Implant Dentistry Definitions
Implant: It is an integral component of the oral implant complex which also consists of supportive bone, interposed kerati- nized and mucosal oral soft tissues and prosthetic superstructure
Splint: Splint is an appliance used for maintaining or stabilizing mobile teeth to their functional position
Osseointegration: It can be defined as “The apparent direct attachment or connection of osseous tissue to an inert alloplastic material without intervening connective tissue”.
Implant Dentistry Important Notes
Implant materials:
- Metals
- Stainless steel
- Gold
- Titanium
- Tantalum
- Zirconium
- Ceramics
- Calcium phosphate
- Bioactive and biodegradable ceramics
- Polymers
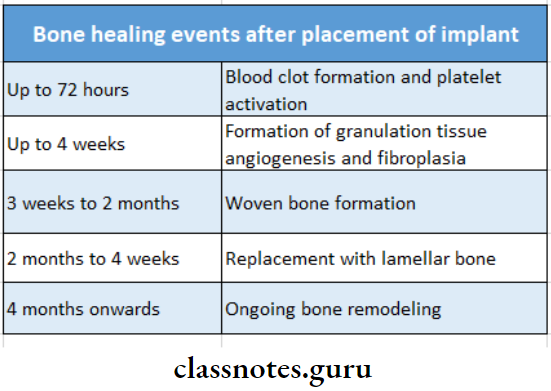
Bone healing events after placement of implant:
Implant Dentistry Short Essays
Question 1. Splints.
Answer:
Definition of Splints:
Splint is an appliance used for maintaining or stabilizing mobile teeth to their functional position
Functions of Solints:
- Stabilize mobile teeth to improve patient comfort and provide stability
- Stabilize moderate to advanced tooth mobility
- Stabilize teeth in secondary occlusal trauma
- Stabilize teeth following acute trauma
- Prevent tipping or drifting of teeth
- Create adequate stability
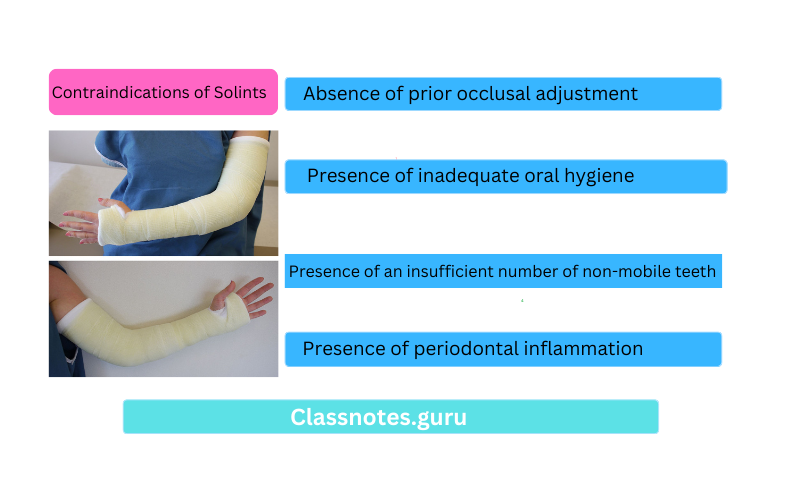
Contraindications of Solints:
- Presence of periodontal inflammation
- Presence of an insufficient number of non-mobile teeth
- Presence of inadequate oral hygiene
- Absence of prior occlusal adjustment
Read And Learn More: Prosthodontics Question And Answers
Question 2. Parts of implants.
Answer:
- Implant body:
- It is the component that is placed within the bone during the first stage of surgery
- It can be threaded or non-threaded
- Healing screw:
- During the healing phase, this screw is placed on the superior surface of the body
- Functions:
- Facilitates the suturing of soft tissues
- Prevents the growth of the tissue over the edge of the implant
- Healing cap:
- They are dome-shaped screws placed over the sealing screw after the second stage of surgery
- Length- 2-10 mm
- Function:
- Prevents overgrowth of tissues around the implant
- Abutments:
- It resembles prepared tooth
- Provides retention to the prosthesis
- Impression posts:
- It facilitates the transfer of the intra-oral location to a similar position on the cast
- Laboratory analogs:
- It represents the body of the implant
- Placed on the cast to fabricate an implant-supported prosthesis
- Waxing sleeves:
- Designed to be attached to the body of the implant
- Prosthesis retaining screws:
- Penetrates the fixed restoration and secures it to the abutment
Question 3. Osseointegration/requirements for successful osseointegration.
Answer:
It can be defined as “The apparent direct attachment or connection of osseous tissue to an inert alloplastic material without intervening connective tissue”.
Requirements of osseointegration:
- Occlusal load:
- To develop a strong interface the implant should not be overloaded during its organization period During this period, the surgical area undergoes remodelling process
- Biocompatibility:
- The material used should be biocompatible for example, pure titanium
- Implant design:
- Most conductive design for oseo-integration is cylindrical
- Implant surface:
- A smooth-surfaced implant is less prone to osseointegration than an implant with mild surface roughness.
- Surgical site:
- It should be healthy
- Surgical technique:
- Site should be subjected to minimal trauma
- Infection control:
- Infection especially from the periodontics should be avoided.
Question 4. Types of Implants.
Answer:
1. Depending on the placement within the tissues:
- Epiosteal:
- It receives its primary bone support by resting on it
- Transosteal:
- It penetrates both cortical plates
- It possesses through the entire thickness of the alveolar bone
- Endosteal:
- It extends into the basal bone
- It transects only one cortical bone
- It is sub-classified into
2. Root form:
- Used over a vertical column of bone
3. Plate form:
- Used over a horizontal column of bone
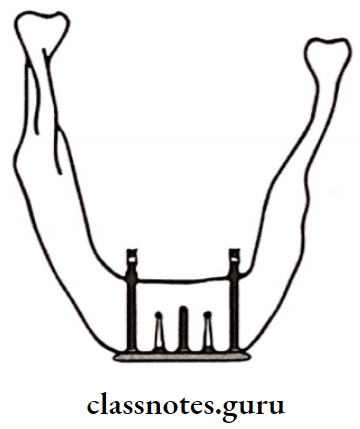
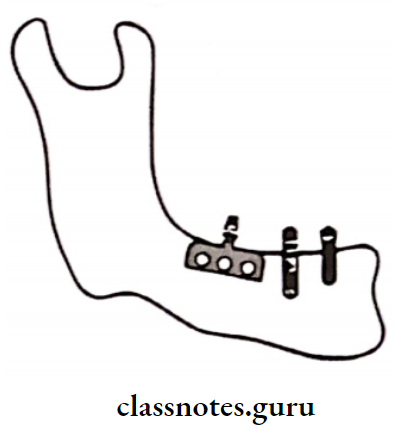
4. Depending on the material used:
- Metallic implants
- Non-metallic implants
5. Depending on their reaction to bone:
- Bio-active (Hydroxyapatite)
- Bio-inert Implants (metal)
6. Depending on the classification of edentulous spaces:
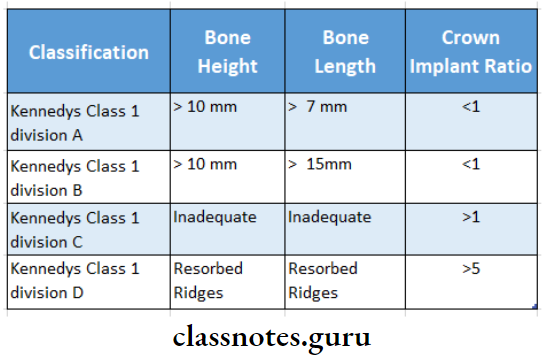
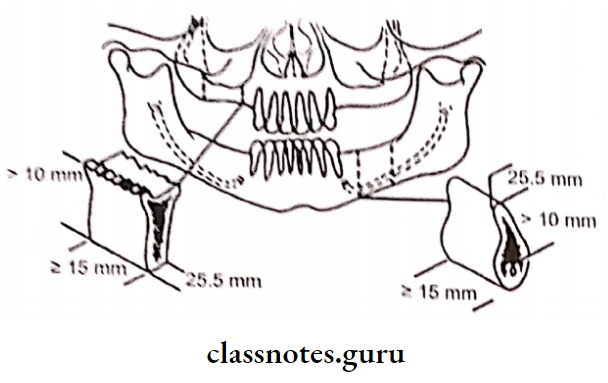
Question 5. Implant materials
Answer:
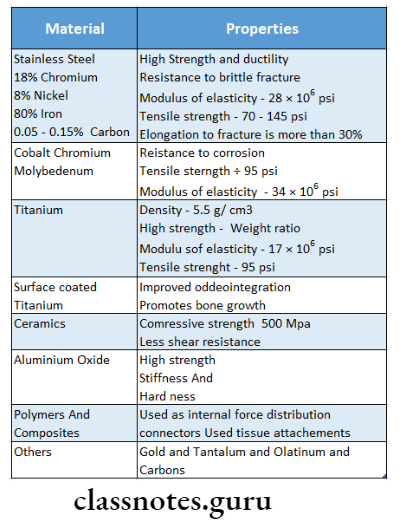
Implant Dentistry Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Implant
Answer:
It is an integral component of the oral implant complex which also consists of supportive bone, interposed keratinized and mucosal oral soft tissues and prosthetic supra structure
Materials Used of Implant:
- Metals
- Stainless steel
- Tantalum
- Gold
- Titanium
- Zirconium
- Ceramics
- Calcium phosphate
- Bioactive and biodegradable ceramics
- Polymers
Implant Dentistry Viva Voce
- The minimum width of ridge needed for a bio-integrated hydroxyapatite-coated dental implant is 5 mm
- The minimum bone height of the ridge needed for a bio-integrated hydroxyapatite-coated dental implant is 8 mm.
- 2 mm of space is needed between the implant and the inferior alveolar canal
