NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 3 In The Earliest Cities Exercises
Question 1. How do archaeologists know that cloth was used in the Harappan civilisation?
Answer:
- According to archaeologists cotton was probably grown in Mehrgarh about 7,000 years ago.
- Actual pieces of cloth were found attached to the lid of a silver vase and some copper objects at Mohenjodaro.
- Archaeologists have also found spindle whorls, made of terracotta and faience. These were used to spin thread.
- We also have indirect evidence to show how cloth was decorated. For example, a stone statue of an important man found at Mohenjodaro shows him wearing an embroidered garment.
Read and Learn More NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science
Question 2. Match the columns
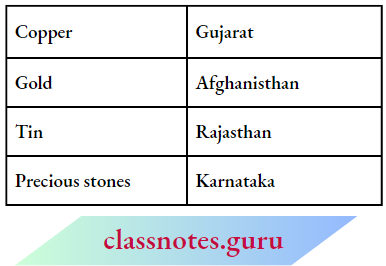
Answer:
In the Earliest Cities NCERT Solutions Chapter 3
Question 3. Why were metals, writing, the wheel, and the plough important for the Harappans?
Answer:
- Metals: The Harappans made tools from copper. They also made ornaments from gold and silver. Tools and weapons, vessels were made from different metals.
- Writing: Writing was very important for the Harappans. There were scribes, people who knew how to write. Scribes helped prepare the seals and perhaps wrote on other materials that have not survived.
- Wheel: The Harappans used the wheel in carts. They also used wheels for spinning. The wheel was used by potters to make or shape pots and other things.
- Plough: Plough was used to prepare land for farming by the Harappans.
Question 4. Make a list of all the terracotta toys shown in the lesson. What do you think children would have enjoyed playing with the most?
Answer:
List Of The Terracotta Toys
- A toy cart made of clay.
- Small clay carts resembling the modern ekhas.
- Puppets
- Whistles are made in the form of birds and rattles of all kinds.
- Marbles
- Dolls
- Models of different cattle and animals. (Humped bull, Rhinoceros, etc.)
- Jewellery articles.
We think that girls would have enjoyed dolls and puppets most, while the male children would have enjoyed carts or has and rattles.
Question 5. Make a list of what the Harappans ate, and put a tick mark against the things you eat today.
Answer:
The Harappans used to eat the following articles/things

Class 6 History Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities Solutions
Question 6. Do you think that the life of farmers and herders who supplied food to the Harappan cities was different from that of the farmers and herders? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Yes, I think that the life of farmers and herders who supplied food to the Harappan cities was different from that of the farmers and herders.
- We know from the remains of plants and bones of animals that the contemporary farmers and herders of the Harappans grew more cereals and collected many types of fruits and other things. They grew wheat, barley, pulses, peas, rice, sesame, linseed and mustard.
- A new tool, the plough, was used to dig the earth for turning the soil and sowing seeds by the farmers of the Harappan times.
- The farmers and herders of the Indus Valley had relations with better or more civilized people who had better houses, roads, drain-system, knowledge of writing and cities. The farmers and herders of the last chapter (or Stone Age) did not know the use of metals.
Question 7. Describe three important buildings in your city or village. Are they located in a special part of the settlement (for example: The Centre)? What are the activities that take place in these buildings?
Answer:
In Our City (Or Village) The Following Three Important Buildings Are Located:
- Community Hall or Gram Panchayat Bhawan or Municipal Committee Bhawan
- School Building
- Hospital
- Temple or Mosque or Church or Gurudwara
The Following Activities Take Place In These Buildings Respectively:

Question 8. Are there any old buildings in your locality? Find out how old they are and who looks after them.
Answer:
Yes, there are some old buildings in our locality. These buildings are looked after by a government department. The name of this department is Archaeological Survey of India.
Question 9. Do you think it is important to preserve old buildings?
Answer:
Yes, it is important to preserve old buildings because they give us a lot of information about the material used, construction methods, need for the building etc. They help us to know about our past.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 History Chapter 3
Question 10. List at least two differences between the houses.
Answer:
Houses In These Cities Were Different From Earlier Ones:
- These houses were planned and made of burnt bricks whereas the houses
- They have wells or storage places and a covered drainage system. The houses of the earlier period had partitions which could have been used for storage.
- Houses of these cities were 1-2 storeyed whereas earlier houses were square or rectangular with pits dug in the ground.
Question 11. Make a list of people who lived in the city.
Answer:
Rulers, scribes and crafts persons along with traders lived in the cities.
Question 12. Was metal used in the villages? Was stone used to make weights?
Answer:
No, metal was not used. Stone was not used for weights.
Question 13. How were goods carried from one place to another?
Answer:
Goods were carried through carts or boats.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 3 In The Earliest Cities Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Write the names of the cities related to the earliest civilisation of the Indian subcontinent.
Answer:
- Mohenjodaro
- Harappa
- Rakhigarhi
- Dholavira
- Kalibangan
- Lothal
Question 2. Which was the earliest city discovered in the Indian subcontinent? Where is it situated nowadays?
Answer:
Mohenjodaro in Sindh. It is in Pakistan now.
Question 3. When were the earliest cities of the Harappan civilisation built?
Answer:
The earliest cities of Harappan civilisation were built about 4700 years ago.
Question 4. Write one major, impressive and unique feature of the earliest cities of India.
Answer:
Covered Drains was one major, impressive and unique feature of the earliest cities of India. Even now, many drains in India are open.
In the Earliest Cities: NCERT Solutions Chapter 3
Question 5. By what name is the Indus Valley Civilisation now called?
Answer:
The Harappan Culture.
Question 6. Into how many parts were the cities of the Mohenjodaro and Harappa divided?
Answer:
Both cities were divided into two main parts
- The upper part is called the citadel.
- The lower part is called the lower town.
Question 7. Write two main characteristics of houses in Harappan City.
Answer:
- Generally, houses were either one or two storeys high with room built around a courtyard.
- Most houses had a separate bathing area and some had wells to supply water.
Question 8. Name the countries with whom the Harappans had trade relations.
Answer:
Oman, Afghanistan, Iran.
Question 9. Which is considered the main foreign trade centre in India during the time of Indus Valley Civilization?
Answer:
Lothal (Gujarat).
Question 10. What was Citadel?
Answer:
The westernmost part of most of the cities was higher but smaller. This was the ‘Citadel’.
Question 11. Define a “Specialist”.
Answer:
A specialist was a person who was trained to do only one kind of work like cutting stones or polishing beads etc.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 3 In The Earliest Cities Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe the drain system of the Harappans.
Answer:
- In cities related to the Harappan civilisation, each drain had a gentle slope so that water could flow through it.
- Very often, drains in houses were connected to those in streets and smaller drains led to bigger ones.
- As the drains were covered, inspection holes were provided at intervals to clean them.
- All three (i.e. drains, houses and streets) were probably planned and built at the same time.
Question 2.
- Where do we find early cities of the Indian subcontinent?
- What unique objects have been found by archaeologists in these cities?
Answer:
- The early cities of the Indian subcontinent are found in present-day Pakistan, and in India. In India, these are found in Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana, Western parts of U.P. and Punjab.
- Archaeologists have found a set of unique objects in almost all these cities:
- Red pottery painted with designs in black,
- Stone weights,
- Seals with writing,
- Special beads,
- Copper tools, and
- Long stone blades.
Question 3. Write a short note on ‘The Cattle Rearing of the Harappans.’
Answer:
The Cattle Rearing
- The Harappans reared cattle, sheep, goats, and buffalo.
- Water and pasture were available around settlements.
- In the dry summer months, large herds of animals were probably taken to greater distances in search of grass and water.
Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities NCERT Class 6
Question 4. Give one word for each of the following terms or sentences:
- The stage when the culture of a country or region is developed and advanced.
- Clay tablets and idols.
- A place where surplus grains were stored.
- A place where ships are loaded, unloaded and repaired.
Answer:
- Civilisation,
- Terracotta,
- Granaries,
- Dockyard.
Question 5. Describe the city of Dholavira in Gujarat.
Answer:
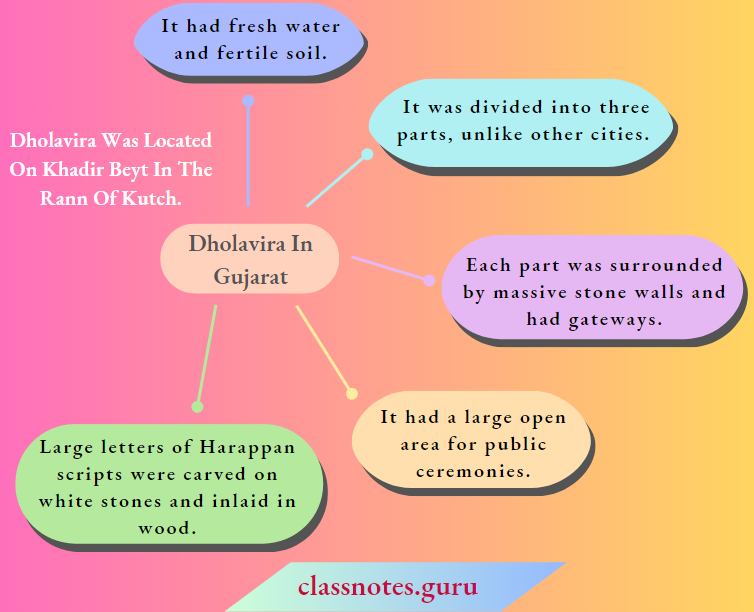
Question 6. Write a note on the city of Lothal.
Answer:
Lothal was situated beside a tributary of Sabarmati, close to the Gulf of Khambat.
- Semi-precious stones were available nearby.
- Lothal was a centre for objects made of shells, metal and stone.
- Lothal had a storehouse in the city, where many seals were found.
- A workshop for making beads and items from it was also found here.
- A dockyard for loading, unloading and trade was also discovered.
Question 7. What do you know about seals and sealings?
Answer:
Seals may have been used to mark the parcels/bags, being sent from one place to another. After a bag was closed, a layer of wet clay was put on the knot and the seal was pressed on it. This impression of the seal was called sealing.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 3 In The Earliest Cities Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Describe the main features of the Great Bath of Mohenjodaro.
Answer:
The Great Bath
- In Mohenjodaro, a very special tank, which archaeologists call the Great Bath, was built in its Citadel Area.
- This special tank was made of bricks, coated with plaster and made water-tight with a layer of natural tar.
- There were steps leading down to it from two sides, while there were rooms on all sides.
- Water was probably brought in from a well, and drained out after use.
- Perhaps important people took a dip in this tank on special occasions.
Question 2. Write in brief the story of Harappa’s finding.
Answer:
The Story Of Harappa
- About 152 years ago (1855 A.D.), when railway lines were being laid down for the first time in west Punjab engineers stumbled upon the site of Harappa in present-day Pakistan. To them, it appeared like a mound which was a rich source of ready-made, high-quality bricks.
- The labourers (working on railway lines) carried off thousands of bricks from the walls of the old building of the city (later named as Harappa) to construct railway lines. Many buildings were completely destroyed.
- Then, nearly eighty-five years ago (1920 A.D.), archaeologists found the site and realized that this was one of the oldest cities in the subcontinent. As this was the first city to be discovered.
NCERT History Chapter 3
Question 3. Discuss in brief the life in Harappa City.
Answer:
Life In The Harappa City
- Probably Harappa was a busy place. There were people who planned the construction of special buildings in the city. These were probably the rulers.
- Most probably the rulers of the Harappan city sent people to distant lands to get metal, precious stones and other things that they desired or required.
- The rulers may have kept the most valuable objects, such as ornaments of gold and silver or beautiful beads for themselves.
- And there were scribes, people who knew how to write, who helped prepare the seals and perhaps wrote (or engraved) on other materials.
- There were craftspersons—men and women making all kinds of things.
- Terracotta toys have been found and children might have played with them.
Question 4. Write a short note on the Script of the Harappan people.
Answer:
- Historians believe that the people of the Indus Valley civilisation were literate. Many seals have been discovered. We can note lines (or symbols) of signs on the top of several seals of the Harappan people. These are parts of what historians call a script. This is the earliest form of writing known in the subcontinent.
- Scholars have made many efforts to read these signs (or decipher the Harappan script), but we still do not know exactly what they mean.
Question 5. Describe in short different objects made and found in different Harappan cities or sites.
Answer:
- Materials used by the people of Harappan cities are made of stone, and metal including copper, tin, bronze, gold, silver and shell.
- Vessels and Ornaments. Copper and bronze were used to make vessels and ornaments.
- Beads. Perhaps the most striking finds are those of beads. The stone was cut, shaped, polished and finally a hole was bored through the centre so that a string could be passed through it.
- Weights. Stones were used to make weights. These were probably used to weigh precious stones or metals.
- Seals. The Harappans also made seals out of stone. These are generally rectangular and usually have animals. Bull or a Rhinoceros) carved on them.
- Faience. Unlike stone or shell, which are found naturally, faience is artificially produced. A gum was used to shape sand or powdered quartz into an object.
- Pottery. The Harappans also made pottery with beautiful designs.
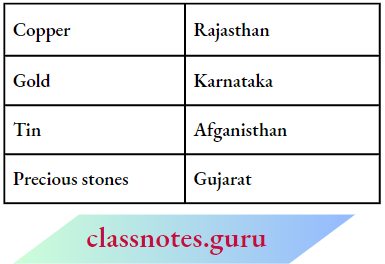
Question 6. What are raw materials? How did the Harappans make their provision?
Answer:
- Raw Materials Meaning
- Raw materials are substances that are either found naturally (such as wood, or ores of metals) or produced by farmers or herders.
- These are generally processed to produce finishing goods.
- For instance, cotton, produced by farmers, is a raw material that is processed to make cloth.
- Provision or Search of Raw Materials
- While some of the raw materials that the Harappans used were available locally many items such as copper, tin, gold, silver and precious stones had to be brought from distant places.
- The Harappans probably got copper from Rajasthan and even from Oman.
- Tin, which was mixed with copper to produce bronze, may have been brought from Afghanistan and Iran.
- Gold could have come all the way from Karnataka and
- Precious stones from Gujarat, Iran and Afghanistan.
- While some of the raw materials that the Harappans used were available locally many items such as copper, tin, gold, silver and precious stones had to be brought from distant places.
Question 7. Discuss ‘agriculture’ as an important occupation of the Harappans.
Or
How was food provided to the people in the Harappan cities?
Answer:
Agriculture of the Harappans or Food for People in the Cities
- While many people lived in the cities, others grew crops and reared animals.
- We know from the remains of plants that the Harappans grew wheat, barley, pulses, peas, rice, sesame, linseed and mustard.
- A new tool, the plough, was used to dig the earth for turning the soil and planting seeds.
- As this region does not receive heavy rainfall, some form of irrigation may have been used.
- Different types of cattle were also used for food supply. They also collected fruits like ber (%), caught fish and hunted wild animals like the antelope.
History Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities Study Material
Question 8. What were the causes of the end of the Harappan culture?
Or
Discuss the mystery of the end of the Harappan civilization.
Answer:
The Mystery of the End of the Harappans or the Probable Causes of the downfall of the Harappan Civilisation. Nearly 3900 years ago we find the beginning of a major change in Harappan cities or sites
- People stopped living in many of the cities (it) Writing, seals and weights were no longer used
- Raw Materials brought from long distances became rare
- In Mohenjodaro, we find that garbage piled up on the streets, the drainage system broke down, and new, less impressive houses that were built encroached onto the streets.
Harappan culture Causes. The following causes were possibly responsible for the end of the Harappan culture
- Some scholars suggest that the rivers dried up.
- Others suggest that there was deforestation. This could have happened because fuel was required for baking bricks and for melting copper ores. Besides, grazing by large herds of cattle, sheep and goats may have destroyed the green cover.
- In some areas there were floods.
- Perhaps the rulers lost control but none of these reasons can explain the end of all the cities.
In short, we can say that we are not the same about the cultures of the end of the Harappan culture. However, flooding or a river drying up would have had an effect in only some areas.
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 History Chapter 3 In The Earliest Cities Multiple Choice Questions
Choose The Correct Answer:
Question 1. When did Harappan cities develop?
- About 4,700 years ago
- About 3,700 years ago
- About 2,700 years ago
- About 1,700 years ago
Answer: 1. About 4,700 years ago
Question 2. How many storeys of houses were generally found in Harappan?
- One or two storeys
- Four to five storeys
- Multi storeys
- None of these
Answer: 1. One or two storeys
Question 3. Where did the craftspeople make the things in the earliest cities?
- In their own homes
- In special workshops
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities Class 6
Question 4. Most of the things found by the archaeologists were made of which metal?
- Bronze
- Copper and gold
- Silver
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 5. What was the thing used to shape sand or powdered quartz into an object?
- Gum
- Ink
- Nails
- Rubber
Answer: 1. Gum
Question 6. Which colours were used for glazing?
- Black or white
- Red or yellow
- Blue or sea green
- Pink or brown
Answer: 3. Blue or sea green
NCERT Solutions Class 6 History Chapter 3 In the Earliest Cities
Question 7. Who supplied food to craftpersons, scribes and rulers in the cities?
- Local citizens
- Farmers and herders
- Postmen
- All of these
Answer: 2. Farmers and herders
Question 8. How did the Harappans irrigate their fields and grow plants?
- Rainfall
- Stored water
- Streams
- Rivers
Answer: 2. Stored water
Question 9. Where did the boats and ships come from from the sea and rivers?
- Ports
- Dockyards
- None of these
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 2. Dockyards
