asked the sages whom they worship, When the sages replied that they worship the universal soul, the beggar said when they know that the universal soul fills everyone’s stomach then he should also be fed as he is also a part of the world. On hearing this the sages realised the truth and shared their food with the beggar.
Question 15. Why do you think the term Jina was used for Mahavira?
Answer:
The term Jina was used for Mahavira because it means one who has conquered temporal and material existence through self-discipline.
Question 16. List at least two ways in which the sangha described in this lesson was different. Were there any similarities?
Answer:
The difference between the two sanghas:
- Sangha or Gana was a form of government and Sangha of this Chapter is a religious group of people who have left their home in search of truth.
- Women, dasas, and kammakaras could not be a part of the political sangha. Anyone irrespective of caste, sex, or creed could join the religious sangha.
- The only similarity was that the political sangha met to discuss political issues and the religious sangha together discussed social issues.
Question 17. In what ways is the system of ‘ashramas’ different from life in the Sangha?
Answer:
Sangha was a place where people who left their homes lived and meditated together. All men were allowed to join sangha whereas children had to take permission from their parents, slaves from their masters, and women from their husbands.
Ashrama does not mean a place where people live and meditate. But ashramas means four stages of life. They were known as brahmacharya, grihastha, vanaprastha, and sannyasa.
Question 18. List the reasons why Xuan Zang wanted to study in Nalanda.
Answer:
Xuan Yang Wanted To Study In Nalanda Because:
- The teachers were of the highest ability and talent.
- The following of Buddha were strictly followed.
- The rules of the monastery were strict and everyone had to follow them.
- The new entrants had to go through a severe level of test to get admitted.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Who was Siddhartha? Where was he born?
Answer:
Siddhartha was the real name of Gautama Buddha. He founded ‘Buddhism’. He was born about 2500 years ago as a Kshatriya in Sakya gana (now in Nepal).
Question 2. Name the exceptions to Upanishadic thinkers.
Answer:
Most of the Upanishadic thinkers were Brahmins or rajas i.e., men. But, there were exceptions like Gargi, a woman, and Jabala, a slave.
Question 3. Who developed the ideas given in the Upanishads?
Answer:
Shankaracharya (Adi), a famous thinker, later developed the ideas given in the Upanishads.
Chapter 6 New Questions and Ideas NCERT Solutions
Question 4. Which changes came in India about 2500 years ago?
Answer:
The New Changes Were:
- Mahajanapadas were growing and cities were being established.
- New religions: Buddhism and Jainism were taking shape.
Question 5. What do we mean by “Karma”?
Answer:
Karma refers to our actions—good or bad. As per the religious leaders karma affects our present and future life.
Question 6. Which book gives the rules of Buddhism?
Answer:
Rules of Buddhist sangha are given in “Vinaya Pitaka”.
New Questions And Ideas Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Discuss in brief the story of the Buddha.
Answer:
- When Gautama Buddha was a young man, he left the comforts of his home in search of knowledge. He wandered for several years, meeting and holding discussions with other thinkers (philosophers). He finally decided to find his own path to realization.
- He meditated for many years under a peepal tree at Bodhgaya, where he attained enlightenment. After that, he was known as the Buddha or the Wise One.
- After attaining enlightenment Buddha went to Samath, near Varanasi, where he taught for the first time. He spent the rest of his life traveling on foot, going from place to place, teaching people, till he passed away at Kusinara.
Question 2. Write in short the life story of Vardhamana Mahavira.
Answer:
- Vardhamana Mahavira was a Kshatriya prince of the Lichchhavis. Lichchhavis was a part of the Vajji Sangha.
- At the age of thirty, Mahavira left home and went to live in a forest. For twelve years he led a hard and lonely life, at the end of which he attained enlightenment.
- The teachings of Mahavira and his followers were written down at a place called Valabhi, in Gujarat, about 1500 years ago.
Question 3. Write a short note on the six schools of philosophy.
Answer:
The Truth Was Explored By Indian Intellectuals Centuries Ago. It Has Been Represented By Six Systems Of Philosophy. These Are Known As
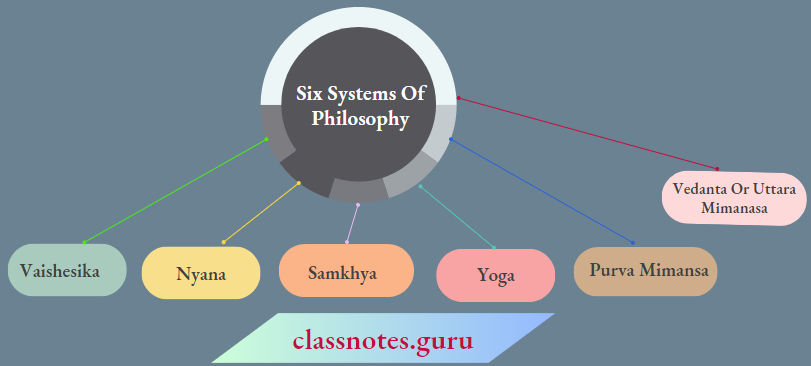
It is believed that these systems of philosophy were founded by sages Konda, Gotama, Kapila, Patanjali, Jamini, and Vyasa respectively.
The scholarly discourse of these philosophies still guides the country. Friedrich Max Muller, German-bom British indologist has observed that these theories have been developed by individual thinkers. But they underlay harmony in their understanding of truth.
New Questions And Ideas Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What were the main teachings of the Buddha?
Answer:
The main Teachings Of The Buddha Were:
- The Buddha taught that life is full of suffering and unhappiness. This is caused because we have cravings and desires (which cannot be fulfilled).
- Sometimes, even if we get what we desire, we are not satisfied (permanently) and want (or desire) even more and more (or other things). The Buddha described this as thirst or tanka.
- The Buddha taught that thirst or tanha or constant craving could be removed by following moderation in everything.
- He also taught people to be kind and to respect the lives of others, including animals.
- The Buddha believed that the result of our actions (called Karma), whether good or bad, affects us both in this life and in the next life.
- He also encouraged, people to think for themselves rather than simply follow what he (the Buddha) said.
- The Buddha taught in Prakrit. This was the language of the ordinary people. So everybody could understand his message.
Question 2. Write a short note on the following:
- Upanishads
- Panini, the grammarian.
Answer:
- Upanishads
- Background. Around the time of Buddha or a little earlier, other thinkers also tried to find answers to difficult questions about life.
- Some of them wanted to know about life after death, others wanted to know why sacrifices should be performed.
- Many of these thinkers felt that there was something permanent in the world, which would last even after death. They described this as the atman or the individual soul. They also described the Brahman or the universal soul.
- They believed that ultimately, both the atman and the Brahman were one and the same.
- Many ideas of the ancient thinkers were recorded in books called the Upanishads. These were part of the later Vedic texts (i.e., all three Vedas, other than the Rigveda are called the later Vedas).
- Upanishad literally means “approaching and sitting near” and the texts contain conversation between teachers and students. Generally, ideas were presented through simple dialogues.
- Background. Around the time of Buddha or a little earlier, other thinkers also tried to find answers to difficult questions about life.
- Panini, the grammarian
- He was a great scholar. He prepared grammar for Sanskrit, He arranged the vowels and the consonants in a special order. He used to create formulae like those found in Algebra.
- He used them to write down the rules of the language in short formulae (around 3,000).
New Questions and Ideas: NCERT Solutions Chapter 6
Question 3. Discuss Jainism, in brief.
Answer:
- The word Jaina comes from the term Jina, meaning conqueror.
- Followers of Vardhamana Mahavira, who were known as Jainas, had to lead very simple lives and begging for food.
- They had to be truthful and honest. They were especially asked not to steal.
- The followers of Mahavira had to observe celibacy. And men preachers had to give up everything, including their clothes.
- Mahavira taught a simple doctrine: men and women who wished to know the truth must leave their homes. They must follow the rules of ahimsa.
- The Jain Munnies had to cover their mouth and nose with a piece of cloth, ensuring that they did not kill small insects with their breath.
- Ordinary people could understand the teachings of Mahavira and his followers because they used Prakrit, the language of the people of that time.
Question 4. Why did the Jainism could not become popular among most of the people?
Or
What were the reasons for the low popularity of Jainism?
Answer:
- It was very difficult for most men and women to follow the main principles (or rules) strictly as desired by the founders and preachers of Jainism.
- Nevertheless, thousands left their homes to learn and teach the new way of life, preached by Jainism, Many more remained behind and supported those who became monks and nuns providing them with food.
- Jainism was supported mainly by traders. Farmers (the main portion of India’s population), who had to kill insects to protect their crops, found it more difficult to follow the rules.
Question 5. Discuss the Sangha.
Answer:
- Buddha (the founder of Buddhism) felt that only those who left their homes could gain true knowledge. He arranged for them to stay together in the sangha.
- The rules made for the Buddhist sangha were written down in a book called the Vinaya Pitaka. From this book, we know that there were separate branches for men and women.
- All men could join the sangha. However, children had to take the permission of their parents, slaves of their masters, those who worked for the king had to take his permission, and debtors that of creditors.
- Women had to take their husband’s permission.
- Men and women of the sangha led simple lives. They meditated for most of the time.
- They went to villages, towns, and cities to beg for their food during fixed hours. That is why, they were known as hhikkhus and hhikkhunis.
- They taught others and helped one another. They held frequent meetings to settle any quarrels that took place.
- Those who joined the sangha included Brahmins, Kshatriyas, merchants, laborers, barbers, and slaves. Many of them wrote down the teachings of the Buddha. Some of them also composed beautiful poems, describing their life in the sangha.
Question 6. Discuss the Vihars of the Jainas and the Buddhists.
Answer:
- To begin with, both Jaina and Buddhist bhikkhus went from place to place throughout the year, teaching people about their religions. They stayed in one place during the rainy season, when it was very difficult to travel,
- As time passed, the supporters of the bhikkhus built temporary shelters for them in gardens or they lived in natural caves in hilly areas.
- Then, several supporters of bhikkhus and bhikkhunis, and they themselves, felt the need for more permanent shelters, These were called Viharas. Initially, Viharas were made of wood, but later, Viharas were made of bricks. Some were even dug out in hills, especially in western India.
- Generally, the land for Vihara was donated by a rich merchant or the ruler. The local people came with gifts of food, clothing, medicines, etc. for the monks and nuns.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 6 Multiple Choice Questions
Choose The Correct Answer:
Question 1. When was Gautama Buddha’s horn?
- About 3,000 years ago
- About 2,500 years ago
- About 1,500 years ago
- About 1,000 years ago
Answer: 2. About 2,500 years ago
Question 2. Where did Buddha give his first sermon?
- Pataliputra
- Gaya
- Samath
- All of these
Answer: 3. Samath
Question 3. Who thought that people should be kind and respect others?
- Gautama Buddha
- Ajatasattu
- Shiva
- Alexander
Answer: 1. Gautama Buddha
Question 4. Who is the famous Tirthankara of Jains?
- Lord Krishna
- Lord Buddha
- Lord Mahavira
- Lord Mahesh
Answer: 3. Lord Mahavira
Question 5. What does Upanishad literally mean?
- Approaching and sitting near
- Go far away
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 1. Approaching and sitting near
Question 6. Who went door to door to find out the home, where nobody had died?
- Kisagotami
- Rajula
- Sita
- Ahiliya
Answer: 1. Kisagotami
Question 7. Who believed that the result of our action is karma?
- Mahavira
- Buddha
- Indra
- Ram Chandra
Answer: 2. Buddha
History Chapter 6 NCERT Solutions New Questions and Ideas
Question 8. At what age did Mahavira leave his home and go to live in a forest?
- At 15 years
- At 30 years
- At 40 years
- At 45 years
Answer: 2. At 30 years
Question 9. What was Mahavira’s teachings?
- Live and let to be live
- Neither live nor to be lived
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 1. Live and let to be live
Question 10. What did bhikkhus mean?
- Beggar
- Achiever
- Gainer
- Loser
Answer: 1. Beggar
New Questions And Ideas Objective Type Questions
Question 1. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1. Real name of Gautama Buddha was _______
Answer: Siddhartha
2. The word Jain comes from the term _______
Answer: Jina
3. The Vinaya Pitaka is a sacred book of _______
Answer: Buddhism
4 ______ language was used by Buddha for his teachings.
Answer: Prakrit
5. Prakrit spoken in Magadha was known as _______
Answer: Magadhi
6. Buddha passed away at _______
Answer: Kusinara
Question 2. State whether the given statements are true or false:
1. Satyakama was the son of Gargi.
Answer: False
2. Jain teachings were first written at Samath.
Answer: False
Class 6 History Chapter 6 NCERT Solutions: Key Points
3. The universal soul has been referred to as ‘Brahman’
Answer: True
4. Jainism was initially supported by only the traders.
Answer: True
5. The earliest viharas were made of wood.
Answer: True
6. Upanishads are the part of Rigveda.
Answer: False
Question 3. Match the contents of Column A with that of Column B.
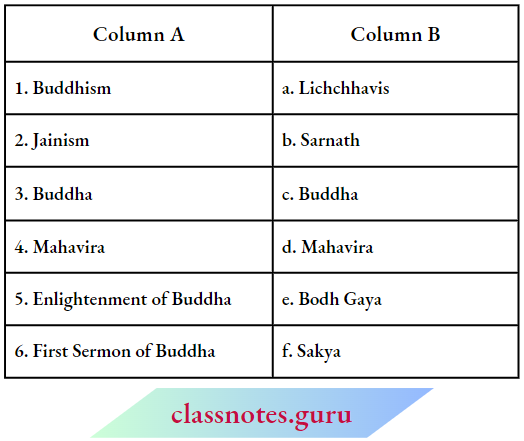
Answer: 1-c, 2-d, 3-f, 4-a, 5-e, 6-b
