Instrumentation Of Endodontics Important Notes
- Classification of instruments
- Grossman’s classification
- Exploring instruments – smooth broaches, endodontic explorer
- Debridement – barbed broaches
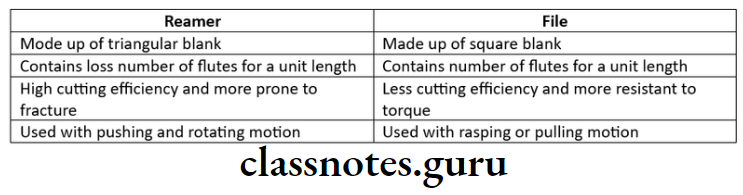
- Shaping instruments – reamers and files
- Obturating instruments – pluggers, spreaders, lentulospirals
- ISO grouping of instruments
- Group 1 – hand use only
- Group 2 – made to be attached to a handpiece
- Group 3
- Engine given latch type
- Rotary canal instruments
- Group 4 – root canal points
- Grossman’s classification
- Standardization of instruments
- By Ingle le Vine
- Numbering from 10 – 100
- Advance by 5 up to 60
- Advance by 10 up to 100
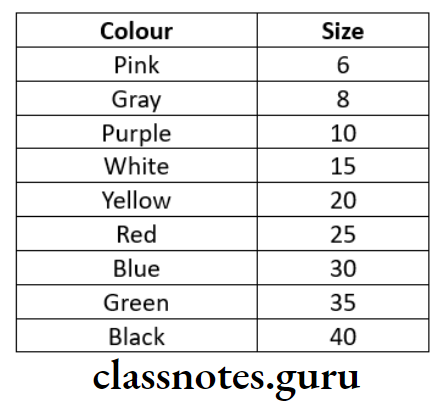
- Diameter
- D at tip – 1/10 of a mm
- Ex. For instrument No.25 D1 = 0.25mm
- D2 at the end of shaft
- Length of working portion
- 16mm from D1 to D2
- Taper of 0.02 mm per mm
- Angle of the tip 75 ± 15 degrees
- Color coding
- Numbering from 10 – 100
- By Ingle le Vine
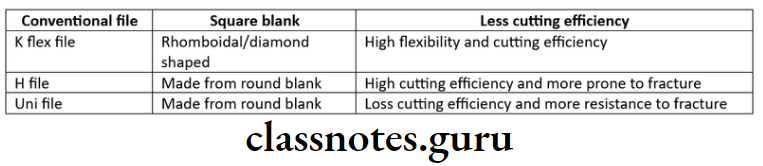
- H files
- Made from a round blank to produce spiral flutes
- They show higher cutting efficiency but is more prone to fracture
- The angle between cutting edge and the long axis of the instrumentis about 60-65°
- They are designed primarily for a linear filling motion
- Due to positive rake angle they cut in one direction only
Read And Learn More: Endodontics Question and Answers
Endodontic Instruments Names
- K flex files
- Cross section is rhombus or diamond shaped
- They have better cutting ability and flexibility
- The instrument is fabricated of V-4 steel
- Unifiles
- Mc-Spadden modified the traditional H files
- The blade present a S shape or double helix design
- It has two continuous cutting edges
- It can be used for cutting in both filling and reaming action
- They are less subject to fracture
- They are stiff in coronal and middle thirds but bends in apical 1/3rd
- Nickel – titanium files
- Composition
- Nickel – 54%
- Titanium – 44%
- Cobalt – 0.2%
- Boran – added to improve surface hardness
- At high temperature, it exists a body centered cubic lattice referred to as autestentic phase – a stronger phase
- On cooling, this phase transfers to close packed hexagonal, weak phase known as martensitic phase
- Two unique features of it are: shapre memory and super elasticity
- The main disadvantage of it is its cutting efficiency is only 60%
- Composition
Instrumentation In Endodontics
- Flexogates
- Derivative of Gates Glidden drills
- Used to enlarge the apical region of the canal
- Less likely to cause apical transporation
- Less fracture resistant
- Non cutting guiding tip
- Giromatic and Racer handpiece
- Giromatic
- It is commonly used reciprocating handpiece
- It accepts only latch-type instrument
- In this type the quarter turn motion is delivered 300 times per minute
- It uses a barder broach or reamer through 90° reciprocating arc at a speed of 1000 cycles/min
- Racer handpiece
- It uses a standard file and oscillates the file in root canal
- These instruments can be used for opening root canals but should not be used for root canal preparation
- Giromatic
- Peaso reamer
- They are more often used in preparing coronal portion of the root canal for past and core
- Instrument fractures always near the shank
- Ultrasonic and sonic instruments
- Used for cleaning and shaping of root canals
- Ultrasonic instruments contains a magnetostrictive hand piece which hold a K file or diamond file
- Ultrasonic and sonic instruments is operated at 2000 – 25000/section
- Ultrasonic and sonic instruments uses sodium hypochlorite as irrigant
- Sonic instruments operate at 1500 – 6500 cycles/min
- Ultrasonic and sonic instruments uses water as irrigant
- Colour coding
- Lentulospirals
- They are used for the placement of sealer, cement, and calcium hydroxide
- Lentulospirals must be operated clockwise in the handpiece and started or stopped outside the root canal
- If started in the canal it may cut into the wall of the root canal and break
Endodontic Instruments Names
- Modifications of H file
- Safety hed stroem
- Hyflex file
- Unifiles
- S file
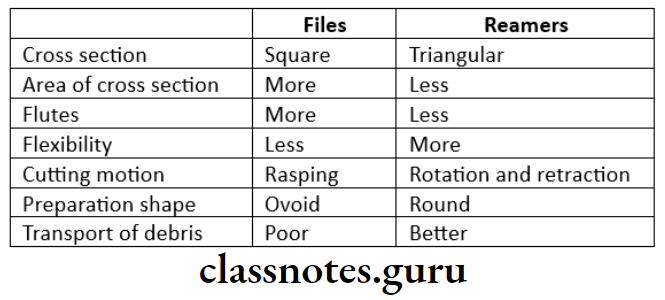
- Differences between reamer and file
Endodontic Instruments
- Gates Glidden drill
- Uses
- To remove lingual shoulder during access cavity preparation
- To enlarge root canal orifices
- For shaping cervical third of root canal in step back preparation
- Uses
Endodontic Instruments List
Instrumentation of Endodontics Long Essays
Question 1. Classify Endodontic Instruments. Describe standardization and sterilization of them.
Answer.
Grossman’s Classification:
- Exploring Instruments – Smooth broach
- Extripating Instruments – Barked broach
- Cleaning and Shaping Instrument – Files and Reamers
- Obturating Instruments – Pluggers and Spreaders
ISO And FDI Classification
- Group 1 – Hand operated Instruments
- Group 2 – Engine driven Instruments
- Parts
- Cutting head
- Latch type of attachment
- Group 3 – Fabricated from single piece of metal Ex. Gates Glidden drill
- Group 4 – Usually materials Ex. GP points, paper points
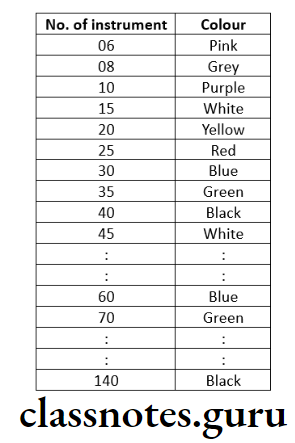
Standardization: By Ingle le Vine
- Numbering from 10-100
- Advance by 5 up to 60
- Advance by 10 up to 100
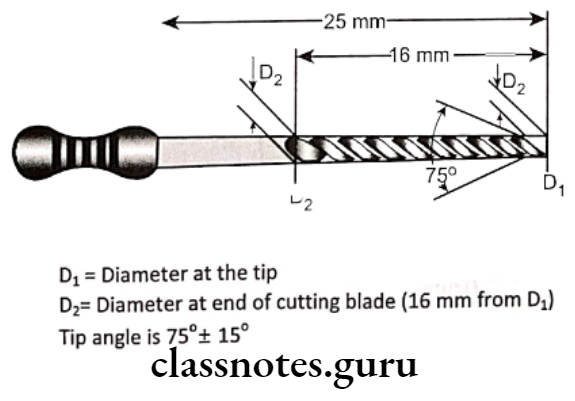
- Diameter
- D at tip – 1/10 of a mm
- Ex. For instrument No.25 D1 = 0.25mm
- D2 at the end of shaft
- Length of working portion
- 16mm from D1 to D2
- Taper of 0.02 mm per mm
- Angle of the tip 75 ± 15 degrees
- Color coding
Endodontic Instruments
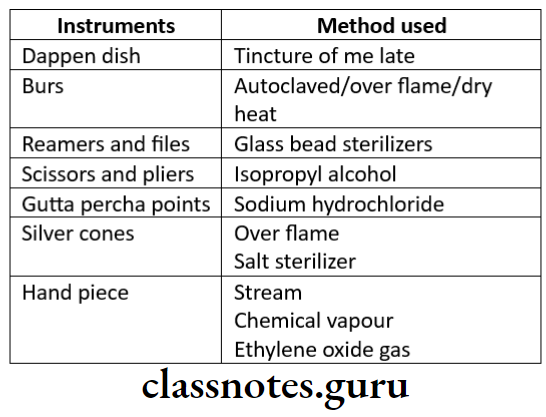
Sterilization:
Instrumentation of Endodontics Short Essays
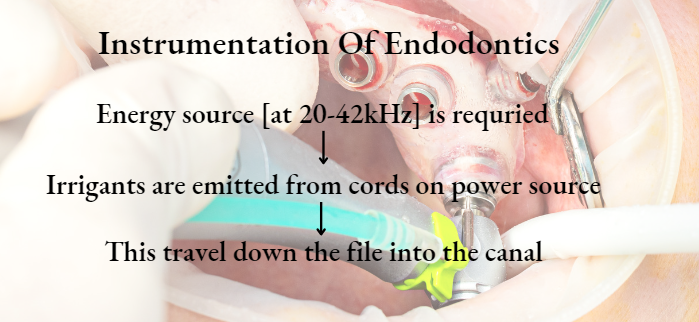
Question 1. Endosonic Instruments.
Answer.
Introduced By Richman
Activation:
Endodontic Instruments Advantages
- Cleans the canal
- Enhances the action of NaOCl
Endodontic Instruments Types:
- Magnetostrictive
- Piezoelectric
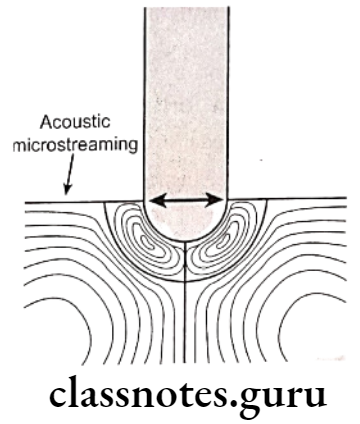
Endodontic Instruments Mechanism:
- Navigation
- Acoustic streaming
Endodontic Instruments Names
Endodontic Instruments Uses:
- Access enhancement
- Orifice location
- Irrigation
- Sealer placement
- Guttapercha obturation
- MTA placement
- Endodontic retreatment.
Root Canal Instrumentation Techniques
Question 2. Obturating Instruments.
Answer.
- Obturating Instruments Spreaders:
- Use: For lateral compaction
- Material Used: Stainless steel/Nickel titanium
- Types:
- Hand – Do not have standardized size and shape
- Finger – Standardized and color-coded to match the size of GP points
- Obturating Instruments Pluggers:
- Use: For vertical compaction, For sectional method
- Material Use To Pack: Calcium hydroxide/MTA
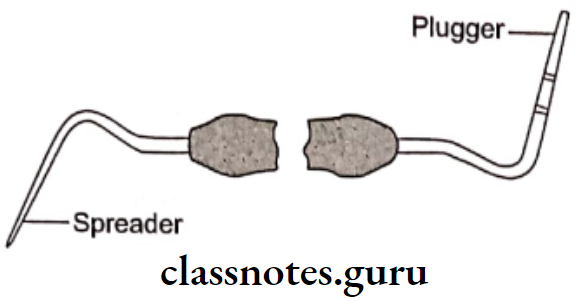
- Lentulospiral:
Question 3. Broaches.
Answer.
Broaches Types:
- Smooth broaches
- Barbed broaches
Broaches Broaches:
- Short handles instruments
- Made from round steel wires
Broaches Uses:
- Extripation of pulp tissues
- Removal of dressing
- Loosen necrotic debris
- Pathfinder [smooth broach]
Broaches Method Of Use:
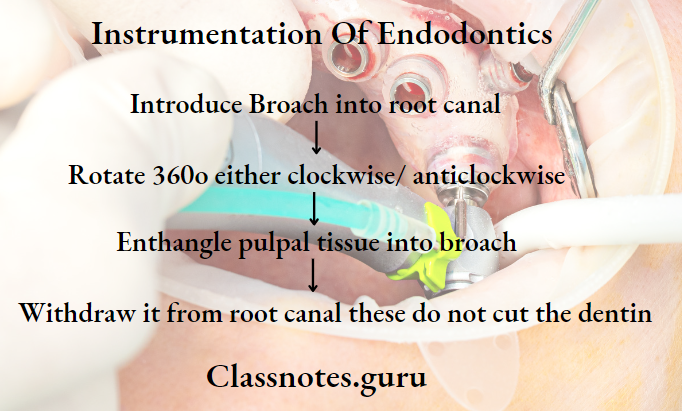
Broaches Precaution:
- Should not be forced apically into canal
Question 4. H-files.
Answer.
H-Files Manufacture:
- Round steel wire, machined to produce spiral flutes
H-File Advantage:
- Higher cutting efficiency
- Push debris coronally
H-files Manner Of Use:
- Pull motion, cut dentin when the instrument is withdrawn
H-Files Features:
- Positive Rake angle
- Distance between the flutes
H-Files Disadvantages:
- Aggressive
- Lack flexibility
- Tend to fracture
H-Files Use:
- For flaring coronal half of preparation
- To machnie straight canals
H-Files Modifications:
- Unifiles
- Helifile
- S-file

Rotary Vs Hand Files In Endodontics
Question 5. NiTi Files.
Answer.
NiTi Files
Known as Nitinol [NiTi Navol Ordinance Laboratory]
NiTi Files Types And Composition:
- 55 NiTinol [55% Ni, 45% Ti]
- 60 NiTinol [60% Ni, 40% Ti]
NiTi Files Advantages:
- Shape memory
- Super elasticity
- Softer
- Corrosion resistance
- Resiliency is good
NiTi Files Disadvantage:
- Poor cutting efficiency
- Do not show signs of fatigue
- Poor resistance to fracture
Instrumentation of Endodontics Short Answers
Question 1. Lentulospirals.
Answer.
Lentulospirals
- Lentulospirals is a obturating instrument
- Have latch-type attachment
Lentulospirals Used:
- To coat the walls of the root canal for sealer
Lentulospirals Significance:
- By sealing the canal walls, space between the canal wall and the material is avoided
Instrument Used Along With It: Giromatichand piece.

Question 2. Peaso – Reamer.
Answer.
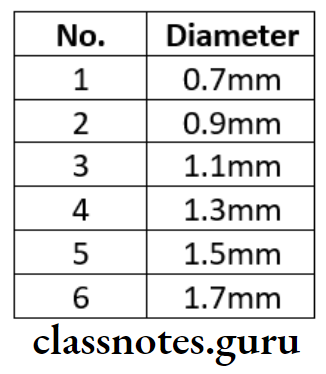
Peaso – Reamer
- Peaso – Reamer is a latch type of rotatory instruments
- Have cutting sides
- Made up of stainless steel
Peaso – Reamer Used For:
- For parallel post-preparation
- To remove gutta-percha from the canal
Peaso – Reamer Precaution:
- Peaso-Reamer does not follow canal curvature
- Peaso – Reamer is not flexible
- Should be used with low speed to prevent over-instrumentation and perforation
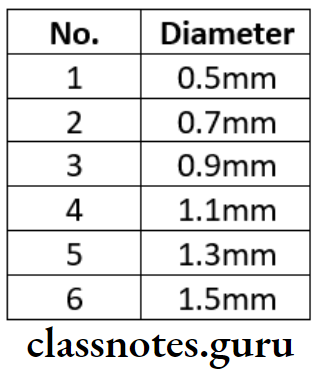
Peaso – Reamer Sizes:

Endodontic File Systems
Question 3. Gates glidden Drill.
Answer.
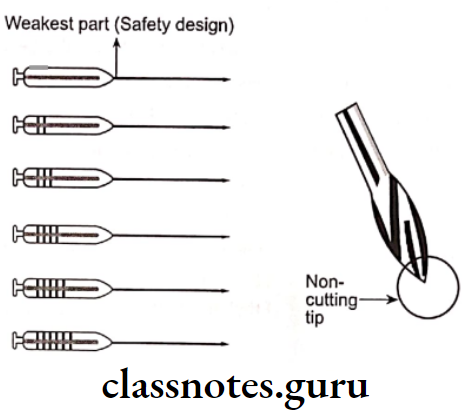
Gates Glidden Drill Description:
- Head – flame shaped with safe tip
- Culting end – Resembles American football
- Shank – long, elliptical shaped
Gates Glidden Drill Used Along With:
- Latch attachment, slow speed handpiece
Gates Glidden Drill Uses:
- Enlarging orifice in coronal 3rd of tooth
- To prepare post-space
- To remove guttapercha/instrument
Gates Glidden Drill Sizes:
Question 4. Files and Reamer
Or
Cross section of files and reamers.
Answer.
Files And Reamer
- These are cleaning and shaping instrument
- Difference

Endodontic File Systems
Question 5. Sterilization of instruments.
Answer.
Sterilization Of Instruments

Instrumentation Of Endodontics Viva Voce
- Broaches break easily
- Broaches should not be inserted unless the root canal is enlarged to a size of 20 or 25 reamer or file
- File contains more number of flutes and is four sided instrument
- Giromatic and Racer are contra angled engine driven instruments
- The instrument should be used with a 1/4 – 1/2 turn and withdrawn with a pull stroke
- Gates Glidden drill and Peaso reamer are power driven instruments
- Over instrumentation causes forcing of debris into periapocal area
- Instrumentation short of apex causes ledging of canal
- Instrumentation with large instruments causes enlarging of canal
- Reamers are used with pushing-rotating motion
- Files are used with rasping or pulling motion
- H file is used to finish the instrumentation of the coronal third of the root canal
- Endodontic explorer are most commonly used diagnostic and exploring instruments for idenfication of canal orifices
