Median Nerve Anatomy Notes
Explain in detail about the Median Nerve under headings—origin, root value, course, branches, and innervation. Write a note on the injury to the nerve.
Answer:
- The median nerve is called the median because it runs in the median plane of the forearm.
- Median Nerve is called the eye of the hand because it gives sensory supply to the pulp of the thumb and index fingers.
- Median Nerve is also known as the laborers’ nerve.
Median Nerve Origin
- By the union of the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus.
Median Nerve Root Value
- C5, C6, C7, C8, T1.
Median Nerve Function
Median Nerve Course
- In the axilla:
- The median nerve goes down to enter in the arm from the lateral side of 3rd part of the axillary artery.
- In the arm:
- The median nerve lies lateral to the brachial artery.
- But at the level of the middle of the arm, it crosses the brachial artery and runs medial to enter the cubital fossa.
- In the cubital fossa:
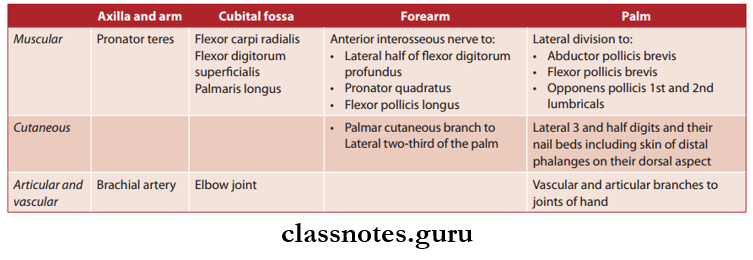
- It gives of muscular branches to flexor carpi radialis, flxor digitorum superfiialis and palmaris longus.
- The median nerve leaves the cubital fossa between two heads of pronator teres and then deep to the fibrous arch of the flexor digitorum superficial.
- In the forearm:
- In the forearm, it is adhered to the deep surface of the flexor digitorum superficial and leaves the muscle along its lateral border.
- It runs deep to the palmaris longus and gives of the palmar cutaneous branch before getting under the carpal tunnel.
- In the palm:
- After passing through the carpal tunnel, the median nerve divides into lateral and medial divisions.
- Lateral division supplies 3 out of 4 thenar muscles, 1st and second lumbricals.
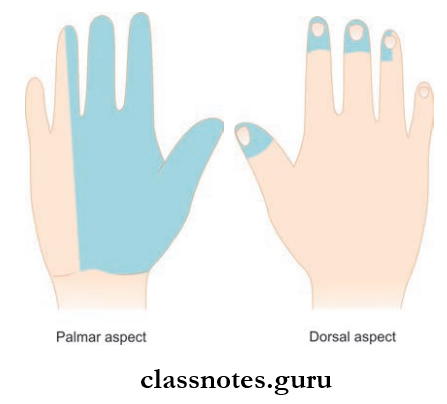
- Medial division along with the remaining fingers of lateral division provides cutaneous supply to the lateral 3 and half digits and their nail beds including the skin of distal phalanges on their dorsal aspect.
Median Nerve Anatomy
Median Nerve Branches and Innervations
Mnemonic: Median Nerve: Hand Muscles Innervated
‘The LOAF muscles’:
- lumbrical 1 and 2
- Opponents pollicis
- Abductor pollicis brevis
- Flexor pollicis brevis
- Alternatively: LLOAF, with 2 L’s, to recall there is 2 lumbricals.
- To remember that these are the Median nerve muscles, think ‘Meat LOAF’.
Median Nerve Clinical Anatomy
- Injury to the median nerve can occur at various levels and the clinical features vary accordingly.
- Injury At The Level Of The Elbow
- Median Nerve can be due to:
- Supracondylar fracture of humerus.
- Entrapment of nerve between the two heads of pronator teres during its course.
- Tight tourniquet usage during venipunctures.
- The clinical features are:
- Loss of pronation as pronator teres is paralyzed.
- Weak wrist flexion due to paralysis of flexors supplied by the median nerve.
- The wrist will be adducted due to weakening of the flexor carpi radialis and unopposed action of the flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of flexor digitorum profundus.
- Median Nerve can be due to:

- Benedicts Deformity:
- Median nerve injury leads to no flexion at interphalangeal joints of the index and middle fingers due to paralysis of the flexor digit running the superficial and lateral half of the flexor digitorum profundus. It results in placing of hand in a position comparable to Benedict’s hand.
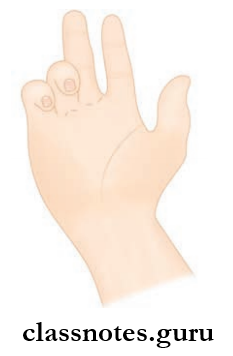
- Ape thumb deformity:
- It is characterized by flttening of thenar eminence with lateral rotation and adduction of thumb due to paralysis of thenar muscles supplied by the median nerve

Median Nerve Injury
1. Injury At The Level Of The Forearm
2. Injury At The Carpal Tunnel:
- Median nerve can get compressed in the tightly packed carpal tunnel due to:
- Myxedema
- Tenosynovitis of flxor tendons
- Dislocation of lunate bone following fracture
- Retention of fluid in pregnancy
- Osteoarthritis in the wrist joint
- Median Nerve is presented with:
- Burning sensation over the area of sensory supply of median nerve in the hand (lateral 3½ digits) more during the night
- Weakening of thenar muscles
- Ape thumb deformity, if left untreated
- Reduced conduction velocity in nerve conduction studies
- Phalen’s test and Tinel’s test were positive.
Median Nerve Pathway
Mnemonic: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Causes
MEDIAN TRAP
- Myxoedema
- Edema premenstrually
- Diabetes
- Idiopathic
- Acromegaly
- Neoplasm
- Trauma
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Amyloidosis
- Pregnancy
Mnemonic fits nicely since the median nerve is trapped.
