Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Question And Answers
Question 1. Write a note on the nose and nasal septum.
Answer:
Nose
- Act as a respiratory passage as well as the organ of smell
- Consist Of Two Parts:
- External nose formed by root, dorsum, tip, anterior nares, nasal septum and columella
- The nasal cavity extends from external nares to posterior nasal apertures divided into right and left, halves by nasal septum.
- Each half has a roof, floor, medial and lateral walls
- The roof is formed by parts of ethmoid, frontal, and nasal bones and is involved in olfactory function
- The floor is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and palatine bone.
Nasal Septum
- Nasal Septum is a osteocartilaginous partition between two halves of the nasal cavity
- Nasal Septum is covered by mucous membrane and forms the medial wall of the nasal cavity
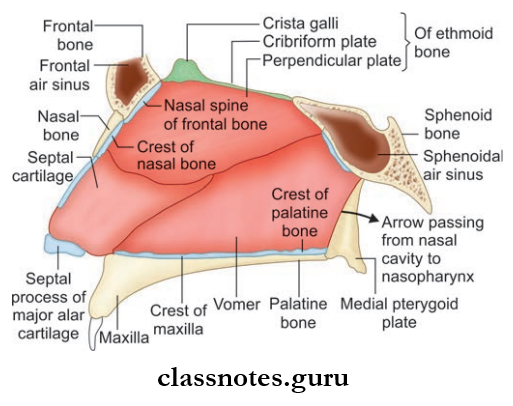
The nasal septum consists of three parts:
- Columellar septum: Formed by the alar cartilage covered with fatty tissue and skin
- Membranous septum: Formed by a dual layer of skin and lies between the columella and septal cartilage
- Septum proper: Formed by cartilage and bone
The cartilaginous part is formed by septal cartilage and the septal process of inferior nasal cartilage
The bony part is formed by:
- Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid
- Vomer
- Also parts of the frontal bone, sphenoid, palatine, and maxillary bones.
Nose And Nasal Septum Blood Supply
- Arterial Supply: Mainly by the following arteries:
- Anterosuperior by anterior ethmoidal artery
- Anteroinferior part by superior labial artery (branch of a facial artery)
- Posterosuperior part by greater palatine artery
- Posteroinferior part by the sphenopalatine artery.
- Venous Drainage: Drains into facial vein anteriorly and sphenopalatine vein posteriorly and ultimately to pterygoid venous plexus.
Nose And Nasal Septum Nerve Supply
- General
- Anterosuperior part by nasal branch of anterior ethmoidal nerve
- Anteroinferior part by anterior superior alveolar nerve
- Posterosuperior part by a medial posterosuperior branch from pterygopalatine ganglion
- Posteroinferior part by nasopalatine branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion.
- Special Sensory: In the form of olfactory rootlets in the roof and adjoining area.
Nose And Nasal Septum Lymphatics
- Anterior part to submandibular nodes
- Posterior part to deep cervical nodes and retropharyngeal nodes.
Nose And Nasal Septum Applied
- Rhinitis refers to the inflammation of the nasal mucosa as a result of infection or an allergic reaction.
- Rhinitis can be caused by viruses as in the common cold or by allergies as in allergic rhinitis.
- The nasal septum commonly deviates to the sides from the midline which can be anterior deviation, Cshaped deviation, Sshaped, etc.
- Nasal septum deviation is corrected by procedures like septoplasty or submucous resection.
- Septal hematoma refers to the collection of blood under the periosteum of nasal septum.
- Secondary infection of septal hematoma can lead to septal abscess.
- Bleeding from the nose is known as epistaxis and is most commonly caused due to rupture of blood vessels in the Little’s area (anterior inferior part of nasal septum just above vestibule).
Question 2. Write a short note on the lateral wall of the nose.
Answer:
Lateral Wall Of Nose
- The lateral wall is highly irregular due to the presence of bony shelf-like elevation called turbinates/conchae and space between them called meatuses.
- These are mainly present in order to increase surface area for air conditioning of inspired air.
Nasal Conchae/Turbinate: These are curved bony projections directed downwards and medially and are three in number.
- Superior Turbinate: Smallest of the three and is present at the posterior part of nasal cavity and is the projection from the ethmoid bone
- Middle Turbinate: Middle Turbinate is a projection from medial surface of the ethmoid bone
- Inferior Turbinate: Inferior Turbinate is an independent bone.
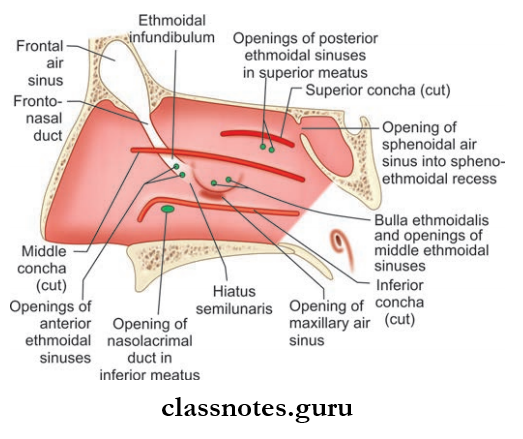
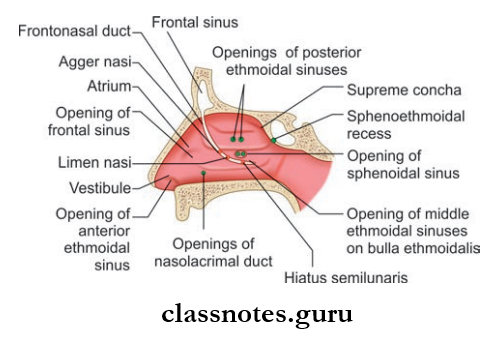
Lateral Wall Of Nose Meatuses: These are spaces between or enclosed by conchae and include the following:
- Inferior Meatus: Present below the inferior turbinate and is the largest one. The nasolacrimal duct opens here and is guarded by valve of Hasner.
- Middle Meatus: Middle Meatus is present between the middle turbinate and inferior turbinate.
- It consist Of The Following:
- Bulla Ethmoidal: A rounded elevation produced by underlying ethmoid sinuses
- Hiatus Semilunaris: Hiatus Semilunaris is a deep curved cleft/sulcus below bulla ethmoidalis
- Infundibulum: Infundibulum is a short passage present at the anterior end of hiatus semilunaris and the anterior ethmoidal sinus open here
- Opening Of Frontal Sinus: Seen in the anterior part of hiatus semilunaris
- Two opening of the maxillary sinus is seen in the posterior part of hiatus semilunaris
- Opening of the middle ethmoidal sinus is present at the upper margin of bulla ethmoidal.
- Superior meatus lies between the superior turbinate and the middle turbinate and has openings of posterior ethmoidal sinus.
- Sphenoethmoidal recess is present just above superior turbinate and has opening of sphenoid sinus.
Lateral Wall Of Nose Blood Supply
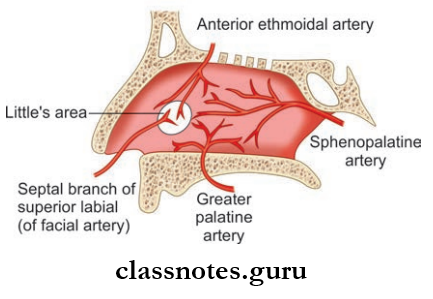
- Arterial Supply
- Anterosuperior quadrant by anterior ethmoidal artery and assisted by posterior ethmoidal and facial artery
- The anteroinferior quadrant is supplied by the branch of the facial artery and the greater palatine artery
- Posterosuperior quadrant is supplied by the sphenopalatine artery
- The posterior inferior quadrant is supplied by branches from greater palatine artery.
- Venous Drainage
- Anteriorly it drains to the facial vein
- Posteriorly it drains to the pharyngeal plexus
- The middle part drains to the pterygoid plexus of veins.
Lateral Wall Of Nose Nerve Supply
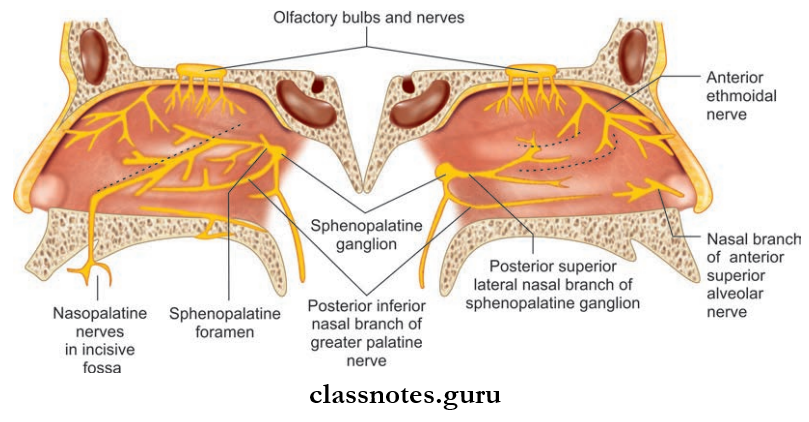
- General Sensory Supply
- The anterosuperior quadrant is supplied by the anterior ethmoidal nerve a branch of ophthalmic nerve
- The anteroinferior quadrant is supplied by the anterior superior alveolar nerve branch of the infraorbital nerve
- The posterosuperior quadrant is supplied by posterior superior lateral nasal branches from the pterygopalatine ganglion
- Posteroinferior quadrant is supplied by greater palatine branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion.
- Special Sensory Supply: Olfactory nerves are present in the upper part of lateral wall ust below the cribriform plate of ethmoid to superior turbinate.
Lateral Wall Of Nose Lymphatic Drainage
- Anterior half drains into submandibular lymph nodes
- Posterior half to retropharyngeal and upper deep cervical nodes.
Lateral Wall Of Nose Applied
- Rhinosporidiosis is a common fungal infection of the nose where a pink granulomatous mass protrudes from the nose which usually arises from the lateral wall. It usually bleeds on touch.
- The adhesions formed between the nasal septum and turbinates by scar tissue is known as nasal synechia which is most commonly a result of injuries to the nose.
- Nasal polyps refer to the nonneoplastic masses of edematous nasal or sinus mucosa.
Question 3. Write a short note on the maxillary sinus.
Answer:
Maxillary Sinus
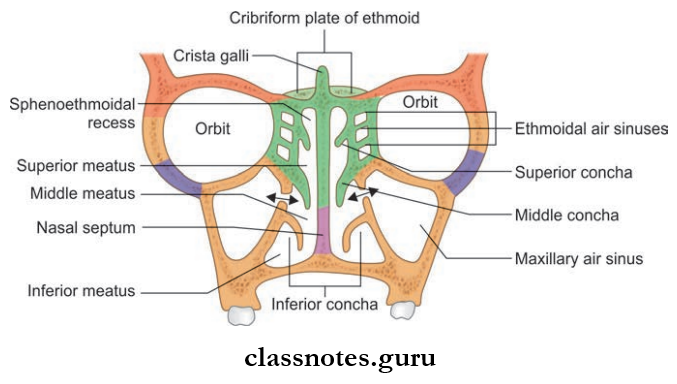
- One of the air filed spaces present within the body of the maxilla
- The largest paranasal sinus of the body.
Maxillary Sinus Dimensions
- Variable in size
- Measures about 3.5 cm in height, 2.5 cm in width, and has an anteroposterior depth of 3.5 cm.
Maxillary Sinus Features
- Maxillary Sinus is pyramidal in shape and has a base and apex
- The apex is directed laterally in the zygomatic process of the maxilla and base is directed toward the lateral wall of nose
- Maxillary Sinus also has a roof and a floor
- The roof is formed by the floor of the orbit and flor by the alveolar process of the maxilla
- Maxillary Sinus opens into the middle meatus of nose in the lower part of the hiatus semilunaris and a second opening is present at the posterior end of the hiatus.
Maxillary Sinus Blood Supply
- Arterial: By facial artery, infraorbital artery, and greater palatine artery
- Venous Drainage: Drains into facial vein and pterygoid plexus of veins.
Maxillary Sinus Lymphatics: Drain into submandibular lymph nodes.
Maxillary Sinus Nerve Supply: By infraorbital nerve, anterior, middle, and posterior superior alveolar nerves.
Maxillary Sinus Applied
- Inflammation of the sinus mucosa is called sinusitis.
- Maxillary sinusitis occurs commonly as a result of dental infections.
- Pain of maxillary sinusitis may be referred to upper teeth and infraorbital skin.
- Oroantral fistula refers to abnormal connections between the oral cavity and the maxillary antrum. It occurs usually as a result of dental extraction
Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. All of the following sinuses open into hiatus semilunar is except:
- Frontal
- Anterior ethmoidal
- Posterior ethmoidal
- Maxillary
Answer: 3. Posterior ethmoidal
Question 2. Toothache in maxillary sinusitis occurs due to stimulation of:
- Inferior alveolar nerve
- Superior alveolar nerves
- Greater palatine nerves
- Nasopalatine nerves
Answer: 2. Superior alveolar nerves
Question 3. The nasolacrimal duct opens into:
- Middle meatus
- Inferior meatus
- Superior meatus
- Vestibule
Answer: 2. Inferior meatus
Question 4. The chief artery supplying nasal mucosa is:
- Greater palatine
- Sphenopalatine
- Anterior ethmoidal
- Posterior ethmoidal
Answer: 2. Sphenopalatine
Question 5. The chief nerve innervating the nasal mucosa is:
- Anterior ethmoidal
- Greater palatine
- Nasopalatine
- Posterior ethmoidal
Answer: 3. Nasopalatine
