Developmental Disorders Important Notes
1. Developmental Defects
2. Syndromes Associated With Fissured Tongue
- Melkerson Rosenthal syndrome
- Down’s syndrome
3. Synonymsforgeographictongue
- Erythema migrans
- Wandering rash
- Benign migratory glossitis
4. Ghost Teeth/ Regional Odontodysplasia
- Etiology:
- Defect in mineralization
- Clinical Features:
- Enamel and dentin are very thin
- The pulp chamber is extremely large
- Maxillary anterior teeth are more frequently involved
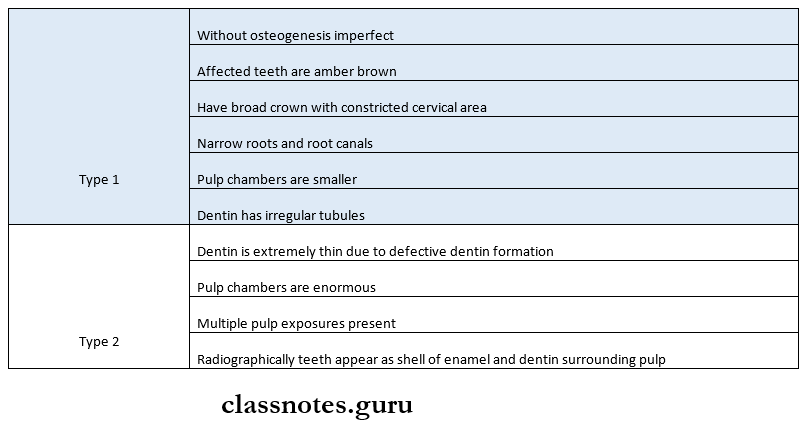
5. Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
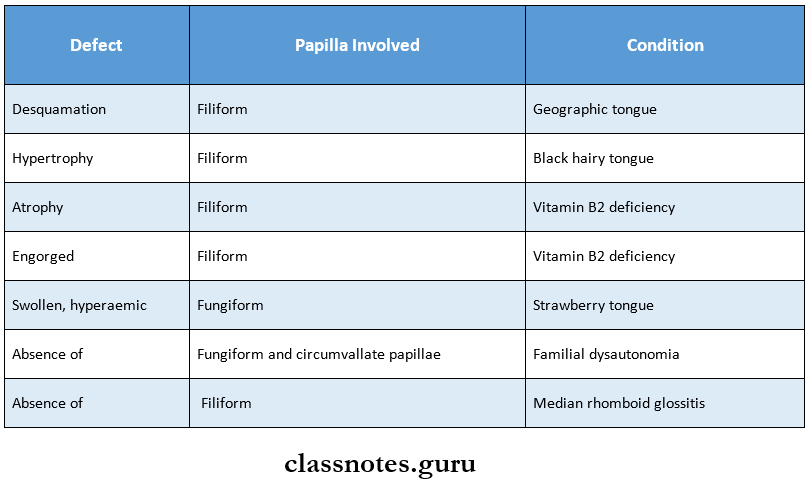
6. Defect In The Papilla Of The Tongue
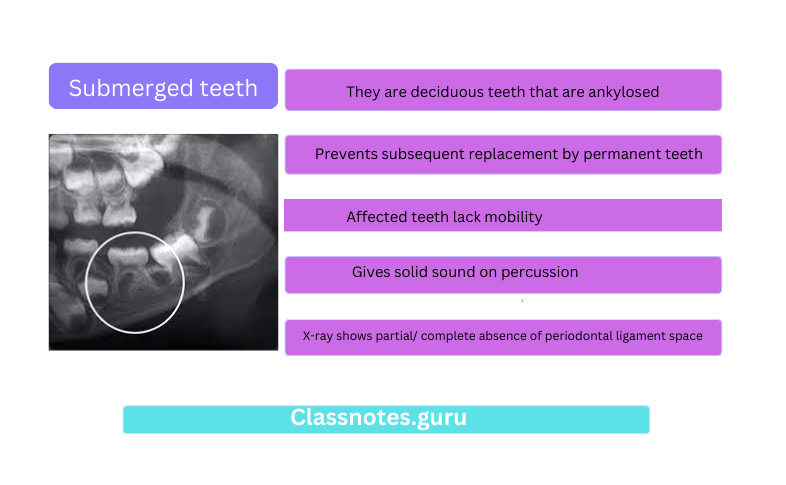
7. Submerged Teeth
- They are deciduous teeth that are ankylosed
- Prevents subsequent replacement by permanent teeth
- Affected teeth lack mobility
- Gives solid sound on percussion
- X-ray shows partial/ complete absence of periodontal ligament space
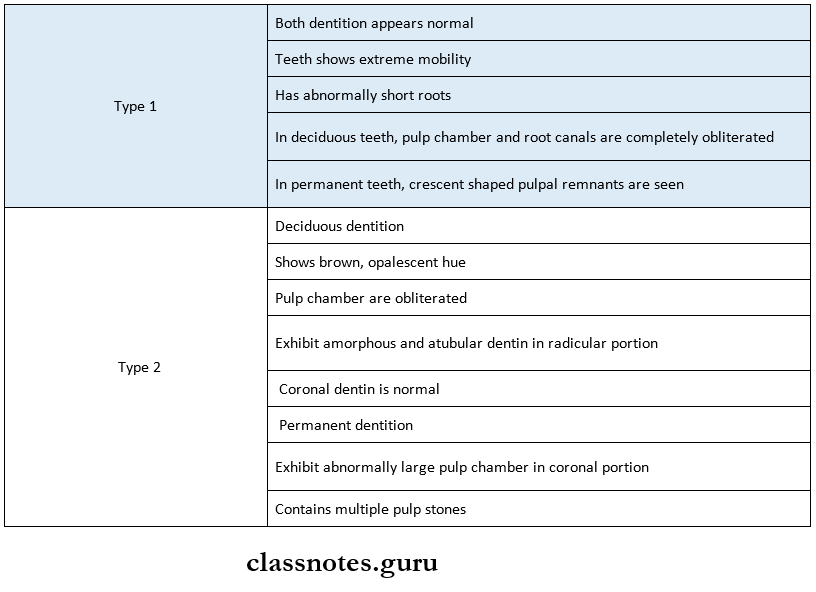
8. Dentin Dysplasia
9. Talon’s Cusp
- Located on the lingual surface of anterior teeth
- Extends half distance for CEJ to incisal edge
- Composed of normal enamel and dentin
- Contains horn of pulpal tissue
- Seen in
- Mohr syndrome
- Rubinstein Taybe syndrome
- Sturge Weber syndrome
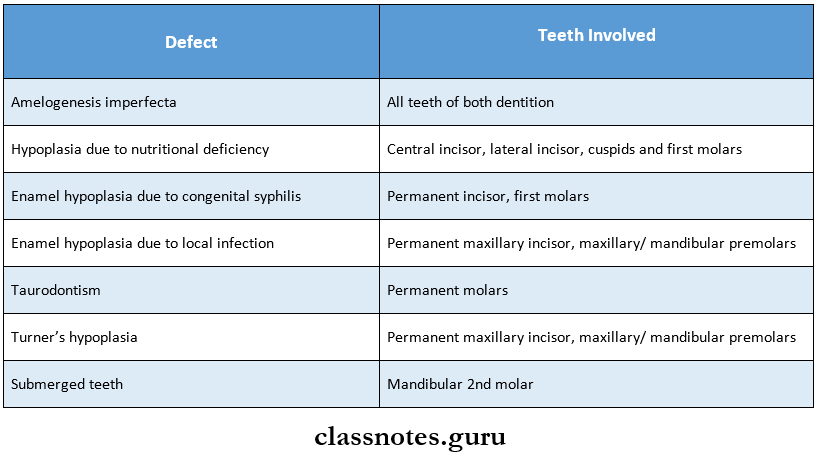
10. Teeth Involved In Different Defects
11. Taurodontism
- The body of the tooth is enlarged at the expense of the root
- Pulp chambers are elongated
- Apical displacement of bifurcation/trifurcation
- The Crown has a rectangular shape
- Classification
- Hypotaurodont – bifurcation is slightly apical. It is a mild form
- Hypertaurodont – it is in extreme form. Bifurcation is near apices
- Mesotaurodont- between Hypertaurodont and hypotaurodont
12. Syndromes Associated With Taurodontism
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Tricho-into-osseous syndrome
13. Turner’s Hypoplasia
- Turner’s Hypoplasia Etiology
- Trauma
- Periapical infection of deciduous teeth
- Turner’s Hypoplasia Clinical features
- The teeth affected are – permanent maxillary incisors, maxillary or mandibular premolars
- Teeth have Hypoplastic crown
- Range from mild discoloration to severe pitting.
Oral Medicine Developmental Disorders Long Essays
Question 1. Clinical examination of the tongue. Describe clini¬cal features of glossodynia and its treatment plan.
Answer:
Tongue
Tongue is defined as a painful tongue
Etiology:
- Local factors:
- Excessive use of tobacco
- Excessive drinking
- Bruxism
- Irritating dentures, clasp, prosthesis
- Referred pain from tonsils
- Malformed teeth, malocclusion
- TMJ disturbances
- Systemic factors
- Multiple myeloma
- Amyloidosis
- Pernicious anemia
- Pellagra
- Diabetes
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question and Answers
- Gastric disturbances
- Xerostomia
- Prolonged antibiotic activity
- Neurological factors
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Cerebrovascular accident
- Idiopathic
- Depression
- Cancerophobia
- Neurosis
Tongue Clinical Features:
- Presence of burning, tingling, or numbness of the tongue
- Tongue may occur as isolated features or a group of symptoms
- Tongue may occur with observable changes over the tongue
Tongue Management:
- Removal of local cause- construction of plastic retainers
- Treatment of muscular problems- use of muscle relaxants like diazepam
- Treatment of the systemic cause
- Surgical exploration with neuropathy
- Use of topical analgesia- 0.5% lidocaine
