Diseases Of Blood And Blood Forming Organs Important Notes
1. Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Carcinoma of hypopharynx
- Koilonychias
2. Types of anaemia
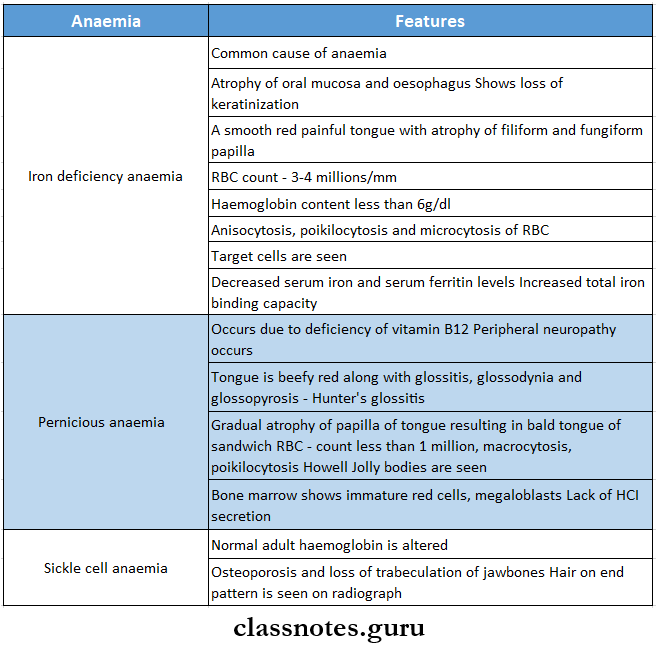
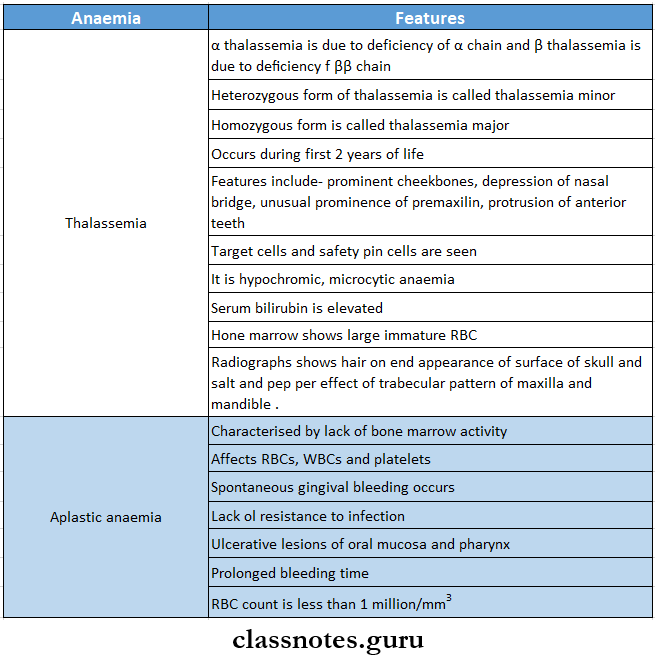
3. Hair on-end appearance is seen in
- Thalassemia
- Sickle cell anemia
4. Anitschow cells
- They are modified epithelial cells with
- Elongated nuclei
- Linear bar of chromatin
- Seen in
- Sickle cell anemia
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Aphthous ulcer
- Rheumatic heart disease
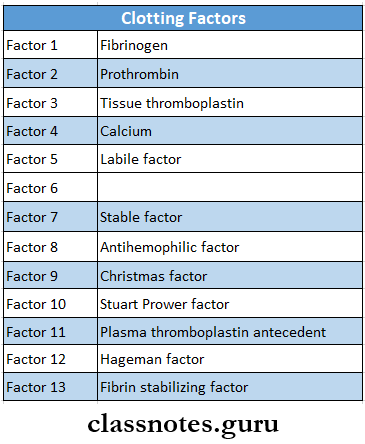
5. Clotting factors
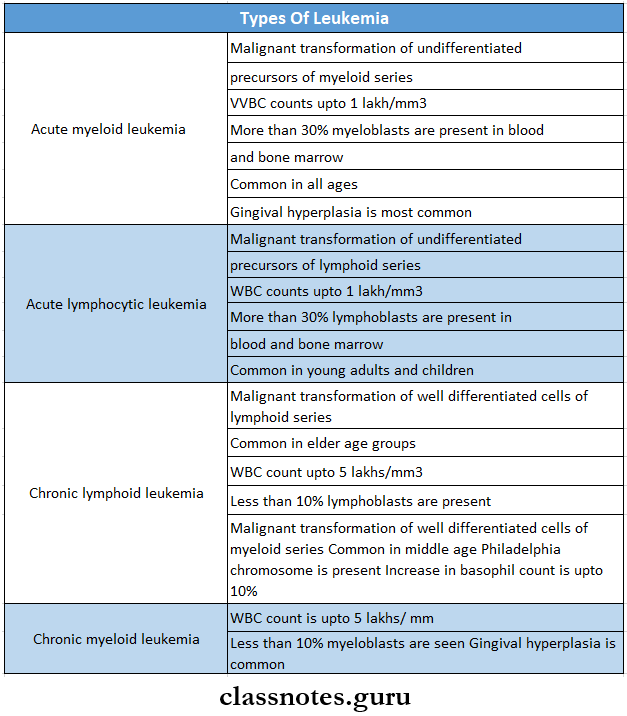
6. Types of leukemia
7. Agranulocytosis
- Mostly occurs due to the ingestion of drugs like
- Amidopyrine
- Barbiturates
- Chloramphenicol
- Quinine
- Sulfonamides
- Features
- Presence of infection in the oral cavity, GIT, genitourinary tract, respiratory tract, and skin
- Oral manifestation
- Necrotizing ulcerations of oral mucosa, pharynx, tonsils
- Rapid destruction of supporting tissues of the teeth
8. Cyclic neutropenia
- It is characterized by periodic cyclic diminution of leukocytes
- Cycle commonly occurs every 3 weeks
- Loss of alveolar bone around the teeth is an important oral manifestation
Diseases Of Blood And Blood Forming Organs Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Describe leukemia
Answer:
Leukemia
Leukemia: Leukemia is a disease characterized by the progressive overproduction of white blood cells which usually appears in the circulating blood in an immature form
Leukemia Etiology:
- Chromosomal abnormality-presence of Philadelphia chromosome
- Exposure to high doses of radiation therapy
- Exposure to certain chemicals- benzene, phenyl butanone
- Following chemotherapy treatment
- Myeloproliferative disorders like polycythemia vera
- Congenital or genetic abnormalities- Down’s syndrome
- The presence of primary immune deficiency
- Infection with human leukocyte virus
- Hereditary
Leukemia Classification:
- Acute leukemia
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia
- Acute myeloblastic leukemia
- Chronic leukemia
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Questions and Answers
Clinical Features:
- Acute type is more common in children and young adults while chronic is more common in adults of middle age
- Males are more affected than females
- Fatigue
- Generalised weakness, malaise
- Easy bruising
- Epitaxis
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Generalised pain
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Anaemia
- Persistent fever
- Weight loss
- Heat intolerance
- Scattered petechiae, ecchymosis
- Generalised lymphadenopathy
- Shortness of breath
- Tachycardia
- Hyperuricaemia
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Cranial nerve palsies
Leukemia Oral Manifestations:
- Gingiva
- Gingivitis
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Enlargement of interdental papillae
- Gingival tissues become swollen
- Cyanotic bluish discoloration of gingiva
- Thrombosis of gingival vessels
- Teeth
- Rapid loosening of teeth
- Alterations in developing tooth crypts
- Destruction of lamina dura
- Displacement of teeth
- Oral mucosa
- Thinning of oral mucosa
- Petechiae and ecchymosis develop over oral mucosa
- Multiple large irregular necrotic ulcers develop
- Other
- Large hematomas over the lower lip
- Oral infections
- Palatal ulcerations
- Mental nerve neuropathy
- Prolonged post-extraction bleeding
- Osteomyelitis of jaw
Leukemia Diagnosis:
- Blood
- WBC count- reduced
- Presence of abnormal leukocytes
- Platelet count- low
- Hemoglobin levels- reduced
- Bone marrow aspiration
- Detects increase in the number of bone marrow cells
- Lumbar puncture
- Determines the presence of blast cells in CNS
- Radiographic appearance
- Chest X-ray- detects mediastinal involvement
- Skeletal X-ray- Detects skeletal lesions
- MRI and CT scan- detects lesions and site of infection
- Lymphangiogram
- Locates malignant lesions
Leukemia Treatment:
- Chemotherapeutic drugs
- Radiation therapy
- Corticosteroids
Question 2. What is anemia? Classify anemia. Write about clinical features and treatment of pernicious anemia.
Answer:
Anaemia: It is defined as an abnormal reduction in the number of circulating red blood cells, the quantity of hemoglobin, and the volume of packed red cells in a given unit of blood
Anaemia Classification: Etiological classification
- Loss of blood
- Acute posthemorrhagic anaemia
- Chronic posthemorrhagic anaemia
- Excessive destruction of red cells
- Extracorpuscular causes
- Antibodies
- Infections
- Drugs
- Chemicals
- Trauma to RBC
- Intracorpuscular causes
- Hereditary
- Disorders of glycolysis
- Abnormalities of RBC membrane
- Acquired
- Lead poisoning
- Impaired blood production
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Pernicious anemia
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Protein deficiency
- Ascorbic acid deficiency
- Hereditary
- Extracorpuscular causes
- Inadequate production of mature erythrocytes
- Deficiency of erythroblasts
- Infiltration of bone marrow
- Endocrine abnormality
- Chronic renal disease
- Chronic inflammatory diseases
- Cirrhosis of liver
Pernicious Anaemia: Pernicious anemia is a relatively chronic hematological disease
Pernicious Anaemia Clinical Features:
- Occurs after the age of 30
- Males are commonly affected
- Triad of symptoms: generalized weakness, sore and painful tongue, and numbness or tingling of the extremities
- Easy fatigability
- Headache, dizziness
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite
- Shortness of breath
- Loss of weight
- Pallor
- Abdominal pain
Pernicious Anaemia Oral Manifestations:
- Glossitis
- Painful ami burning lingual sensation
- Inflamed and beefy red tongue
- Hunter’s glossitis
- Presence of small and shallow ulcers
- Atrophy of papillae- bald tongue
- Dysphagia
- Pallor of oral mucosa
- Hyperpigmentation of oral mucosa
- Increased susceptibility to oral infections
Pernicious Anaemia Treatment: Administration of Vitamin B12 and folio acid
Question 3. Hemophilia
Answer:
Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a potentially fatal inherited bleeding disorder characterized by profound hemorrhage due to genetic deficiency of clotting factors
Hemophilia Etiology:
- Hereditary
- Se-linked recessive trait
- Spontaneous mutations
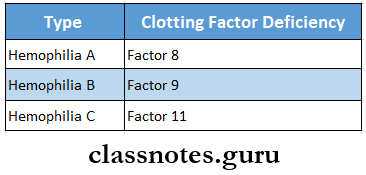
Hemophilia Types
Hemophilia Clinical features
- Persistent bleeding following mild injury or spontaneously
- Easy bruising
- Bleeding into muscles and joints causing pain
- Spontaneous bleeding into subcutaneous tissues or internal organs resulting in hematoma formation
- Epitaxis
- Haemarthrosis
- Gastric hemorrhage
- Spontaneous hematuria
- Intracranial hemorrhage
Hemophilia Oral Manifestations:
- Massive and prolonged gingival hemorrhage
- Internal blooding Into the glottis
- Recurrent subperiosteal hematoma
- Deep tissue blooding In the oropharyngeal region
- Severe periodontal disease
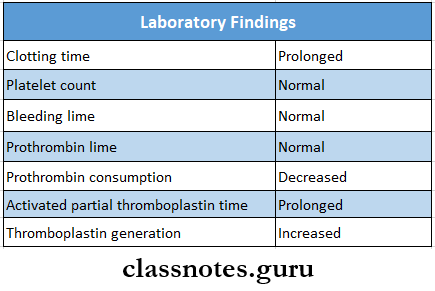
Laboratory Findings
Hemophilia Treatment:
- Immediate transfusion of factor 8 or 9
- Transfusion of packed red blood cells or white blood cells to replace blood volume
- Prophylactic transfusion of factor 8 to a level of 50% above normal
- Use of local hemostatic agents to control topical bleeding
- Analgesics and corticosteroids to reduce joint pain and swelling
- Joint immobilization
- Use of intravenous desmopressin
Question 4. Cyclic neutropenia
Answer:
Cyclic neutropenia
Cyclic neutropenia is a rare form of agranulocytosis characterized by periodic decrease in circulating neutrophils due to bone marrow maturation arrest
Cyclic neutropenia Clinical Features:
- Can affect any age group
- Fever, malaise
- Sore throat
- Stoamtitis
- Regional lymphadenopathy
- Headache
- Arthritis
- Cutaneous infection
- Conjunctivitis
Cyclic neutropenia Oral Manifestations:
- Severe gingivitis
- Stomatitis
- Aphthous tike ulceration
- Serve gingival recession
- Rapid alveolar bone loss
- Tooth mobility
- Cyclic neutropenia
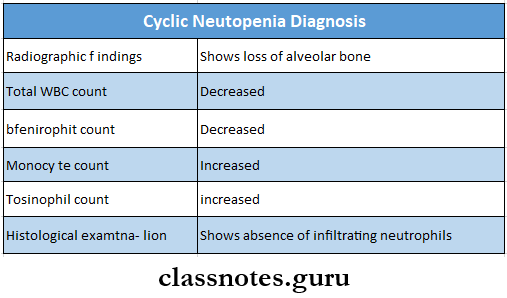
Cyclic neutropenia Diagnosis
Question 5. Agranulocytosis
Answer:
Agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis is a serious acute leukopenia characterized by a significant decrease in neutrophil count
Agranulocytosis Etiology:
- Toxic effects of drugs
- Ionizing radiation
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid fever
- Malaria
Agranulocytosis Clinical Features:
- Occurs at any age- common in adult women
- High fever with chills and sore throat
- Malaise, weakness
- Pallor skin
- Regional lymphadenopathy
- Severe dysphagia
- Urinary tract infections
- Weak and rapid pulse
Agranulocytosis Oral Manifestation:
- Necrotizing ulcerations Involving gingiva, soft palate, tonsils, lips, pharynx, and check.
- Gingival Weeding
- Excessive salivation
- Dysphagia
- The halitosis-Excessive tendency for secondary Infections
- Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
- Opportunistic fungal infections
Agranulocytosis Treatment:
- Elimination of causative factors
- Antibiotics
- Vitamin
- Antipyretics
- High-caloric soft diet
Question 6. Iron deficiency anemia
Answer:
Iron deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a chronic, microcytic, hypochromic anemia
Iron deficiency anemia Etiology:
- Chronic blood loss
- Inadequate dietary intake
- Faulty iron absorption
- Increased demand for iron
Iron deficiency anemia Clinical Features:
- Fatigue
- Palpitations
- Dizziness
- Sensitivity to cold
- Generalized weakness
- Lemon-tinted pallor skin
- Koilonychia- spoon-shaped nails
Iron deficiency anemia Oral Manifestations:
- Pallor of oral mucosa
- Loss of keratinization of gingiva
- Atrophic mucositis
- Atrophic glossitis
- The tongue appears smooth, bald, and red with a burning sensation
- Abnormal bleeding from ulcers
- Angular cheilitis
- Delayed wound healing
Iron deficiency anemia Diagnosis:
- Peripheral blood smear- shows microcytic, and pale RBCs
- Hemoglobin level- reduced
- RBC count- reduced
- Serum iron- reduced
- Total iron binding capacity- elevated
- MCV, MCH, and MCHC- reduced
- Hemosiderin- absent
Iron deficiency anemia Treatment:
- High protein diet
- Replacement of iron by 300 mg ferrous sulfate tablet, 3-4 tablets per day for 6 months
Question 7. Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Answer:
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- It is a feature of iron deficiency anemia
- It mainly occurs in women in the 4th-5th decade of life
- It consists of a triad of symptoms
- Angular cheilitis
- Cracks or fissures at the corners of the mouth
- Glossitis
- Smooth, red, and painful tongue
- Atrophy of filiform and fungiform papillae
- Dysphagia
- This leads to the limitation of diet to a soft diet
- Such patients are susceptible to oral cancers and pre-cancers
- Angular cheilitis
Question 8. Sickle cell anemia
Answer:
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary type of chronic hemolytic disease
Sickle cell anemia Clinical Features:
- More common in females younger than 30 years
- Fever
- Weakness, fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Joint pain
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite
- Systolic murmur
- Cardiomegaly
- Jaundice
- Loss of consciousness-sickle cell crisis
- Increased susceptibility to infection
- Renal failure
- Hypoxia, hypothermia
Sickle cell anemia Diagnosis:
- Total RBC count-reduced
- Hemoglobin level-reduced
- Serum unconjugated bilirubin-raised
- Presence of Hb-S in blood
Question 9. Rh pump
Answer:
Rh pump
- Rh pump is the term by Waston
- It is seen in erythroblastosis fetalis
- Enamel hypoplasia involves the p[ortion of the deciduous cuspid and first molar crown
- This results in a characteristic ring-like defect
- This is called the Rh pump
Question 10. Eosinophilic granuloma
Answer:
Eosinophilic granuloma
- Eosinophilic granuloma was introduced by Lichtenstein
- It describes a lesion of bone which is primarily a histiocytic proliferation with an abundance of eosinophilic leukocytes
Eosinophilic granuloma Clinical Features:
- Initially asymptomatic
- Later causes local pain, swelling, and tenderness of the involved bone
- General malaise, weakness
- Fever
- Sites Involved are:
- Skull
- Mandible
- Femur
- Humerus
- Ribs
Eosinophilic granuloma Treatment:
- Surgical currettage
- Radiotherapy
Question 11. Polycythaemia
Answer:
Polycythaemia
It is a chronic stem cell disorder with an insidious onset
Polycythaemia Clinical Features:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Weakness, lassitude
- Tinnitus
- Visual disturbances
- Mental confusion
- Slurring of speech
- Inability to concentrate
- Flushing or diffuse reddening of skin
Polycythaemia Oral Manifestations:
- Oral mucosa appears deep purplish red
- Cyanosis
- Gingiva are often engorged and swollen and bleed easily
- Submucosal petechiae
- Hematoma formation
- Increased susceptibility to infections
Question 12. Purpura
Answer:
Purpura
Purpura is defined as purplish discoloration of the skin and mucous membrane due to spontaneous extravasation of blood
Purpura Types:
- Non-thrombocytopenic purpura
- Thrombocytopenic purpura
- Primary purpura
- Secondary purpura
Purpura Clinical Features:
- Commonly occurs in females below 40 years of age
- Petechiae, ecchymosis
- Hematoma formation
- Purpuric spots
- Excessive gingival bleeding
- Blister formation over oral mucosa
- Excessive bruising
- Epitaxis
- Hematuria
- Melena and hematemesis
- Spontaneous bleeding
- Prolonged bleeding per surgery or injury
- lnlmerenlel bleeding
Question 13. Strawberry tongue
Answer:
Strawberry tongue
- It Is the oral manifestation of scarlet fever
- The tongue exhibits a white coating
- Fungiform papillae are edematous and by pernnomlc
- The project above the surface of the tongue as small red knobs
- So-called strawberry tongue
Question 14. Thalassaemia
Answer:
Thalassaemia
Thalassaemia is a genetically determined disorder of hemoglobin synthesis with decreased production of either alpha or beta polypeptide chain of the hemoglobin molecule
Thalassaemia Clinical Features:
- Jaundice
- Fever with chills
- Anaemia
- Malaise with generalized weakness
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Bone marrow hyperplasia
- Leg Ulcers
- Severe infections in tissues
- Mongloid prominent forehead, depressed time bridge, prominent cheekbones, protrusion of maxillary anterior teeth, and slanting eyes
- High cardiac failure
- Xerostomia
- Severe malocclusion
- Retracted upper lip
- Discoloration of teeth
Question 15. Hair on-end appearance
Answer:
Hair on-end appearance
- It is a radiographical feature of the skull bone
- Appears as a thin, poorly defined inner and outer cortex of the bone
- Trabeculae between them are coarse, elongated and bristle-like
- This produces hair with an end appearance
- Seen in
- Thalassemia
- Sickle cell anemia
Question 16. Chloroma
Answer:
Chloroma
- It is a solid collection of leukemic cells occurring outside of bone marrow
- Seen in
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- Myeloproliferative
- syndrome
- Eosinophilic leukemia
Chloroma Clinical features
- Skin lesions appear as raised, nontender plaques or nodules
- Oral lesions appear as swollen and painful gingiva that bleeds profusely
Diseases Of Blood And Blood Forming Organs Viva Voce
- Rh hump is seen in erythroblastosis fetalis
- The bald tongue of the sandwich is a feature of pernicious anemia
- Howell Jolly bodies are seen in pernicious anemia
- Safety pin cells are seen in thalassemia
- Sickle cell anemia occurs due to the substitution of valine for glutamic acid of the sixth position of the beta globulin chain
- Philadelphia chromosome is seen in chronic myeloid leukemia
- Most common form of leukemia in children is acute lymphocytic leukemia
- Splenomegaly of moderate grade is seen in acute leukemia
- Massive splenomegaly is seen in chronic leukemia
- Purplish discoloration of skin occurs in purpura
- The presence of Hb-S is seen in sickle cell anemia
- Hunter’s glossitis is seen in pernicious anemia
