Management Of Malocclusion Important Notes
- Overbite
- It is a vertical overlapping of anterior teeth
- Value – 2-3 mm
- Normal over-bite percentage – 33.33%
Management Of Malocclusion Long Essays
Question 1. Discuss a treatment plan for Angle’s Class 2 malocclusion.
Answer.
Treatment Objectives:
Class 2 Div. 1:
- Reduction of overjet
- Reduction of over-bite
- Correction of crowding
- Correction of molar relationship
- Correction of posterior cross-bite
- Normalizes muscles
Class 2 Div. 2:
- Correction of incisor relation
- Relief of gingival trauma
- Correction of crowding
- Correction of molar relation
Treatment Plan:
Growing Patient:
- Skeletal Class 2
- Maxillary Prognathism
- Headgear
- Maxillarly Prognathism and Mandibular Retrognathism
- Headgear & Myofunctional Therapy
- Mandibular Retrognathism
- Myofunctional Therapy
- Maxillary Prognathism
- Dental Class 2
- Orthodontic Treatment
Non-Growing Patient:
- Skeletal class 2
- Mild to Moderate Class 2
- Orthodontic Camouflage
- Severe Class 2
- Maxillarly Prognathism
- Surgical Maxillary Setback
- Mandibular Retrognathism
- Surgical Mandibular Advancement
- Dental Class 2
- Orthodontic Treatment
- Maxillarly Prognathism
- Mild to Moderate Class 2
Read And Learn More: Orthodontics Short And Long Essay Question And Answers
Treatment Approaches:
Growth modification:
- Reduces the severity of skeletal relationship
- Carried out during mixed dentition period before cessation of growth
- Involves
Correction of mandibular deficiency
- Mixed dentition period – Activator, FR 2
- After growth cessation – Herbst appliance
- Jasper Jumper
Correction of maxillary prognathism
- Face bow with headgear
Camouflage:
- Done by extraction of teeth
- To reduce overjet, overbite, molar relation, crowding, deep bite
- In excellent inter occupation – Extraction of the upper first premolar
- In unstable molar relation – Extraction of all first premolars
Surgical Correction:
- After cessation of growth
- mandibular advancement and maxillary set back is done
Question 2. Define Preventive, Interceptive orthodontics. Enumerate various modes of bilateral posterior cross bite correction and discuss any one.
Answer.
Definitions: Refer to Interceptive Orthodontic topics
Treatment Of Bilateral Posterior Cross Bite:
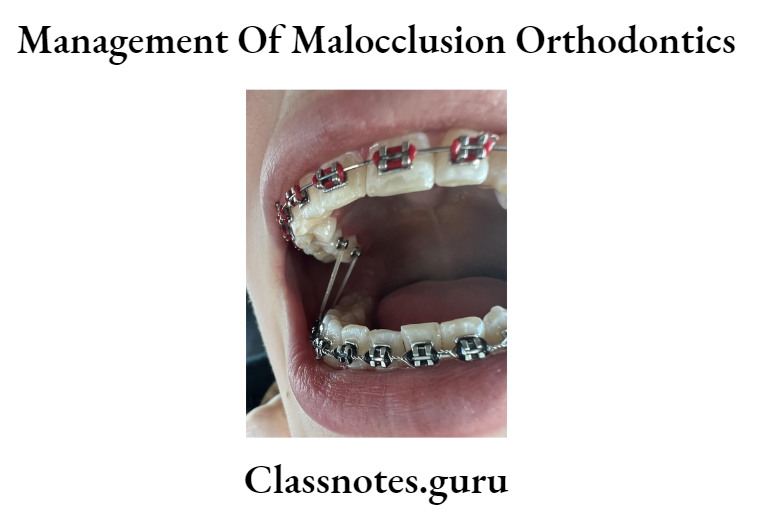
Crossbite elastics:
- Stretched between palatal surfaces of maxillary molars and buccal surfaces of mandibular molars
- Worn day and night
- Not worn for more than six weeks as it extrudes teeth
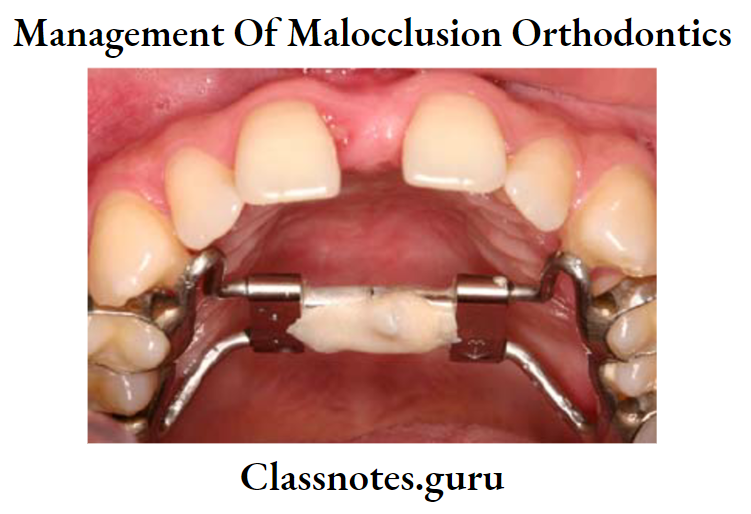
Coffin Spring:
Parts:
- Omega-shaped wire – In mid mid-palatal region
- Free ends of wire – Over slopes of the palate
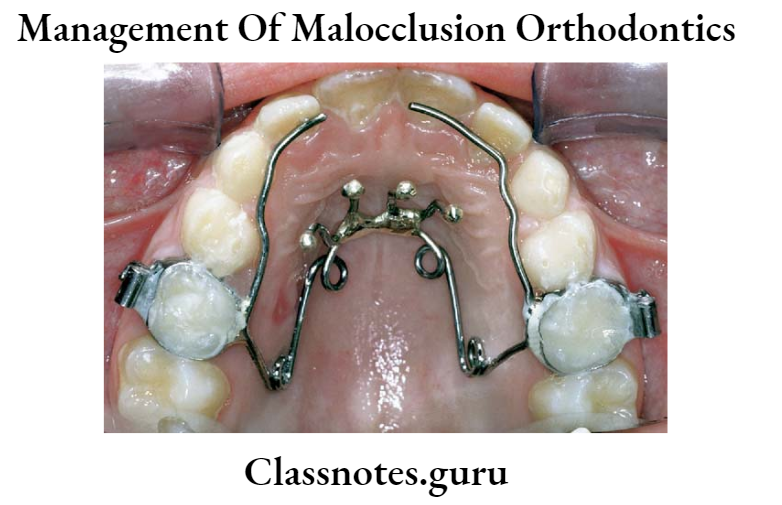
Quad helix:
- Consist of four helices
- 2 anterior helices
- 2 posterior helices
- Connected by anterior bridge and palatal bridge
Rapid maxillary expansion:
Incorporating screws by splitting of mid-palatal suture
Management Of Malocclusion Short Essays
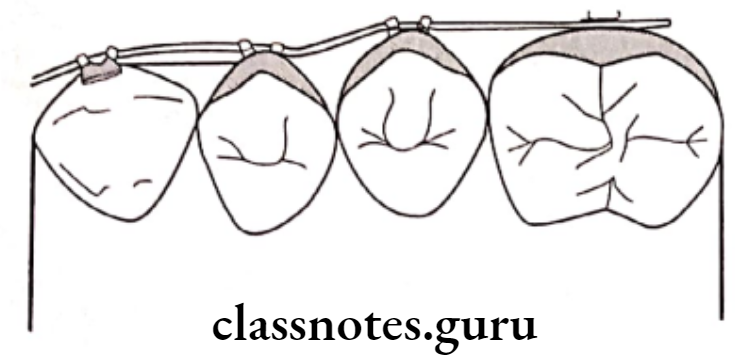
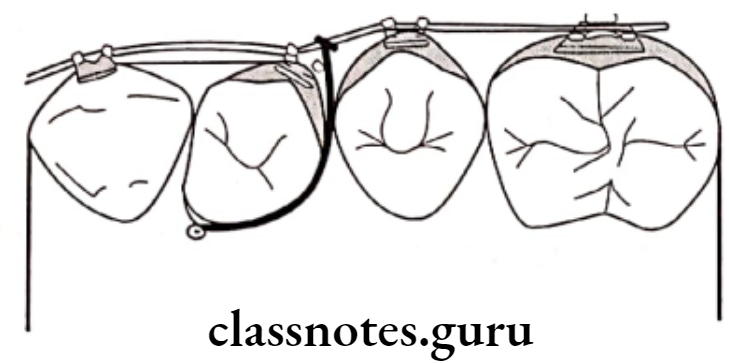
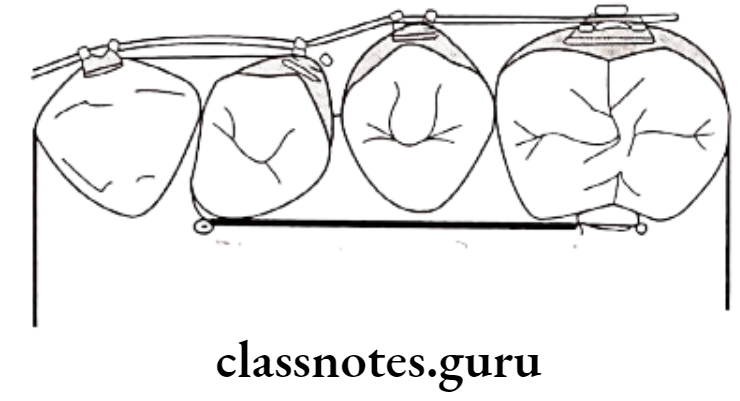
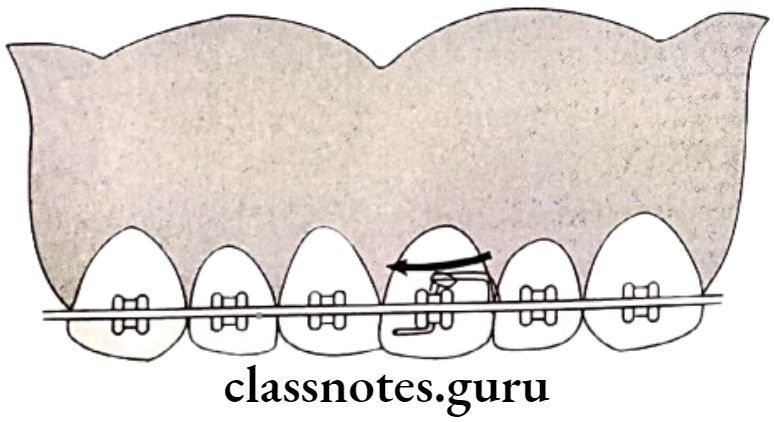
Question 1. Rotations.
Answer.
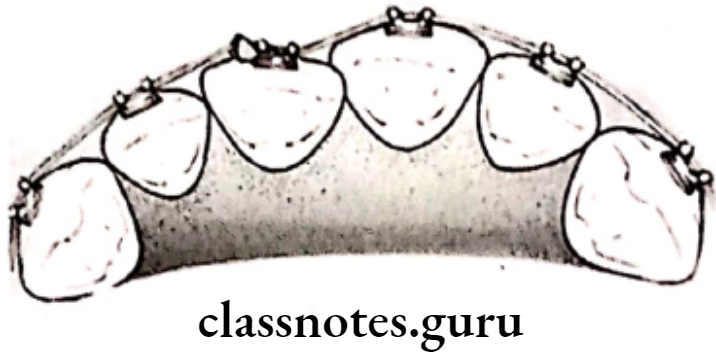
- They are tooth movements occurring around the long axis
Types Of Rotations:
- Mesiolingual/Disto-buccal rotation
- Disto lingual/Mesio-buccal rotation
- Rotated interiors occupy less space
- Rotated posterior occupies more space
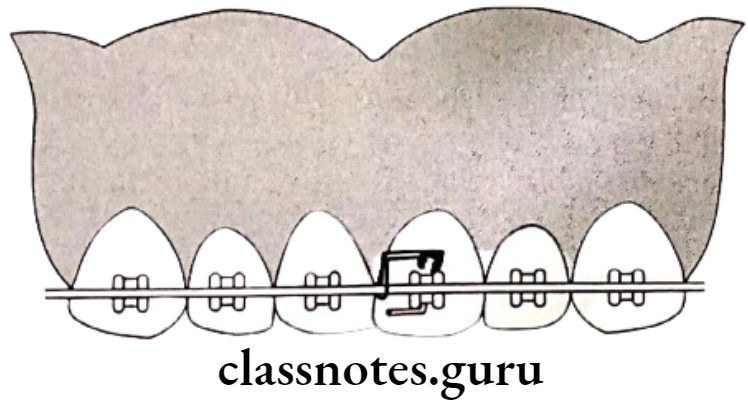
Treatment Of Rotations:
- Space Management – For rotated anterior
- Removable appliances – Z spring along with labial bow
- Fixed appliances
- Rotation wedges
- Elastic threads engaged in lingual attachments
- Force couple
- Retention – By circumferential suprarenal fibrotomy/precision
Question 2. Features of openbite.
Answer.
- Skeletal features:
- Increase in lower anterior facial height
- Decrease in upper anterior facial height
- Increase in anterior and decrease in posterior facial height
- Vertical maxillary increase
- Long and narrow face
- Steep anterior cranial base
- Downward and forward rotation of mandible
- Steep mandibular angle
- Upward tipping of maxillary skeletal base
- Divergent cephalometric planes
- Dental features:
- Proclination of upper anterior
- Narrow maxillalry arch
- Upper and lower anteriors fail to over lap each other resulting in space between incisal edges of maxillary and mandibular anteriors
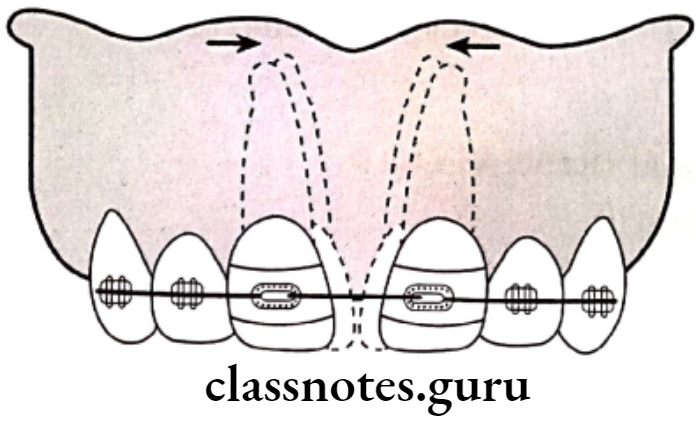
Question 3. Midline Diastema.
Answer.
Refers to any spacing/gaps existing in the midline of the dental arch
Etiology:
- Abnormal frenal attachment
- Ugly duckling stage
- Mesiodents
- Congenital missing teeth
- Trauma
- Hereditary
- Pressure habits
Diagnosis:
- Blanch test
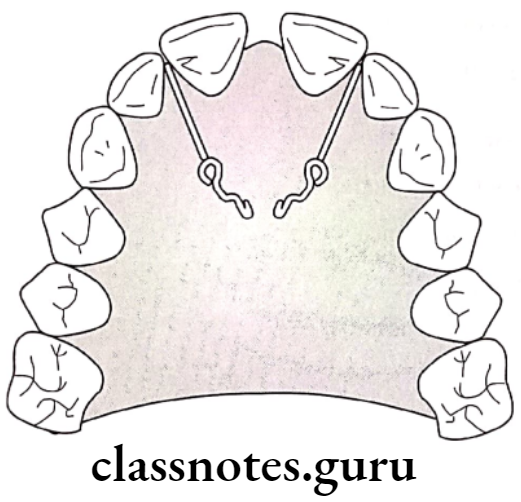
Management Of Midline Diastema:
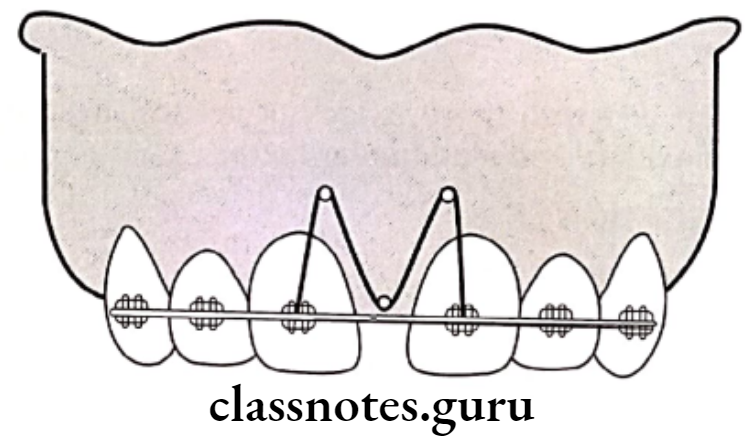
Removable appliance:
- Hawley’s appliance along with finger springs
- Split labial bow along with Adam’s clasp
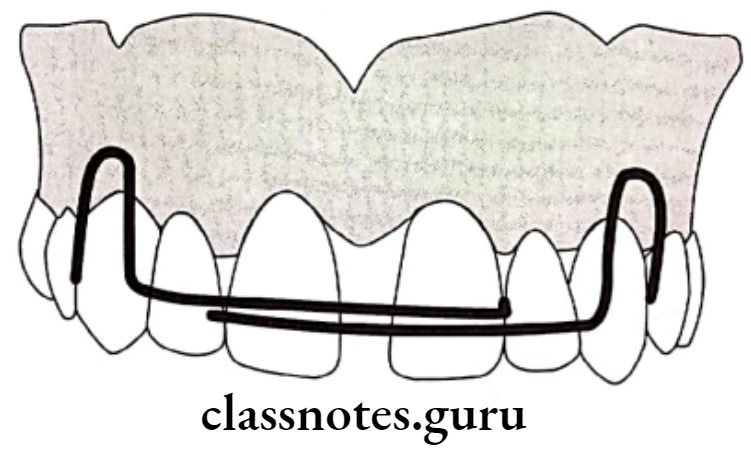
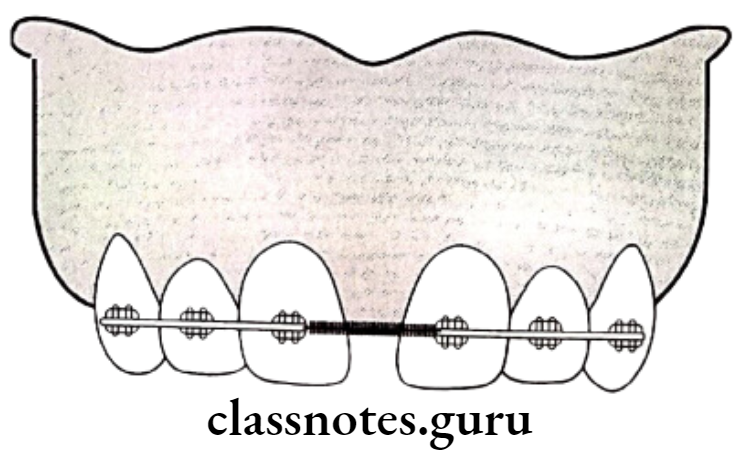
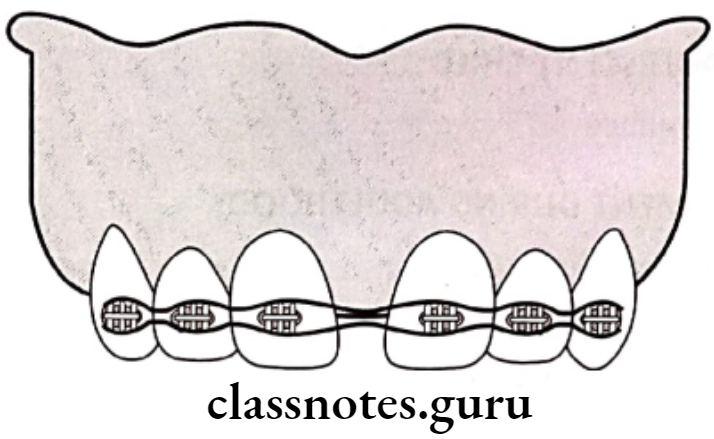
Fixed Appliances:
- M springs
- Elastic threads
- Elastic chains
- Closed coil spring
Question 4. Management of Class 2 Div. 1 Malocclusion.
Answer.
Interception of Habits associated with it:
- By habit breaking appliances
During Mixed Dentition period:
- In maxillary Prognathism – Headgear
- In mandibular deficiency – Activator
Management of Dento alveolar – Class 2:
- Maintenance of premolar – to prevent mesial drifting of molars
- In premature loss of premolars – Space regainers
Management in Adults
- Camouflage
- Orthoguathic surgery
- Mandibular advancement in mandibular retrognathism
- Maxillary setback in Maxillary prognathism
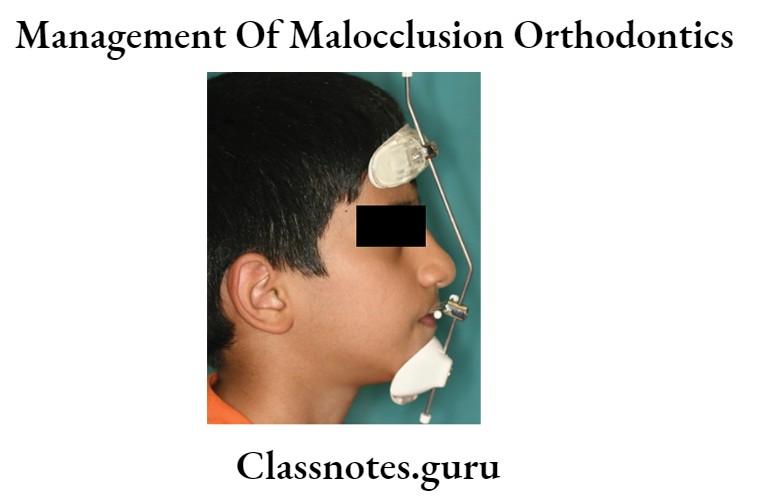
Question 5. Treatment of Class 3 malocclusion.
Answer.
In Pre – Adolescent Child:
- Frankel 3
- Chin cup
- Anterior Facemask
- RME with anterior facemask
- 3D – screws
In Adolescent Child:
- Camouflage
Treatment During Adulthood:
- Orthognathic surgery
- Maxillary advancement by Lhefort 1 osteotomy
- Mandibular setback
Question 6. Open Bite.
Answer.
Condition in which there is lack of vertical overlap between maxillary and mandibular teeth.
Classification of Open Bite:
Based on location:
- Anterior open bite
- Posterior open bite
Based on components:
- Skeletal open bite
- Dental open bite
Etiology:
- Habits
- Abnormal tongue size
- Inherited
Abnormal Growth Pattern:
Management of Open Bite:
- Anterior open bite
- Interception of habits
- Box elastics
- Chin cup with vertical pull head cap
- Skeletal Open bite
- Lefort I osteotomy
- Muscle retraining exercises
- Posterior open bite
- Interception of habits
- Vertical elastics
Question 7. Anterior Crossbite.
Answer.
Crossbite: Condition where one/more teeth may be malposed abnormally, buccally or lingually, or labially about the opposing tooth/teeth.
Classification:
- Single tooth crossbite
- Segmental crossbite
Treatment of Anterior Crossbite:
- Use of tongue blade
- Catlan’s appliance
- Z spring
- Screw appliances
- Face mask
- Frankel 3
- Chin cup appliances
Question 8. Deepbite.
Answer.
Excessive vertical overlapping of mandibular anterior by maxillary anterior
Classification of Deepbite:
- Skeletal deep bite
- Dental deep bite
Etiology:
- Over eruption of anteriors
- Infra occlusion of molars
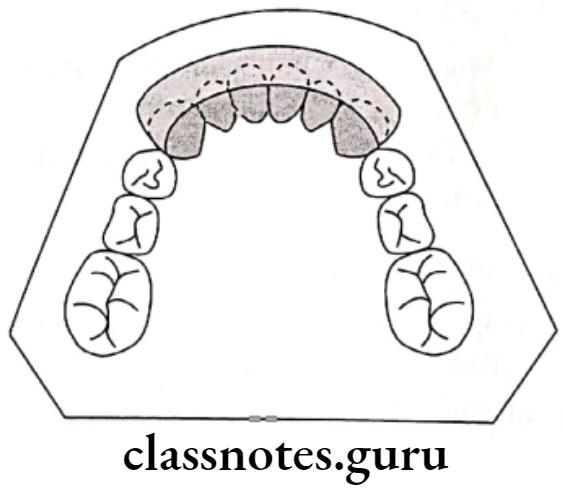
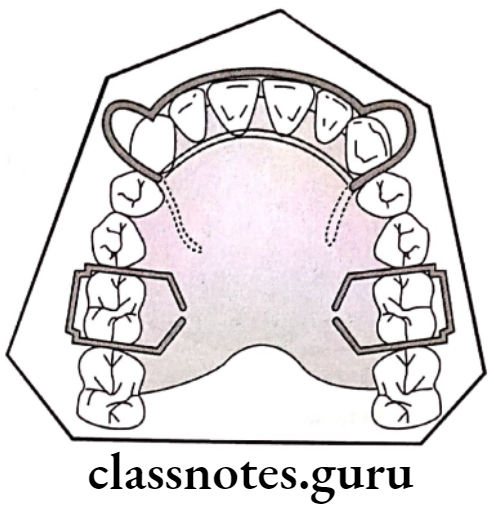
Treatment of Deepbite:
Removable appliances:
Anterior bite plane:
Parts: Adam’s clasps on molars
- Labial bow
- Acrylic behind maxillary anteriors
Mode of action:
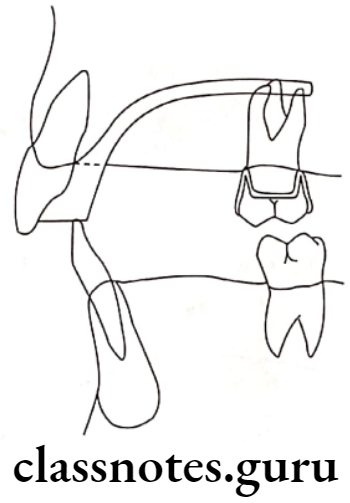
As the posteriors erupts upto height of bite plane, its height is further increased.
Myofunctional appliances:
- Activator – Trimmed to allow extrusion of teeth
- Bionator.
Fixed Appliance Therapy:
Use of anchorage bends:
- Bends given in arch wire mesial to molar tubes
- Creates intrusive force on incisors
Reverse curve of spee:
- Resilient arch wires curved in a direction opposite to curve of spee
Utility arches:
- Arch wires are bent to by pass buccal teeth and engaging incisors
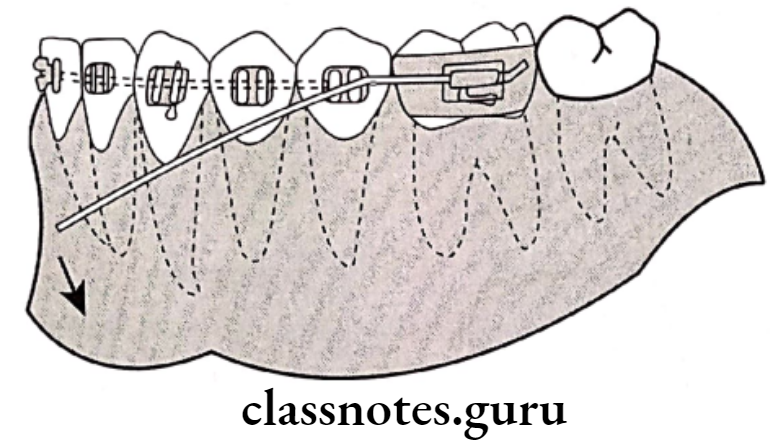
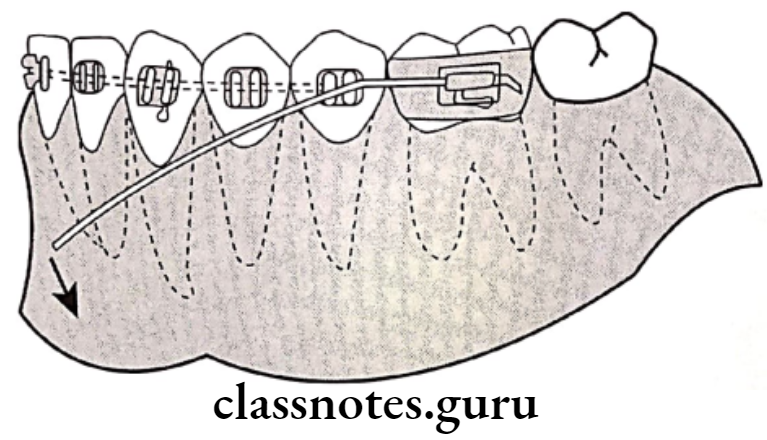
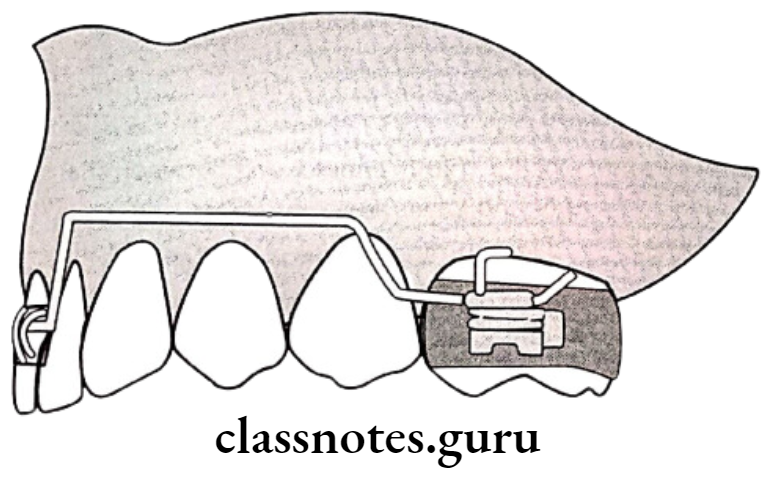
Question 9. Cross bite.
Answer.
Cross bite: Condition where one/more teeth may be malposed abnormally, buccally or lingually or labially with reference to the opposing tooth/teeth.
Classification of Cross bite
- Based on location
- Anterior cross bite
- Single tooth
- Segmental
- Posterior cross bite
- Unilateral
- Bilateral
- Anterior cross bite
- Based on the nature of crossbite
- Skeletal crossbite
- Dental crossbite
- Functional crossbite
Etiology of Cross bite:
- Persistence of a deciduous teeth
- Arch length – tooth material discrepancy
- Presence of habits such as thumb sucking and mouth breathing
- Retarded development of maxillalry
- Narrow upper arch
- Collapse of maxillary arch
- Unilateral hypo or hyperplastic growth of any of the jaws
- Persistence of a deciduous teeth
- Arch length – tooth material discrepancy
- Presence of habits such as thumb sucking and mouth breathing
- Retarded development of maxilla
- Narrow upper arch
- Collapse of maxillary arch
- Unilateral hypo or hyperplastic growth of any of the jaws
Question 10. Anterior cross bite – etiology and management
Answer.
Definition of Anterior cross bite:
- It is defined as malocclusion resulting from lingual position of the maxillary anterior teeth in relationship with the mandibular anterior teeth.
Etiology of Cross bite:
- Persistence of a deciduous teeth
- Arch length – tooth material discrepancy
- Presence of habits such as thumb sucking and mouth breathing
- Retarded development of maxilla
- Narrow upper arch
- Collapse of maxillary arch
- Unilateral hypo or hyperplastic growth of any of the jaws
Management of Anterior Cross bite:
- Use of removable appliances
- Use of tongue blade
- It is used to treat single tooth anterior cross bite
- It resembles ice cream stick
- It is placed inside the mouth contacting th epalatal aspect of the tooth in crossbite
- Rest the blade on the mandibular tooth
- Patient is asked to rotate the oral part of blade upwards and forward
- Repeat the exercise for 1-2 hours for about 2 weeks
- Catlan’s appliance
- It is lower inclinded plane constructed on maxillary arch
- Have 45 angulation
- Forces the maxillary teeth to a more labial position
- Use of Z spring
- Used to treat anterior cross bites involving one or two maxillary teeth
- Used when there is adequate space for labialization
- Use of tongue blade
- Use of fixed appliances
- Multilooped archwires or nickel titanium arch-wires are used for corrections
- Indications
- Dental anterior crossbites involving one or more teeth
- Requirement of more tooth movement along with correction of crowding and rotations
- Patients who exhibit minimal overbite
Management Of Malocclusion Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Camouflage treatment.
Answer.
- Done by extraction of teeth
- To reduce overjet, overbite, molar relation, crowding, deep bite
- In excellent inter cuspation – Extraction of upper first premolars
- In unstable molar relation – Extraction of all first premolars
Question 2. Treatment of cross bite.
Answer.
Cross bite: Condition where one/more teeth may be malposed abnormally, bucally or lingually or labially with reference to the opposing tooth/teeth.
Classification Of Cross bite:
- Single tooth cross bite
- Segmental cross bite
Treatment Of Cross bite:
- Use of tongue blade
- Catlan’s appliance
- Z spring
- Screw appliances
- Face mask
- Frankel 3
- Chin cup appliances
Question 3. Imbrication.
Answer.
- Imbrication denotes especially lower incisors arranged in an irregular manner within the arch due to lack of space
Etiology of Imbrication:
- Tooth material-arch length deficiency
- Presence of supernumerary teeth
- Discrepancy in individual tooth size and shape
- Abnormal eruption path
- Rotation and transposition of tooth
- Premature loss of deciduous or prolonged retention of primary tooth
Question 4. Spacing.
Answer.
Etiology of Spacing:
- Disproportion between arch length and tooth material
- Alteration in tooth morphology
- Habits
- Macroglossia
- Premature loss of permanent
Treatment of Spacing:
- Interception of habits
- Removable appliances – labial bow
- Fixed appliance – Elastic chains/threads
- Use of crowns and prosthesis
Question 5. Causes of Crowding.
Answer.
- Arch length – tooth material discrepancy
- Supernumerary teeth
- Prolonged retentiono f deciduous
- Abnormal tooth size and shape
- Premature loss of deciduous causing drifting of adjacent
- Late mandibular growth
- Pressure from erupting third molars
- Reduction of inter-canine width
Question 6. Inclined Plane/Catlan’s Appliance.
Answer.
Uses Of Catlan’s Appliance:
- Treatment of anterior cross bite
- Palatally displaced maxillary incisor
Design Of Catlan’s Appliance:
- Acrylic/metal covering the maxillary incisor at 45 angulation
Disadvantages Of Catlan’s Appliance:
- Problem in speech
- Dietary restriction
- Supra eruption of posteriors
Question 7. Midline Diastema.
Answer.
Refers to any spacing/gaps existing in the midline of the dental arch.
Etiology Of Midline Diastema:
- Abnormal frenal attachment
- Ugly duckling stage
- Mesiodens
- Congenital missing teeth
- Trauma
- Hereditary
- Pressure habits
Management Of Malocclusion Viva Voce
- Rotated posterior teeth occupy more space than normal
- Rotated anterior teeth occupy less space than normal
- Brodie syndrome is scissor bite of first premolar of patient with class 2 division 1 malocclusion
- Narrow upper arch is feature of skeletal posterior cross bite
- Cross bite is abnormal occlusion occuring in transverse plane
- Cross elastic is stretched from palatal surface of maxillary posterior teeth to buccal surface of mandibular teeth
- Cross elastic is best to treat single posterior cross bite
- Coffin spring causes slow and bilateral symmetrical expansion
- Tongue blade therapy is used for anterior cross bite correction
- Flat anterior bite plane is used to correct deep bite in angle class 2 division 2 malocclusion
- Skeletal deep bite is seen in skeletal class 2 division 2
- Deep bite is increased overbite
- Skeletal open bite is treated in adults by surgical correction
- Anterior openbite can be treated in mixed dentition by vertical pull head gear with chin cup
- Closure of space in midline is done by composite build up it th espace is upto 0-2 mm
- Abnormal labial frenum is cause of midline diastema
- Class 3 bionator and Frankel appliance type 3 is used for class 3 malocclusion
- Sagittal split osteotomy is used for management of class 3
- Class 3 malocclusion management involves extraction of lower first premolars and second premolars
- Class 3 elastics are placed between upper molar to lower canine
- For management of class 2 requires correction of maxillary retrognathism
- Class 2 malocclusion is most difficult to treat
- Mild rotations can be treated by NiTi arch wires
- Face mask is used for treatment of class 3 malocclusion
