Cranial Cavity Question And Answers
Question 1. Write a short note on cerebral dura mater.
Answer:
Cerebral Dura Mater
It Is A Strong Fibrous Membrane Consisting Of Two Layers:
- Inner meningeal layer
- Outer endosteal layers
The two layers are fused with each other except where venous sinuses are present.
Cerebral Dura Mater Outer Layer
- The outer layer is the periosteum lining the inner surface of skull bones and is continuous with periosteum.
- Cerebral Dura Mater Outer Layer is loosely attached to the inner surface of the cranial vault but is fimly attached to base of skull and around the foramen magnum.
Cerebral Dura Mater Inner Layer
- Cerebral Dura Mater Inner Layer encloses brain and at the foramen magnum, it is continuous with dura of spinal cord.
- The meningeal layer is folded on itself at some places to form dural folds.
Folds Of Dura Mater: The folds are as follows
- Falx cerebri
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Falx cerebelli
- Diaphragma sellae
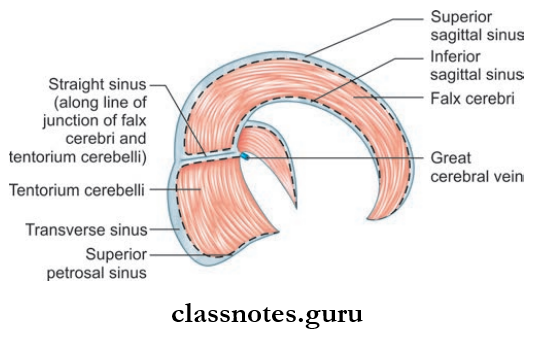
Falx Cerebri
- The large sickle-shaped fold of dura is situated between the two cerebral hemispheres and occupy the median longitudinal fissure between them.
- The narrow anterior end is attached to the crista galli and the broad posterior end to the upper surface of the tentorium cerebelli.
- Falx Cerebri encloses superior and inferior sagittal sinuses in its upper and lower margins respectively.
- Falx Cerebri also encloses straight sinus along the attachment with tentorium cerebelli.
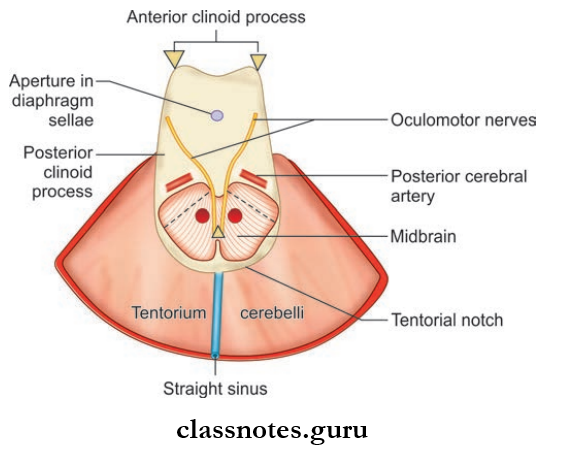
Tentorium Cerebelli
- Tentorium Cerebelli is a tent-shaped fold of dura forming roof of posterior cranial fossa
- Tentorium Cerebelli separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe of the cerebrum
- Tentorium Cerebelli consists of inner margin and outer margin, which are attached to anterior and posterior clinoid processes respectively.
- Consists of upper surface and inferior surface to which falx cerebri and falx cerebelli are attached respectively.
- Tentorium Cerebelli encloses transverse sinus, superior petrosal sinus, and straight sinus.
Falx Cerebelli
- Small sickle-shaped dural fold is a sagittal plane extending from internal occipital protuberance to the posterior margin of foramen magna
- Falx Cerebelli has a free anterior margin and attached posterior margin
- Falx Cerebelli encloses occipital sinus.
Question 2. Write a short note on intracranial dural venous sinuses.
Answer:
Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses
- These are venous channels present in the cranial dura.
- These are formed by either separation of two layers of dura or by the reduplication of the meningeal layer.
- The sinuses have thin walls lined by endothelium and drain blood from brain.
- The blood is ultimately drained to internal jugular vein.
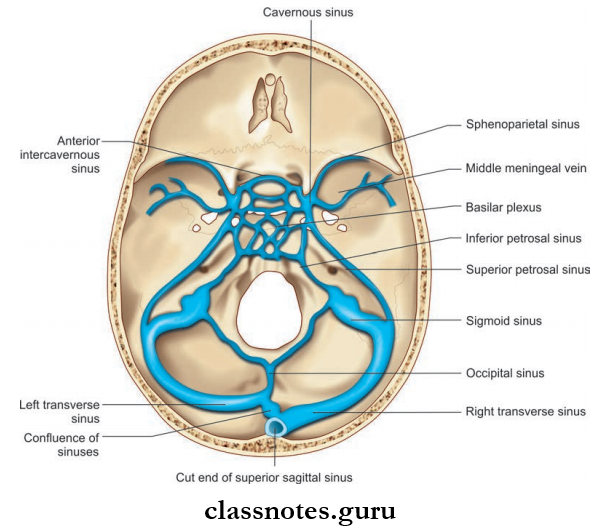
The Venous Sinuses Are Divided Into:
- Paired Sinuses Consisting Of:
- Cavernous sinus
- Superior petrosal sinus
- Inferior petrosal sinus
- Transverse sinus
- Sigmoid sinus
- Sphenoparietal sinus
- Petrosquamous sinus
- Middle meningeal sinus
- Unpaired Sinuses Consisting Of:
- Superior sagittal sinus
- Inferior sagittal sinus
- Straight sinus
- Occipital sinus
- Anterior intercavernous sinus
- Posterior intercavernous sinus
- Basilar venous plexus.
Question 3. Write a short note on cavernous sinus.
Answer:
Cavernous Sinus
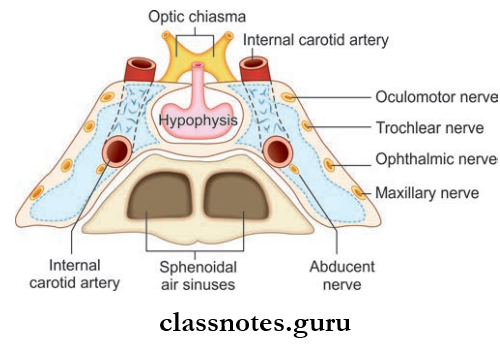
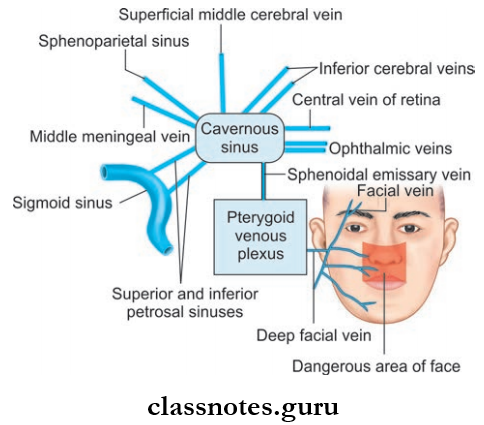
Cavernous Sinus Situation And Extent
- Situated in the middle cranial fossa along the body of the sphenoid and sella turcica
- Anteriorly, it extends up to the medial end of the superior orbital fissure and posteriorly up to apex of the petrous temporal bone
- Each sinus is divided into number of small spaces/ caverns by trabeculae
- The floor is formed by the endosteal layer, the lateral and medial wall, and roof is formed by the meningeal dura mater.
Cavernous Sinus Relations
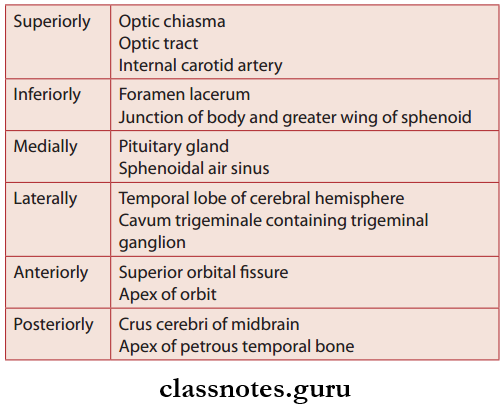
Structures Present In The Lateral Wall Of Sinus
- Oculomotor nerve
- Trochlear nerve
- Ophthalmic nerve
- Maxillary nerve
- Trigeminal ganglion
Structures Passing Through Sinus
- Internal carotid artery and sympathetic plexus of nerves
- Abducent nerve
Tributaries Of Cavernous Sinus: Receives blood from three sources—orbit, meninges and brain
- From Orbit
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Inferior ophthalmic vein
- Central vein of retina
- From Meninges
- Sphenoparietal sinus
- Anterior trunk of middle meningeal vein
- From Brain
- Superficial middle cerebral vein
- Inferior cerebral vein
Communications Of Cavernous Sinus
- Transverse sinus through superior petrosal sinus
- Internal jugular vein through inferior petrosal sinus
- Pterygoid venous plexus via emissary’s veins
- Facial vein through a superior ophthalmic vein
- Opposite cavernous sinus through anterior and posterior intercavernous sinuses
- Superior sagittal sinus through superfiial middle cerebral vein
- Internal vertebral venous plexus through basilar venous plexus.
Applied For Cavernous Sinus
- Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis – the sinus gets infected from different septic foci like:
- Meningitis, brain abscess through a superficial middle cerebral vein, inferior cerebral vein, shenoparietal sinus
- Infections of face, nose, paranasal sinus, and orbit it reaches the sinus through a superior and inferior ophthalmic vein
- Otitis media (labyrinthine veins) mastoid abscess (mastoid emissary veins) through superior and inferior petrosal sinus reach the cavernous sinus.
- Infections from the face spread in a retrograde direction via the facial vein and pterygoid plexus and cause thrombosis of cavernous sinus
- Cavernous sinus syndrome caused by various parasellar pathological conditions that involves the cavernous sinus along with cranial nerves (3,4,5,6), internal carotid artery, and sympathetic plexus
- Carotid cavernous fitula
Question 4. Write a short note on superior sagittal sinus.
Answer:
Superior Sagittal Sinus
- Located between two layers of falx cerebri
- Begins at crista galli and passes backward and deviates to the right at internal occipital protuberance to become continuous with right transverse sinus.
- The right transverse sinus becomes continuous with right sigmoid sinus.
Superior Sagittal Sinus Features
- Triangular in shape
- Drains the diploic and meningeal veins
- Arachnoid granulations project to the lumen
Superior Sagittal Sinus Tributaries
- Superior cerebral vein
- Parietal emissary vein
- Veins of frontal air sinus
- Small vein from nasal cavity
Question 5. Write a short note on sigmoid sinus.
Answer:
Sigmoid Sinus
- S-shaped sinus
- Each sinus in the direct continuation of transverse sinuses
- It grooves the inner surface of mastoid part of the petrous bone
- The terminal part curves downwards and forwards to the posterior margin of the jugular foramen through which it passes and continues as the internal jugular vein.
Sigmoid Sinus Tributaries
- Mastoid and condylar emissary veins
- Cerebellar veins
- Internal auditory veins
Question 6. Write a note on hypophysis cerebri.
Answer:
Hypophysis Cerebri
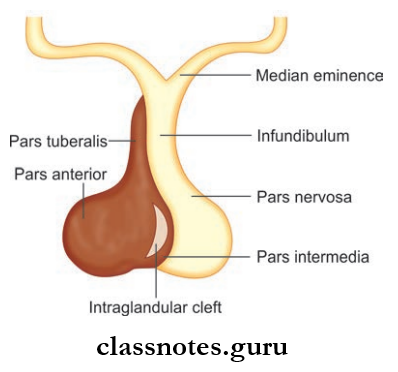
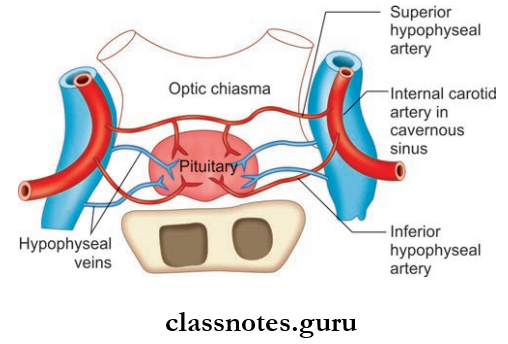
Hypophysis Cerebri Location And Extent
- It is a small oval-shaped endocrine gland situated in the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone.
- It is suspended from the floor of the third ventricle by a narrow stalk called an infundibulum.
- It measures about 8 mm anteroposteriorly and 12 mm transversely and weighs about 500 mg.
Hypophysis Cerebri Relations
- Superiorly: Optic chiasma, diaphragm a sellae
- Inferiorly: Sphenoid air sinuses, hypophyseal fossa
- Laterally: Cavernous sinus on each side
Hypophysis Cerebri Subdivisions: It is divided into adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis
- Adenohypophysis consists of
- Pars anterior
- Pars intermedius
- Pars tuberalis
- Neurohypophysis consists of
- Pars posterior
- Infundibulum
It Is Associated With The Hypothalamus Through The Following:
- Hypothalamohypophyseal tract
- Hypothalamohypophyseal portal system
Hypophysis Cerebri Blood Supply
- Arterial supply is mainly through superior and inferior hypophyseal arteries (branches of internal carotid artery)
- Venous drainage is through short veins which drain into cavernous and intercavernous sinuses.
Hypophysis Cerebri Applied
- A pituitary adenoma is the most common tumor of the pituitary gland arising from the chromophobe cells.
- Hypophysis Cerebri produces symptoms due to pressure on adjacent structures and due to endocrine disturbances.
Cranial Cavity Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. The contents of the vertebral canal include all of the following structures except:
- Spinal nerve roots
- Spinal cord
- Spinal ganglia
- Spinal meninges
Answer: 3. Spinal ganglia
Question 2. Select the incorrect statement regarding vertebral venous plexus:
- It is a network of veins in subdural space
- It receives basivertebral veins
- It drains into segmental veins
- It is continuous with intracranial dural venous sinuses
Answer: 1. It is a network of veins in subdural space
Question 3. Select the incorrect statement regarding the dural venous sinuses:
- They are lined by endothelium
- They have no valves
- They communicate with extracranial veins
- They possess thin muscular coats in their wall
Answer: 4. They possess thin muscular coat in their wall
Question 4. All of the following dural venous sinuses are paired except:
- Superior petrosal
- Inferior petrosal
- Inferior sagittal
- Cavernous
Answer: 3. Inferior sagittal
Question 5. Lateral wall of cavernous sinus contains all of the following nerves except:
- Oculomotor
- Trochlear
- Ophthalmic
- Abducent
Answer: 4. Abducent
