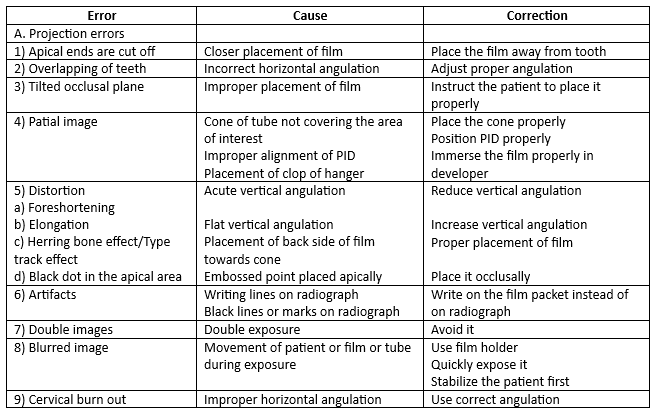
Faulty Radiographs Important Notes
- Image shape distortion can be minimized by:
- Positioning the film parallel to the long axis of the object.
- Orienting the central ray perpendicular to the object and film.
- Causes of image foreshortening:
- The central ray is perpendicular to the film but not to the object.
- More positive vertical angulation
- Cause of image elongation:
- The central ray is perpendicular to the object but not to the film.
- More negative vertical angulation.
- Common problems
Types of errors in radiographic images
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question and Answers
Faulty Radiographs Long Essays
Question 1. Faulty Radiographs.
Or
Discuss in detail various causes for faulty radiographs and measures to rectify them.
Or
Describe artifacts, blemishes, and faults in dental radiographs.
Answer.
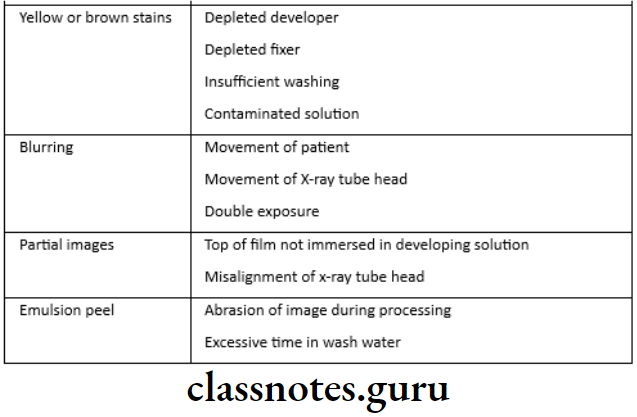
Faulty Radiographs
Processing errors in radiography essay
Faulty Radiographs Short Answers
Question 1. Cone Cut.
Answer.
Cone Cut Causes:
- The cone of the tube did not cover the area of interest
- Improper alignment of PID
- Placement of clip of hanger
- The top of the film is not immersed in the developing solution
- Shape distortion
Cone Cut Correction:
- Place the cone properly
- Position PID properly
- Immerse the film properly in the developer
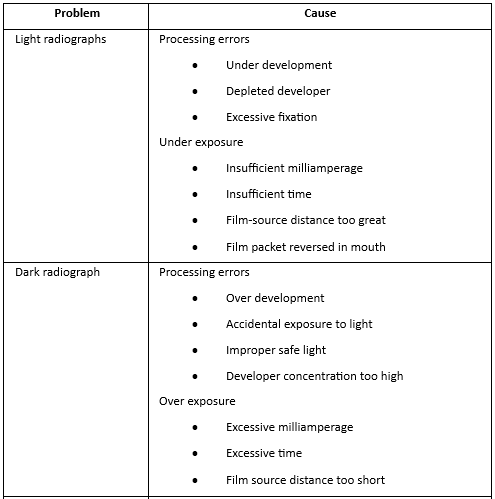
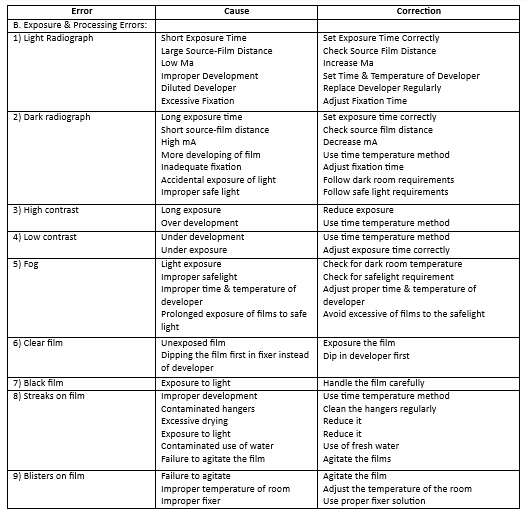
Question 2. Dark radiograph.
Answer.
Dark radiograph

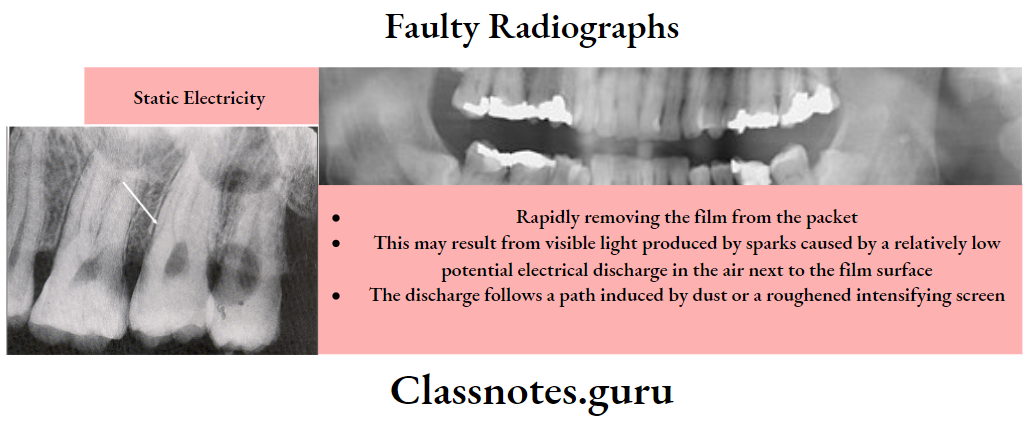
Question 3. Static Electricity.
Answer.
Static Electricity
These are caused by electrical discharges that produce no visible light but occur on the surface of the emulsion
Static Electricity Causes:
- Rapidly removing the film from the packet
- This may result from visible light produced by sparks caused by a relatively low potential electrical discharge in the air next to the film surface
- The discharge follows a path induced by dust or a roughened intensifying screen
Static Electricity Correction:
- Install an electric humidifier in the darkroom
- Avoid rapid removal of film
- Handle the film carefully
- Coat the intensifying screen with an antistatic solution
Exposure errors in X-ray imaging
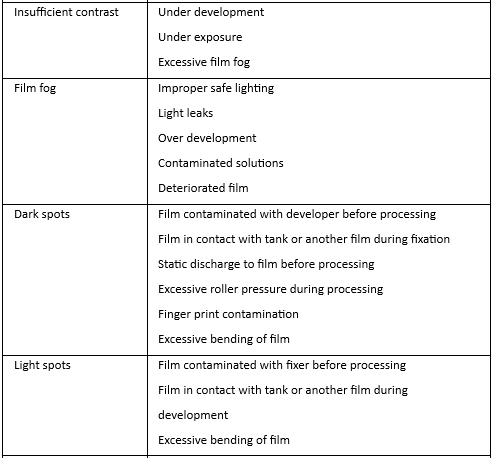
Question 4. Film fog.
Answer.
Film fog Causes:
- Light:
- Light leaks in the darkroom
- Improper safe light
- Improper filter in safe light
- Prolong exposure of the film to the safelight
- Scattered radiation:
- Scattered, stray, leakage or any other radiation not belonging to the primary beam is undesirable as it produces film fog
- For intraoral films, filtration, collimation, and film packets that lead to backed sheets should be used to reduce scattered and secondary radiation
- For intraoral films, grids are used
- Chemical fog:
- It is produced by prolonged development
- Development at high temperature
- Potassium bromide or restrainer prevents chemical fogging in the X-ray film by restraining the action of developing agents on the unexposed silver halide crystals
- After fixing the radiograph should be thoroughly washed to remove all residual processing chemicals and silver salts from the film surface
- If the temperature differences between the processing solution and the rinsing water are more than 15º F an orange peel appearance will appearance
Causes of image distortion in radiographs
Question 5. Tyre track effect.
Answer.
Track Effect Cause:
- The film is reversed while placed in the patient’s mouth
- Thus the tab side of the film faces the beam
Effect:
- The X-rays are partially absorbed by the lead backing
- Tyre track or herringbone pattern is produced on the film
- The film appears light, underexposed and foggy
Track Effect Correction:
- Place the pebbled surface towards the cone
Handling errors in radiographic films
Faulty Radiographs Viva Voce
- Excessive peak kilovoltage leads to insufficient image contrast
- The high temperature of the developer, high concentration of developer, and inadequate fixation lead to dark radiograph