Model Analysis Important Notes
- Carey’s analysis
- Bolton’s analysis
- According to Bolton, tooth size is an important factor to be taken into consideration for diagnosis and there exists a ratio between mesio-distal widths of maxillary and mandibular teeth
- Bolton’s overall ration is 91.3%
- If overall ratio is less than 91.3%, it indicates maxillary tooth material excess
- Bolton’s anterior tooth ratio is 77.2%
- If anterior ratio is less than 77.2%, it indicates maxillary anterior excess
- Tanaka Johnson analysis
- This analysis does not require any radiographs or reference tables
- The width of unerupted canines and premolars can be predicted based on width of mandibular incisors
- Width of maxillary canine and premolars = 11 + 1/2 width of madibular incisors
- Width of mandibular canine and premolars = 10.2 + 1/2 width of mandibular incisors
- Various model analysis
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
- Requirements of various analysis
Model Analysis Long Essays
Question 1. Classify diagnostic aids. Write briefly about Model analysis.
Answer.
Diagnostic Aids:
- Essential Diagnostic aids
- Case history
- Clinical examination
- Study models
- Certain radiographs
- Facial photographs
- Supplemental diagnostic aids:
- Specialized radiographs
- Electromyographs
- Hand wrist radiographs
- Endocrines tests
- Estimation of basal metabolic rates
- Diagnostic set-up
- Occlusograms
Model Analysis:
Involves study of maxillary and mandibular dental arches in all the three planes of space
- Useful in treatment planning
- Useful in maintaining records
Different Analysis:
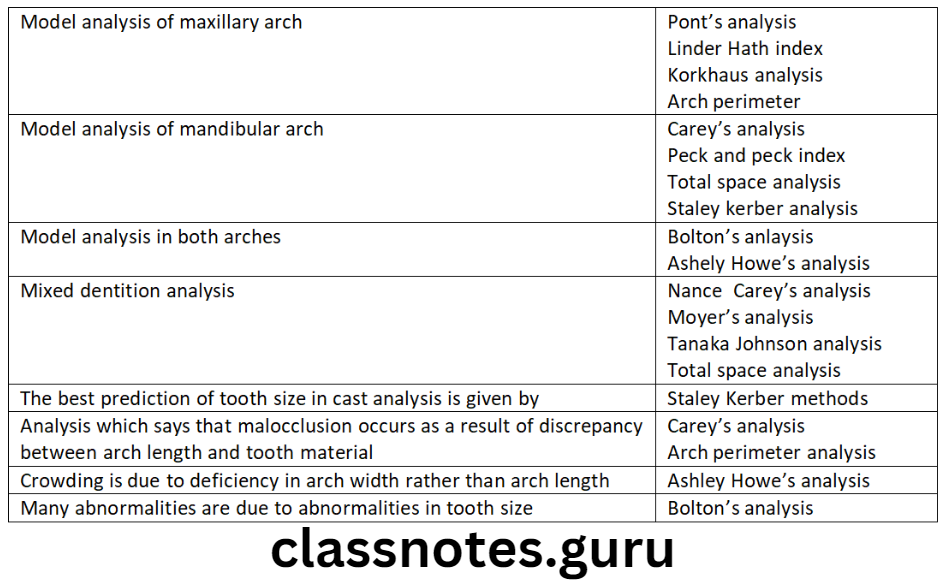
Carey’s analysis:
- Determination of arch length – From anterior of first permanent molar to mesial surface of opposite first permanent molar
- Determination of tooth material – Mesio-distal width of teeth from 2nd premolar to 2nd premolar
- Determination of the discrepancy – Difference between arch length and tooth material
- Interference:
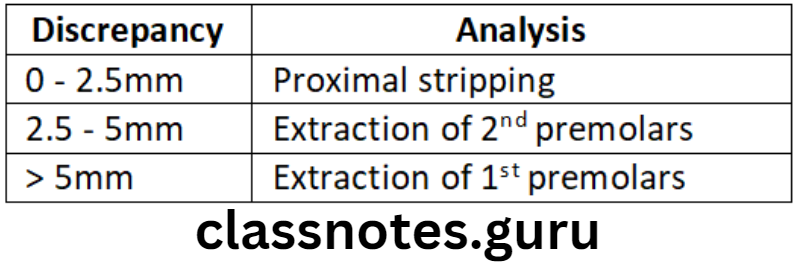
- 0-2.5 mm – Proximal stripping
- 2.5-5 mm – Extraction of 1st premolars
- > 5mm – Extraction of 1st premolars
- Interference:
Ashley Howe’s analysis:
- Determination of total tooth material [TTM] – Mesio-distal width of teeth from 1st molar to 1st molars
- Determination of premolar diameter [PMD] – arch width from tip of buccal cusp of 1st premolar to that of opposite side
- Determination of premolar basal arch width [PMBAW] – width from canine fossa of one side to other
- Interference:
- PMBAW% – \(\frac{\text { PMBAW } \times 100}{\text { TTM }}\)
- 37 or less – Need for extraction
- 44 or more – Non-extraction
- 37 to 44 – Borderline cases
- Interference:
Ponts analysis:
- By 1909
- Determination of sum of incisors [SI] – Total mesio-distal width of 4 maxillary incisors
- Determination of measured premolar value [MPV] – From distal pit of upper first premolar to that of opposite side
- Determination of measured molar value [MMV] – From mesial pit of one upper first molar to that of opposite sid
- Determination of calculated premolar value \((\mathrm{CPV})-\mathrm{CPV}=\frac{\mathrm{SI} \times 100}{80}\)
- Determination of calculated molar value [CMV] – CMV = \(\frac{\text { SI } \times 100}{80}\)
- Interference:
- Measured value < Calculated value
- Need for expansion
- Interference:
Bolton’s analysis:
- Sum of maxillary 12 – Total mesiodistal width of one 1st molar to that of other
- Sum of mandibular 6 – Total mesiodistal width of 6 anteriors
- Sum of maxillary 6 – Total mesiodistal width of 6 anteriors
- Determines of overall ratio – Overall ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 12}{\text { Sum of maxillary } 12} \times 100\)
- According to Bolton, it should be 91.3%
- If less than 91.3% – Maxillary tooth material excess
- Determination of Anterior Ratio:
- Anterior ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 6}{\text { Sum of maxillary } 6} \times 100\)
- According to Bolton, it should be 77.2%
- If less than 77.2% – Maxillary anterior excess
- If more than 77.2% – Mandibular anterior excess
Model Analysis Short Essays
Question 1. Arch perimeter analysis.
Answer.
- Carey’s analysis used for maxillary arch is called arch perimeter analysis
Methods Of Arch Perimeter Analysis:
- Determination of arch length – From anterior of first permanent molar to mesial surface of opposite first permanent molar
- Determination of tooth material – Mesio-distal width of teeth from 2nd premolar to 2nd premolar
- Determination of the discrepancy – Difference between arch length and tooth material
- Interference:
- 0-2.5mm – Proximal stripping
- 2.5-5mm – Extraction of 2nd premolars
- > 5mm – Extraction of 1st premolars
- Interference:
Question 2. Mixed Dentition Analysis.
Answer.
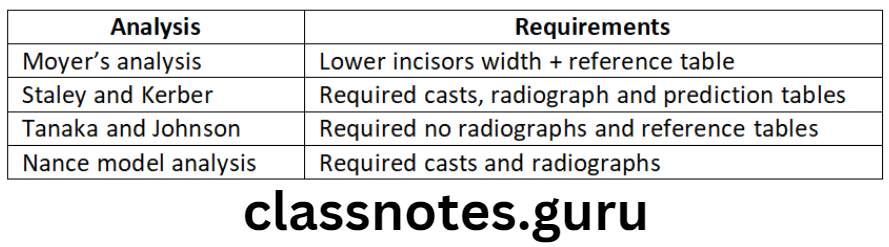
Moyer’s Mixed Dentition Analysis: To evaluate the amount of space available in the arch for erupting permanent canine and premolar
Procedure Of Mixed Dentition Analysis:
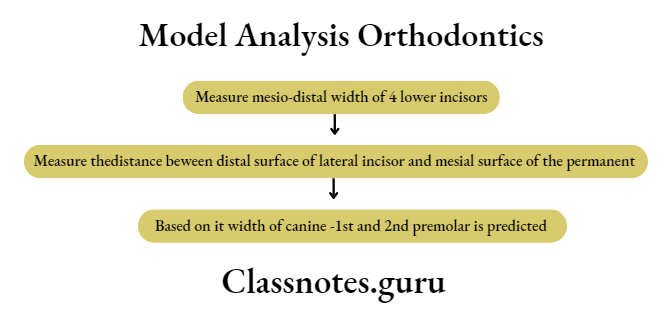
Inference Of Mixed Dentition Analysis:
- Compare tooth sizes 3,4 and 5 and the arch length available
- Predicted value > arch length available → Crowding
Radiographic method:
- Determine the width of unerupted teeth
- Erupted teeth in a radiograph and on a cast
i.e. Width of the unerupted tooth to be determined
\(=\frac{\text { Width of tooth erupted on cast } \times \text { Width of tooth erupted on radiograph }}{\text { Width of erupted tooth in oral cavity on radiograph }}\)Question 3. Bolton’s analysis:
Answer.
Methods Bolton’s Analysis:
- The sum of mandibular 12 – Total mesiodistal width of one 1st molar to that of other
- A sum of maxillary 12 – Total mesiodistal width of one 1st molar to that of other
- Sum of mandibular 6 – Total mesiodistal width of 6 anteriors
- A sum of maxillary 6 – Total mesiodistal width of 6 interiors
- Determination of overall ratio – Overall ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 12}{\text { Sum of maxillary } 12} \times 100\)
- According to Bolton, it should be 77.2%
- If less than 91.3% of maxillary tooth material excess
- Determination of Anterior Ratio:
- Anterior ratio = \(\frac{\text { Sum of mandibular } 6}{\text { Sum of maxillary } 6} \times 100\)
- According to Bolton, it should be 77.2%
- If less than 77.2% – Maxillary anterior excess
- If more than 77.2% of mandibular anterior excess
Model Analysis Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Assessment of tooth mass discrepancy.
Answer.
- Measure the arch length
- Measure the mesiodistal width of teeth
Discrepancy Of Tooth Mass Discrepancy:
- Difference between arch length measures and tooth material
Inference Tooth Mass Discrepancy:
- 0-2.5mm – Proximal stripping
- 2.5-5mm – Extraction of 2nd premolars
- > 5 mm – Extraction of 1st premolars
Question 2. Ashley Howe’s analysis.
Answer.
Methods Of Ashley Howe’s Analysis:
- Determination of total tooth material [TTM] – mesiodistal width of teeth from 1st molar to 1st molars
- Determination of premolar diameter [PMD] – arch width from the tip of the buccal cusp of 1st premolar that of the opposite side
- Determination of premolar basal arch width [PMBAW] – width from canine fossa of one side to other
Interference Of Ashley Howe’s Analysis:
- PMBAW%
- 37 or less – Need for extraction
- 44 or more – Non-extraction
- 37 to 44 – Borderline cases
Question 3. Carey’s analysis.
Answer.
Methods Of Carey’s analysis:
- Determination of arch length – From anterior of first permanent molar to mesial surface of opposite first permanent molar
- Determination of tooth material – mesiodistal width of teeth from 2nd premolar to 2nd premolar
- Determination of the discrepancy – Difference between arch length and tooth material
- Interference:
- 0-2.5mm – Proximal stripping
- 2.5-5mm – Extraction of 2nd premolars
- > 5mm – Extraction of 1st premolars
- Interference:
Question 4. Peck and peck ratio.
Answer.
- It is based on the concept of stability of rotational corrections of lower incisors rather than tooth size considerations
- It is calculated as
- Peck and peck ratio = Mesiodistal width / Faciolingual diameter x 100
- The normal ratio for central incisors is 88-92% and for lateral incisors is 90-95%
- This ratio is used to determine whether lower incisor teeth are excessively wider mesiodistally or not
Question 5. Tanaka-Johnston analysis.
Answer.
- Tanaka-Johnston analysis is a mixed dentition analysis
- It predicts the widths of unerupted canines and premolars based on the sum of the width of lower incisors
Methods Of Tanaka-Johnston Analysis:
- Measure the total arch length
- Measure the mesiodistal width of the lower four incisors and sum them up
- Divide the value obtained by 2 and
- Add 10.5 mm to obtain the sum of widths of mandibular canines and premolars in one quadrant
- Add 10.5 mm to obtain the sum of widths of maxillary canines and premolars in one quadrant
- The formula to calculate the space available is
- Space available = Total arch length – Sum of the lower incisors + 2 x Calculated width of canine and premolar
Advantages Of Tanaka-Johnston Analysis:
- Simple and practical
- Accurate
- Require neither radiographs nor reference tables
Question 6. Korkhaus analysis.
Answer.
- Korkhaus in 1938 proposed a study model analysis that reveals anteroposterior malpositioning of incisors in maxillary and mandibular arches
- A measurement is made from the midpoint of the inter-premolar line to a point between the two maxillary incisors
- According to Korkhaus, for a given width of upper incisors, a specific value of the distance between the two maxillary incisors should exist
- An increase in this measurement denotes proclined upper anterior teeth while a decrease in this value denotes reclined upper anterior teeth
Model Analysis Viva Voce
- Bolton’s analysis proposes that tooth size abnormalities cause malocclusion
- Pont’s analysis indicates the need for expansion rather than extraction
- Peck and Peck is a model analysis of mandibular arch
- Ashley and Howe’s analysis indicates tooth extraction if the premolar basal arch width is less than 37%
