Transplantation Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Types of transplants.
Answer:
Types Of Transplants
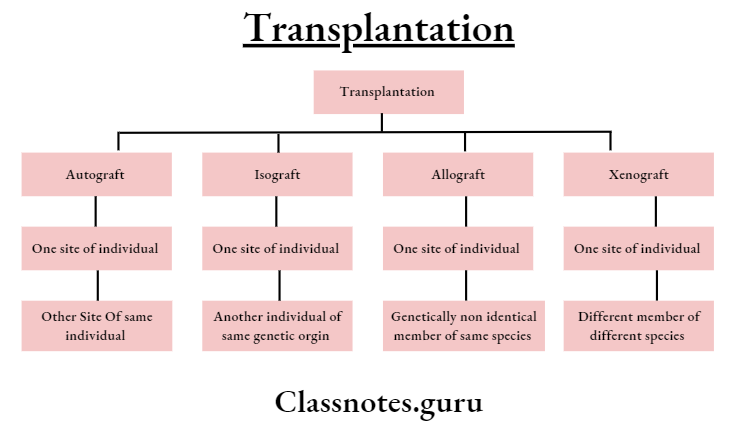
Question 2. Allograft reaction.
Answer:
Allograft Reaction
Rejection of the graft by the recipient is called an allograft reaction.
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question and Answers
Tissue Responses:
1. First Set Response.
- When allograft is applied following changes occur.
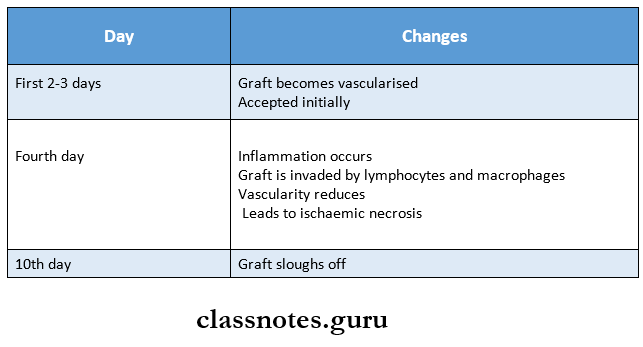
- This sequence of events is called the first set response.
2. Second Set Response.
- Second Set Response occurs when a second allograft from the same donor is applied to the same recipient.
- During this graft is rejected in an accelerated fashion.
- Early necrosis occurs and the graft sloughs off by the sixth day.
- This accelerated rejection is called the second set response.
Question 3. Graft-versus. Host reaction.
Answer:
Graft-Versus. Host reaction
The graft may cause an immune response against the antigens of the host.
- This is known as the graft-versus-host reaction.
- Graft-Versus. Host reaction is a cell-mediated reaction.
Graft-Versus Conditions:
- It occurs in the following conditions.
- Graft containing immune competent T-lymphocytes.
- HLA antigens of the recipient are different from the graft.
- Destroyed or impaired recipient’s immunological response.
Graft-Versus Manifestations:
- Splenomegaly
- Fever
- Rash
- Anaemia.
- Weight loss.
- Rarely death occurs.
Question 4. Antibiogram.
Answer:
Antibiogram
- The overall profile of antimicrobial susceptibility is known as an antibiogram.
- An antibiogramis a chart produced by clinical laboratories which detect the percentage of microbial isolates that are sensitive to particular antibiotics.
- Every 6-12 months the hospitals typically generate antibiograms.
Antibiogram Uses:
- Guide the doctors in antibiotic selection.
- Helps to monitor resistance patterns throughout a region.
- Enables to compare patterns across regions and with other regions.
Transplantation Viva Voce
- IgG is the only immunoglobulin that crosses the placenta
- IgA is predominant immunoglobulin in saliva
- IgA and IgG are secreted in milk
- IgG protects body fluids
- IgA protects body surfaces
- IgM protects bloodstream
- T and B lymphocytes, plasma cells, and antigen-presenting cells are primarily concerned with immune response
- Plasma cells are antibody-secreting cells
- Dendritic cells and macrophage act as antigen-presenting cells
- Most antibodies are produced in the spleen and lymph nodes
- Lysozyme is present in tears, eggs, saliva, and nearly in all secretions except in CSF, sweat, and urine
- BGG is given by intradermal route
- C3a and C5a are anaphylactic and chemotactic
- Smallest unit of antigenicity is known as epitope
- In serum sickness, a single dose of injection can serve both as a sensitizing and shocking dose
