Infectious Diseases Important Notes
- Gas Gangrene
- Caused by clostridium perfrigens
- Gas Gangrene is characterised by skin color change from pallor to bronze/ purple
- Skin is tense and tender
- Gas in the tissues is elaborated by crepitus or visible on radiograph
- Treatment
- Surgical debridement
- Antibiotic therapy with high dose of 4 penicillin, clindamycin, and metronidazole
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- Hyperbaric Therapy Is Used For Treatment Of
- Gas gangrene
- Osteoradionecrosis
- Chronic osteomyelitis
- Rubella ( German Measles)
- Rubella is caused by a paramyxovirus
- Rubella is spread by droplet infection
- Rubella is characterised by Koplik’s spots on the buccal mucosa which is seen as small white spots surrounded by erythema
- Rubella is followed by the appearance of rash first on the back of ears and at hairline and maximum on face
- Rubella in early pregnancy causes
- Congenital abnormalities like deafness
- Spontaneous abortion
- Congenital heart diseases like persistent patent ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defect, etc
- Complications
- Pneumonia
- Encephalitis
- Otitis media
- Hepatitis E
- Hepatitis E is also called Non-A or Non-B hepatitis
- Caused by HEV which is an RNA virus
- Spreads by faeco oral route
- Clinical illness resembles hepatitis A infection
- Pregnant women are particularly liable to acute hepatic failure
- Epidemics are almost exclusively caused by hepatitis E virus
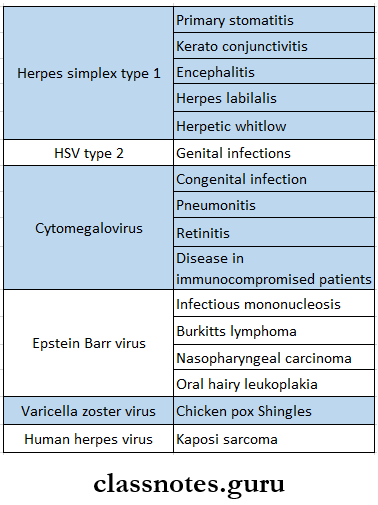
- Viruses And Infections Caused By Them
- Classification Of Virus
- DNA Virus
- Pox viridae
- Small pox
- Molluscus
- Contagiosum
- Herpesviridae
- Adenoviridae
- Major cause for nonbacterial pharyngitis and tonsillitis
- Papovaviridae
- Hepadnaviridae
- Pox viridae
- RNA Virus
- Picornaviridae
- Polio
- Coxsackie
- Hepatitis A
- Rhinovirus
- Orthoviridae
- influenza
- Picornaviridae
- Paramyxoviridae
- Retrovirus
- Togaviridae
- Rhabdoviridae
- Flaviviridae
- Calciviridae
- DNA Virus
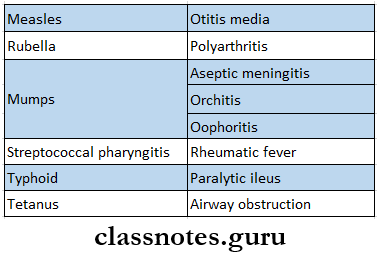
- Types Of Fever In Different Infections
- Saddleback fever – dengue
- Step ladder fever – typhoid
- Pell Ebstein fever – brucellosis and Hodgkin’s disease
- Double rise of temperature in a day – kalaazar
- Clinical Features Of Syphilis
- Congenital syphilis
- Hutchison’s triad
- Saddle nose
- Sabre tibia
- Rhagades
- Bossing of frontal and parietal bones
- Hypoplastic maxilla
- Salt and pepper scars on retina
- Primary syphilis
- Painless chancre
- Painless palpable rubbery inguinal lymph nodes
- Secondary syphilis
- Fever, malaise
- Maculopapular rash on trunks and limbs
- Condylomalata
- Mucous patches in the genitalia, mouth, and pharynx
- Snail track ulcers in mouth
- Tertiary syphilis
- Gumma
- Cardiovascular syphilis
- Aortitis
- Aortic aneurysm
- Aortic incompetence
- Neurosyphilis
- Tabesdorsalis
- Meningovascular disease
- General paralysis
- Congenital syphilis
- Complications Of Different Infection
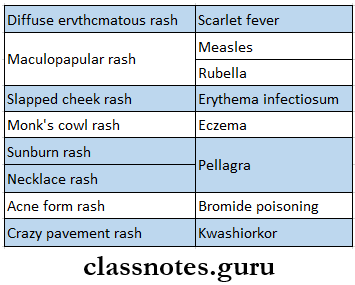
- Rashes In Different Diseases
- Spots In Different Diseases
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Infectious Diseases Important Notes
VIVA VOCE
- Clostridium perfrigens causes gas gangrene
- Clostridium tetani causes tetanus
- Clostridium difficile causes pseudomembranous colitis
- Koplik’s spots is a characteristic feature of measles
- Rubella is transmitted by aerosol infection
- Hepatitis A and E spread by fecal-oral route
- Hepatitis B, C, and D spread by parenteral route
- Hepatitis A affects children more than adults
important notes on infectious diseases for mbbs
