Diseases Of The Gastrointestinal System Short Answers
Question 1. Causes of gum bleeding
Answer:
Causes Of Gum Bleeding
- Local causes
- Toothbrush trauma
- Food impaction
- Presence of plaque and calculus
- Biting into solid foods
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
- Gingival burns
- Systemic causes
- Scurvy
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Purpura
- Haemophilia
- Leukemia
- Drug-induced like salicylates, heparin
Question 2. Stomatitis.
Answer:
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is the inflammation of the mouth.
Etiology:
- Local causes.
- Poor oral hygiene
- Excessive use of tobacco, alcohol & spices.
- Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- General causes.
- Infections.
- Mucocutaneous diseases
- Drug toxicity.
- Diabetes
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Stomatitis Treatment:
- Eliminate causative agent.
- Use of mouthwash.
- Vit. B complex.
- Topical steroids.
Gastrointestinal diseases short Q&A
Question 3. Melaena.
Answer:
Melaena
- Malaena refers to the black, tarry feces that are associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Black color is caused by the hemoglobin in the blood being altered by digestive chemicals and intestinal bacteria.
Melaena Causes:
- Peptic ulcer.
- Bleeding from the upper GIT.
- Drug overdose and Tumours
- Gastritis
- Oesophageal varices
- Iron supplements
Melaena Diagnosis:
- Anaemia.
- Low blood pressure.
- Rectal examination
- Stool examination.
- Endoscopy.
Question 4. Melaena.
Answer:
Melaena
Dietary fiber can be defined as these parts of food that are not digested by human enzymes.
High Fibre Diet Significance:
- Lowers blood sugar
- Reduces cholesterol.
- Prevent colon cancer.
- Avoids hemorrhoids.
- Relieves constipation.
- Reduces absorption of bile salts.
- They are digested more slowly and this slows the rise in blood glucose after eating.
- Examples:
- Pure or unprocessed brans, cereals.
- Beans, legumes.
- Plant foods, root vegetables.
Question 5. Ulcerative colitis.
Answer:
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease affecting mainly the large intestine.
Ulcerative Colitis Causes:
- Genetic factors
- Stress
- High intake of unsaturated fat
- Autoimmune disease
Ulcerative Colitis Clinical Features:
- Diarrhea – bloody stools.
- Abdominal cramps.
- Tenesmus.
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Dehydration
- Anaemia.
Ulcerative Colitis Treatment:
- Intake of high protein & low residue diet
- Blood and plasma infusion.
- Correction of dehydration.
- Medications.
- Corticosteroids – For immunosuppression.
- Loperamide – For diarrhea
- Sulphasalazine – To prevent relapse
- Surgical Management – Surgical removal of the large intestine.
Gastrointestinal system disorders short questions and answers
Question 6. Intestinal nematodes.
Answer:
Intestinal Nematodes
- Ascaris lumbricoides.
- The adult worm lives in the jejunum.
- It is elongated, rounded in shape, and tapers at both ends.
- It passes its life cycle only in one host.
- It causes ascariasis.
- Hookworm.
- Ancylostoma duodenale.
- It is small, greyish-white, and cylindrical.
- Man is the only definitive host
- Causes hookworm disease.
- Characterized by microcytic, hypochromic anemia.
- Necator americanus.
- It is smaller and more slender.
- It is less pathogenic.
- Ancylostoma duodenale.
Question 7. H2 antagonists.
Answer:
H2 Antagonists
H2 antagonists competitively inhibit the action of histamine on H2 receptors.
- It reduces gastric secretion.
- Hastens healing of peptic ulcer.
- They are.
- Cimetidine – 400 mg BD
- Ranitidine – 150 mg BD
- Famotidine – 20 mg BD
- Roxatidine – 75 mg BD
H2 Antagonists Use:
- Peptic ulcer
- Gastritis
- Reflux oesophagitis.
- As pre-anesthetic medication.
Question 8. Leukoplakia.
Answer:
Leukoplakia Definition:
It is a whitish patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically, as any other disease and which is not associated with any other physical or chemical causative agent except the use of tobacco.
Leukoplakia Clinical Features:
- Older age males are commonly affected.
- Represents solitary or multiple white patches.
- Lesions are thick, fissured, indurated, or papilloma.
- The surface may be smooth wrinkled or rough.
- They are usually white or greyish-white in color.
- Thickness varies.
- Causes pain and a burning sensation in the mouth.
Question 9. Oral ulcers.
Answer:
Oral ulcers
Oral ulcers are a common disease characterized by the development of painful, recurrent, solitary ulceration of the oral mucosa.
Etiology:
- Immunological abnormalities
- Genetic abnormalities
- Microbes – α hemolytic streptococci
- Systemic diseases
- Nutritional deficiency
- Cyclic neutropenia.
Oral Ulcers Types:
- Minor aphthae ulcer- less than 1 cm in diameter.
- Major aphthae ulcer-over 1 cm in diameter
- Herpetiform ulcer – small ulcers throughout mucosa.
Oral ulcer Treatment:
- Symptomatic treatment.
Common GI diseases viva questions
Question 10. Complications of peptic ulcers.
Answer:
Complications Of Peptic Ulcers are
- Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Perforation.
- Gastric outlet obstruction H Pancreatitis
- Gastric malignancy.
Question 11. Barium swallow.
Answer:
Barium Swallow
Barium swallow is used to study the gastrointestinal tract
Barium Swallow Us Visualizelise a break in the gut mucosa.
- Detects mucosal abnormalities.
- Detects motility disorders.
- Shows filling defect caused by varices or tumors
- Detects hiatus hernia or diverticulum.
Question 12. Gastritis.
Answer:
Gastritis
It refers to inflammation of the stomach
Gastritis Types:
- Acute gastritis.
- Chronic gastritis.
Gastritis Causes:
- Clinical Features:
- Aspirin and other NSAIDs
- Renal failure
- Autoimmune
- H. Pylori infection
- Alcohol abuse n Iron therapy
- Stress
- Following burns
- Postoperative.

Digestive system diseases questions with answers
Question 13. Diarrhea.
Answer:
Diarrhea
Diarrhea refers to frequent loose stools i.e., more than 3 loose stools in a day.
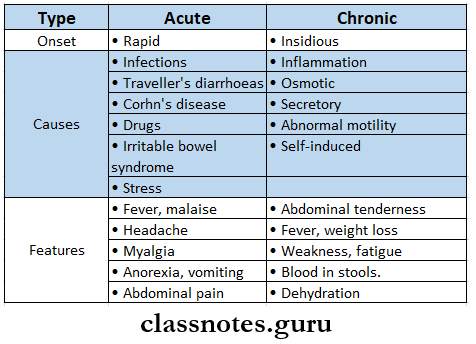
Question 14. Amoebiasis.
Answer:
Amoebiasis
A disease caused by entamoeba histolytica is called amoebiasis.
Amoebiasis Types:
- Intestinal amoebiasis.
- Extraintestinal amoebiasis
Amoebiasis Clinical Features:
- Frequent motions with blood and mucus
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea alternating with constipation
Amoebiasis Management:
- Oral metronidazole – 800 mg hourly for 5 days.
- Tinidazole – 2 g daily for 3 days.
- Diloxanide furoate 500 mg hourly for 10 days.
Question 15. Causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Answer:
Causes Of Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Oesophageal causes.
- Oesophagitis.
- Oesophageal ulcers
- Oesophageal varices
- Oesophageal cancer
- Gastric causes.
- Gastric ulcer
- Gastric erosion
- Gastric cancer
- Duodenal ulcers
- Vascular malformation.
Digestive system diseases questions with answers
Question 16. Lactose intolerance.
Answer:
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance occurs due to a deficiency of the enzyme lactase.
Lactose Intolerance Types:
- Primary – racial.
- Secondary – due to abnormal intestinal biopsy.
Lactose Intolerance Clinical Features:
- Abdominal colic.
- Abdominal distension.
- Increased flatus
- Diarrhea after ingesting milk or milk products.
VIVA Voce
- Haematemesis is red or black-colored vomiting of blood
- Malena is the passage of black, tarry stools containing altered blood
- Odynophagia is pain during swallowing
- Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing
- Aphagia is a complete esophageal obstruction
- Phagophobia is fear of swallowing
- Foul breath from the mouth – halitosis
- Excessive salivation – sialorrhoea
- Reduced salivation – xerostomia
- Loperamide in children may lead to toxic dilatation of the bowel.
