Behavioral Sciences Definitions
Sociology
Sociology is defined as the study of human interactions and interrelations, their conditions and Consequences
Behavioral Sciences Important Notes
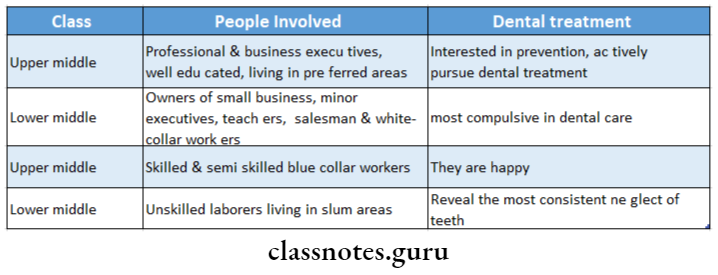
1. Social Stratification
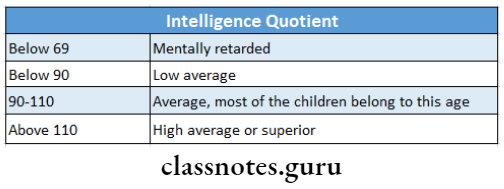
2. Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
Behavioral Sciences Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Nuclear family.
Answer:
Nuclear Family
- The nuclear family is universal in all human society
- Consists of
- Married couple and their children while they are still dependents
Read And Learn More: Percentive Communitive Dentistry Question And Answers
Question 2. Intelligence Quotient.
Answer:
Intelligence Quotient
- Obtained by
- Dividing the mental age by chronological age
- Then multiplying by 100
- IQ=( Mental age / chronological age) 100
Question 3. Sociology-definition.
Answer:
Sociology-Definition
- Sociology-definition is the science concerned with the organization/ structure of social groups
- Sociology-definition is defined as the study of human interactions and interrelations, their conditions and consequences
- Sociology-definition deals with human relationships and human behavior for a better understanding of the pattern of human life
Behavioral Sciences Viva Voce
- Learned behavior that has been socially acquired is culture.
- The term new families is implied to those under 10 years of duration.
- A family in which parents have separated or where death has occurred of either parent is a broken family.
Behavioral Sciences In Management
Behavioural Management Definitions
Reinforcement
Reinforcement means any consequences that increase the likelihood of a behavior being shown
Behavioral Management Important Notes
1. Home Technique
- Indications
- 3-6 years
- A child who can understand simple verbal commands
- Children displaying uncontrolled behavior
- Healthy children displaying uncontrolled behavior
- Contraindications
- Children under 3 years of age
- Handicapped/ immature/ frightened child
- Physical, mental, and emotional handicap.
2. Desensitization
- Desensitization is an effective method for reducing maladaptive behavior
- Desensitization is accomplished by teaching the child a competing response such as relaxation and then introducing progressively more threatening stimuli.
3. Modelling
- Modeling is based on the social learning principle allowing a patient to observe one or more models demonstrating positive behaviour in a situation
- Modelling is brought about by
- Live models
- Filmed models
- Posters
- Audiovisual aids
4. Indications Of Tell Show Do The Technique
- Children more than 3 years of age
- Fearful child
- First Visit
5. Behaviour-Shaping Techniques
- Desensitization
- Modelling
- Contingency management
Behavioral Science In Business Management
6. Physical Restraints Can Be
- Active – restraints performed by dentist or parents or staff
- Passive – with the aid of the restraining device
Behavioural Management Short Essays
Question 1. Management of children in the dental office.
Answer:
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Voice Control:
- The voice should be soft, gentle, modulated
- Management of children in the dental office is a controlled alteration of voice volume, tone, or pace to influence a patient’s behavior
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Non-Verbal Communication:
- Smiling face/ other facial expression
- Walking with the patient around
- Admiration, encouragement, friendliness
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Biofeedback: It includes EMG activity
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Coping:
- Patient differs in coping with stress associated with painful experiences
- It includes distraction/ displacement of attention
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Humour:
Humor is to elevate the mood of the child
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Relaxation:
- Reduces stress
- Reduces reaction to pain
- Reduces anxiety present
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Audio-Analgesia:
- Diverts the attention of the patient
- This reduces stress and decreases reaction to pain
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Hypnosis:
- It includes
- Flattering of closed eyelid ° Deep breathing
- Progressive sense of relaxation
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Implosion Therapy:
Refers to the picturization of animated movies
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Aversive Conditioning:
- Aversive Conditioning includes
- Physical restraints
- Use of mouth props
- Restraint of the patient by the dentist and assistant
- Physical restraints
- Home technique
Role Of Behavioral Science In Management
Management Of Children In The Dental Office Drug Therapy:
- Used when basic techniques do not work
- Management Of Children In The Dental Office Used in
- Very young children
- Very apprehensive children
- Physically handicapped children
- Mentally handicapped children
- Drugs Used
- Sedative and hypnotics
- Anti-anxiety drugs
- Narcotics
Question 2. Dental practice management.
Answer:
Practice Management In The Dental Office Setting:
- Selection of the location
- Locate where there are few dentists
- In town, surrounded by villages, near a bus stop
- In a city near the railway station, a shopping complex
- Close to government commercial offices, corporate and business houses
- Located in a place from where ladies can commute easily without fear
1. Selection Of The Building:
- Select the dental office in a new building
- Selection of the building should be well-ventilated, with a proper electrical, water, and drainage system
- Selection of the building should have a parking facility
2. Designing Of The Dental Office:
- A spacious waiting room, work area, x-ray room, laboratory, resting place, toilet, etc
- Furniture must be durable, aesthetic, and comfortable
- Placement of each electrical equipment and gadget required
- The exact position of the dental chair and unit, wash basin
- Autoclaving and sterilization done in a separate chamber
- The compressor and the generator should be kept as far away as possible
Management Of Dental Office:
- A dentist may appoint a full-time receptionist, a dental assistant
- Fair salaries and good benefits are necessary to avoid job dissatisfaction
Practice Management Patient System:
- Dentists should have good communication with their patients
- He should be aware of the timings, weekly holidays, etc
- An appointment book should be maintained
- The clinic should be open at least 30 minutes before the first appointment
- Should have proper disposal of waste
Behavioural Management Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Home technique.
Answer:
Home Technique
- Home: Hand Over Mouth Exercise
- Home technique is an accepted technique for intercepting and managing demonstrably unsuitable behaviour
Home Technique Procedure
- The dentist gently places his hand on the child’s mouth
- He then whispers in the child’s ear that if he cooperates, the hand will be removed
- Once the child cooperates complements the child for good behaviour
- Physical restraints are used only as a last resort
Behavioral Approach To Management
Question 2. Reinforcement.
Answer:
Reinforcement
Reinforcement means any consequences that increase the likelihood of a behavior being shown
Reinforcement Types:
- Primary
- Based on primary biological needs
- Example: food, clothing
- Secondary
- Involves that are not intrinsically rewarding
- Example: praise
- Positive
- It is a pleasant reinforcement
- It increases the likelihood of behavior
- Example: voice modulation, facial expression
- Negative
- It is an unpleasant event thus it can be avoided
- Example: threats of failing an examination
Question 3. Modeling in behavior management.
Answer:
Modeling In Behavior Management
Developed by Bandura in 1969
Behavior Management Requirements:
- Expended concentrated attention
- Presence of sufficient retention of desirable behavior
- Must reproduce effectively the behavior modeled
- The newly acquired behavior must be appropriately rewarded
Behavior Management Uses:
- To achieve the attention of the child
- To alleviate anxiety
- To encourage preventive care at home
- Reduces uncertainty
Behavioural Management Viva Voce
- Voice control is an effective communicative technique using sudden and firm commands to stop disruptive behavior and to get the child’s attention
- HOME and physical restraints are methods of aversive conditioning
- Behavior followed by termination of an aversive event is negative reinforcement
- The show-do technique shapes the patient’s response to procedures through desensitization
- Tell show-do technique uses verbal explanation, demonstration, and completion of the task
- Modeling is an important component of social learning theory.
Behavioral Science Theories In Management
Cultural Taboos Important Notes
1. Social Norms
- They indicate the established and approved ways of doing things, of dress, of speech, and of appearance
- They are rules that a group uses for appropriate and inappropriate values, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors
- Types: folkways, mores, and taboos
2. Folkways
They are the patterns of conventional behavior in society and norms that apply to everyday matters
3. Mores
- They are norms or lessons that express fundamental values of society
- They are derived from the established practices of society
- Some important mores are converted into laws to ensure implementations
4. Taboos
Taboos is a strong social prohibition or ban against words, objects, actions, or discussions that are considered undesirable or offensive by a group, culture, society, or community
Cultural taboos Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Taboos related to dentistry in India.
Answer:
Taboos Related To Dentistry In India
- Some taboos may lead to severe penalties while others result in embarrassment, shame and rudeness
- Taboos Related To Dentistry In India Example:
- Tooth avulsion
- Lacquering and dyeing of teeth
- Tattooing
