An Introduction To MCA – 21 And Filling In XBRL
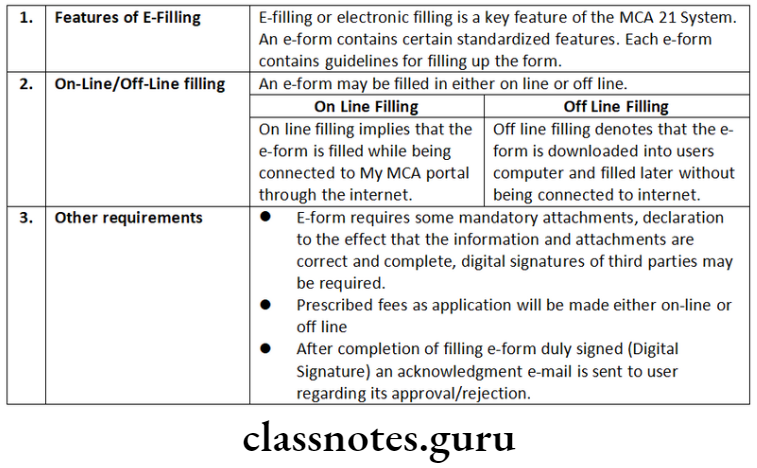
E-form
An e-form is a re-engineered conventional form, represents a document in electronic format.
Feature of E-governance
Director Identification Number (DIN), Corporate Identity Number (CIN) and Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) are the important features under e-governance mode (MCA-21).
MCA-21
MCA-21 system provides for the facility of payment of statutory fees through multiple modes i.e. (i) Off-line payment through a challan generated by the system and payment of fees at the counter of the notified bank branches through DDs/ Cash; (ii) on-line payments through Internet Banking and Credit Cards [Master Card/VISA].
SRN
Each transaction under e-filing is uniquely identified by a Service Request Number (SRN). On filing of an e-form, the system will generate and provide a Service Request Number (SRN). A user can check the status of the document/ transaction, by entering the SRN.
Stamp duty on documents
If the stamp duty on documents which are required to be filed on non-judicial stamp paper is paid electronically through Ministry of Corporate Affairs portal www.mca.gov.in, in such case, the company. shall not be required to make physical submission of such documents, in addition to their submission in the electronic form.
MCA Services
- LLP Services
- LLP Services for Business User
- E-Filing
- Company Services
- Complaints
- Document Related Services
- Fee and Payment Services
- Public Search of Trademark
- Investor Services
Corporate Identity Number(CIN)/ Foreign Company Registration Number (FCRN)
Every company is allocated a Corporate Identity Number (CIN). CIN can be found from the MCA-21 portal through search based on:
- ROC Registration No.
- Existing Company Name
- Old Name of Company (in case of change of name, user is required to enter old name and the system displays corresponding current name).
- Inactive CIN [In case of change of CIN, the user is required to enter previous (inactive) CIN Number]
Foreign Company Registration Number (FCRN)
Every foreign company has been allocated a Foreign Company Registration Number (FCRN).
Director Identification Number (DIN)
DIN is an identification number which the Central Government may allot to any individual, intending to be appointed as director or to any existing directors of a company, for the purpose of his identification
All existing and any person intending to be appointed as a director are required to obtain the Director Identification Number (DIN). DIN is also mandatory for directors of Indian Companies who are not citizens of India. However, DIN is not mandatory for directors of foreign company having branch offices in India.
Every individual, who is intending to be appointed as Director of a company or designated partner of a limited liability partnership is required to make an application electronically in Form DIR -3 to Central Government for obtaining Director Identification Number (DIN) or in case the company is being incorporated through Form SPICE, a maximum of three directors can apply for DIN. DIN is a unique, identification number and once obtained is valid for life time of a director. A single DIN is required to be obtained irrespective of the number of directorships.
Mca 21 Company Law
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
For MCA-21, the following four types of users are identified as users of Digital Signatures and are required to obtain digital signature certificate:
- MCA (Government) Employees.
- Professionals (Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, Cost Accountants, and Lawyers) who interact with MCA and companies in the context of Companies Act.
- Authorized signatories of the Company including Managing Director, Directors, Manager or Secretary.
- Representatives of Banks and Financial Institutions.
e-forms
An e-form is only a re-engineered conventional form notified and represents a document in electronic format for filing with MCA authorities through the Internet. This may be either a form filed for compliance or information purpose or an application seeking approval from the MCA. Due to technical updates, these forms updates regularly, even though their user interface may not change. User always use latest e- forms from the MCA Portal.
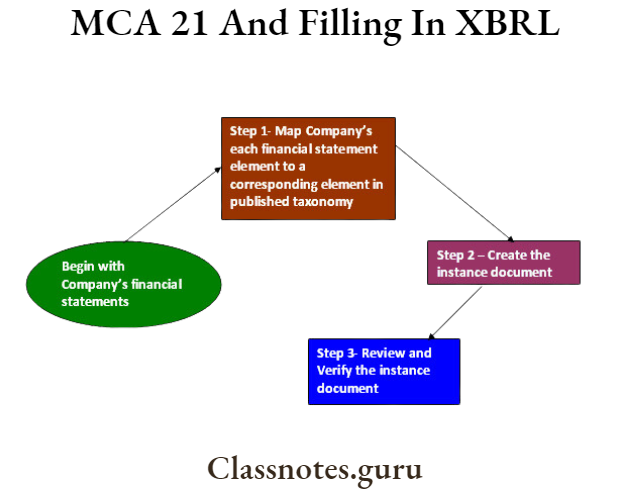
XBRL Extensive Business Reporting Language
XBRL Filing
XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language) is a language for the electronic communication of business and financial data which is revolutionizing business reporting around the world. It helps in the preparation, analysis and communication of business information. It offers cost savings, greater efficiency and improved accuracy and reliability to all those involved in supplying or using financial data.
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has mandated the following select class of companies mentioned below to file financial statements in XBRL (extensible Business Reporting Language) mode and by using the XBRL taxonomy:
- all companies listed with any Stock Exchange(s) in India and their Indian subsidiaries; or
- all companies having paid-up capital of Rupees five crore and above; or
- all companies having turnover of Rupees one hundred crore and above; or
- all companies who were required to file their financial statements for FY 2010-11, using XBRL mode.
However, the companies in banking, insurance, power sector, non-banking financial companies and housing finance companies are exempted from XBRL filing till further orders.
MCA 21 And Filling In XBRL Short Notes
Question 1. Write notes on the following:
XBRL
Answer:
Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) is a language for the electronic communication of business and financial data revolutionizing business reporting around the world. It provides major benefits in the preparation, analysis and communication of business information. It offers cost savings, greater efficiency and improved accuracy and reliability to all those involved in supplying or using financial data.
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has mandated for selected class of companies to file their Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account and other documents as required under Section 137 of Companies Act, 2013 with the Registrar of Companies in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language) mode and by using the XBRL taxonomy.
Question 2. Write notes on the following:
XBRL filing.
Answer:
The applicability of e-form AOC-4 XBRL on classes of companies has been amended.
Filing of financial statements with Registrar. The following class of companies shall file their financial statements and other documents under Section 137 of the Act with the Registrar in e-form AOC-4 XBRL as per Annexure-1:
- companies listed with stock exchanges in India and their Indian subsidiaries;
- companies having paid up capital of five crore rupees or above;
- companies having turnover of one hundred crore rupees or above;
- all companies which are required to prepare their financial statements in accordance with Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015:
Provided that the companies preparing their financial statements under the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 shall file the statements using the Taxonomy provided in Annexure-Il and companies preparing their financial statements under Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015, shall file the statements using the Taxonomy provided in Annexure-II A:
Provided further that non-banking financial companies, housing finance companies and companies engaged in the business of banking and insurance sector are exempted from filing of financial statements under these rules.
Key benefits of XBRL filing are as under:
Relevant data has tags and selective information can be fetched for specific purposes by various government and regulatory agencies.
It is in conformity with Global Reporting Standards, which helps in improved data mining and relevant information search.
Question 3. Write notes on the following:
Keeping documents, records, registers, minutes, etc., of the company in electronic form
Answer:
According to Section 120, the documents, records, registers, minutes etc. may be kept and inspected in electronic form.
Rule 27 of Companies (Management and Administration) Rules, 2014 initially mandated every listed company or a company having not less than one thousand shareholders, debenture holders and other security holders may maintain its records, as required to be maintained under the Act or Rules made thereunder in electronic form.
According to Rule 27(2) the records in electronic form shall be maintained in such manner as the Board of Directors of the company may think fit, provided that:
- the records are maintained in the same formats and in accordance with all other requirements as provided in the Act or the rules made thereunder;
- the information as required under the provisions of the Act or the rules made thereunder should be adequately recorded for future reference;
- the records must be capable of being readable, retrievable and reproducible in printed form;
- the records are capable of being dated and signed digitally wherever it is required under the provisions of the Act or the rules made thereunder;
- the records, once dated and signed digitally shall not be capable of being edited or altered:
- the records shall be capable of being updated, according to the provisions of the Act.or the rules made thereunder and the date of DISTINGUISH BETWEEN updating shall be capable of being recorded on every updating. Space to write important points for revision
Question 4. Write notes on the following:
Pre-certification of e-forms
Answer:
Pre-certification of e-forms
Apart from authentication of e-forms by authorized signatories using digital signatures, certain e-forms are also required to be pre-certified by practicing professionals who are members of professional bodies namely ICAI, ICSI or ICWAI with the responsibility of ensuring correctness, completeness and integrity of documents filed by them with MCA in electronic mode including filing of financial statements in XBRL mode. Pre-certification is not required in the case of one person companies and small companies.
Once an e-form has been pre-certified by a professional towards its authenticity based on the particulars contained in the books of accounts and records of the company, MCA21 system takes that e-form on file by way of straight through process. Professionals are responsible for certifying documents through digital signature and the system would accept the documents online without approval by ROC.
This process of taking the forms on record by way of straight through process requires professionals to be extra cautious and vigilant towards the information, he/she certifies in the forms. If a professional certifies incorrect information or omits any material information, which later on proves that the same was done knowingly, he/she will be liable for the punishment under Section 448 read with Section 447 of the Companies Act, 2013, besides disciplinary action by the respective Institute, which issued the certificate of practice to the professionals.
Xbrl Filing Process
MCA 21 And Filling In XBRL Distinguish Between
Question 1. Distinguish between the following:
‘Pre-scrutiny’ and ‘check form’.
Answer:

Question 2. Distinguish between the following:
‘Informational services’ and ‘approval services (Registrar of Companies)’ for categories of e-forms.
Answer:
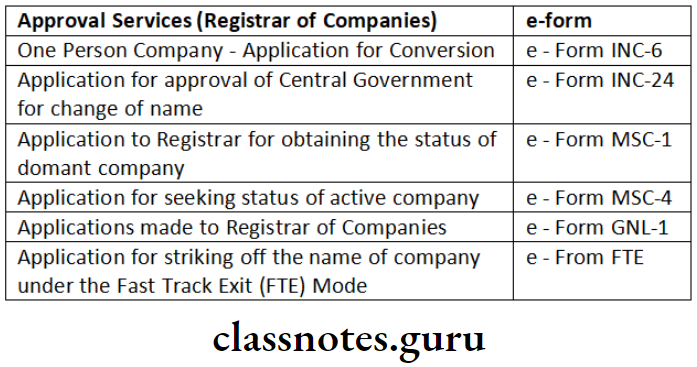
Informational Services:
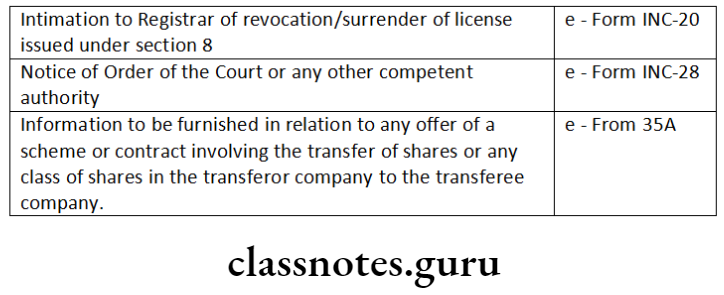
Question 3. Distinguish between the following:
XBRL tags and XBRL taxonomies.
Answer:
In XBRL, information is not treated as a static block of text or set of numbers. Instead, information is broken down into unique items of data (e.g. total liabilities = 100). These data items are then assigned mark-up tags that make them computer-readable. For example, the tag<Liabilities>100</Liabilities> enables a computer to understand that the item is liabilities, and it has a value of 100.
Computers can treat information that has been tagged using XBRL ‘intelligently’; they can recognize, process, store, exchange and analyze it automatically using software.
Because XBRL tags are formed in a universally-accepted way, they can be read and processed by any computer that has XBRL software XBRL tags are defined and organized using categorization schemes called taxonomies.
XBRL Taxonomies:
Different countries use different accounting standards. Reporting under each standard reflects differing definitions. The XBRL language uses different dictionaries, known as ‘taxonomies’, to define the specific tags used for each standard. Different dictionaries may be defined for different purposes and types of reporting.
Taxonomies are the computer-readable ‘dictionaries’ of XBRL. Taxonomies provide definitions for XBRL tags, they provide information about the tags, and they organize the tags so that they have a meaningful structure.
As a result, taxonomies enable computers with XBRL software to:
- understand what the tag is (e.g. whether it is a monetary item, a percentage or text);
- In tagging Section, “N” refers to navigation, “A” refers to attaching the disclosures “T” refers to text entry etc.
- what characteristics the tag has (e.g. if it has a negative value);
- its relationship to other items (e.g. if it is part of a calculation).
Taxonomies differ according to reporting purposes, the type of information being reported and reporting presentation requirements.
MCA 21 And Filling In XBRL Descriptive Questions
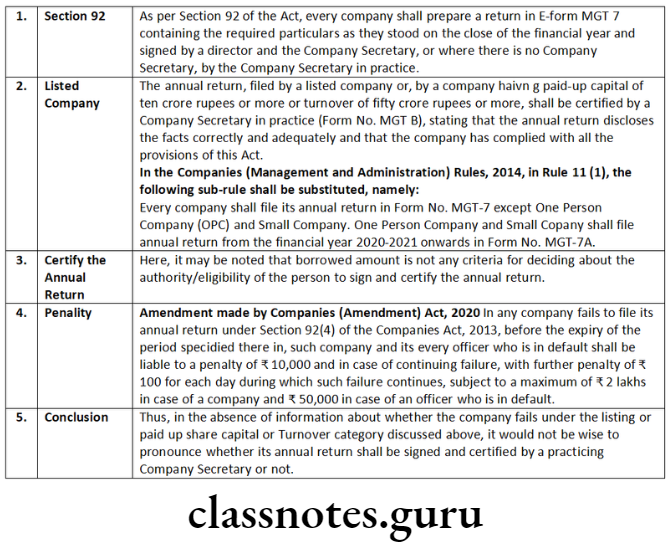
Question 1. In relation to e-form CRA-2, state the:
- Reasons for filing this form
- Particulars required to be filled in the form
- Documents required to be enclosed with the form
- Person who is to sign and certify the form.
Answer:
- Reasons for filling this form
- This is a form of application to the Central Government for appointment of cost auditor.
- Particulars required to be filled in the form
- Corporate Identity Number (CIN) or Foreign Company Registration Number (FCRN) of the company;
- Name of the company;
- Category of cost audit order;
- Details of the cost auditor proposed to be appointed;
- Proposed remuneration of the cost auditor; and
- Date of Board Meeting of Directors proposing the name of the cost auditor.
- Documents required to be enclosed with the form
- Copy of the board resolution of the company sanctioning the proposal for which the Government approval has been sought.
- Copy of the certificate obtained from cost auditor.
- Person who is to sign and certify the form
- The form is required to be digitally signed by Managing Director or Director or Manager or Secretary of the company (in case of Indian Company) or an authorized representative (in case of a Foreign Company).
Question 2. Who are the persons required/obliged to use digital signature for filing/certifying e-forms?
Answer:
Digital signature certificate is essential for every users who is required to sign in e-form for submission with MCA. For MCA – 21 there are four types of users that is given below are identifies as user of digital signature and are. required to obtain digital signature certificate:
- MCA (Government) Employee.
- Professional (Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, Cost Accountants).
- Authorised signatories of the company including managing director, directors, manager or secretary.
- Representatives of Banks and Financial Institutions.
Question 3. When a Director Identification Number (DIN) application is rejected by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs portal, does the applicant necessarily need to apply for a fresh DIN? Discuss.
Is online viewing of public documents of a company open to any member of the public? How one (who is eligible) can view online public documents of a company? Is a copy of a public document available to the public? Give two examples of company documents filed online with the Registrar of Companies.
Answer:
- Common causes of Rejection for Director Identification Number (DIN)
- The applicant details are not as per the PAN.
- The particulars filed in form DIR 3 do not match with the details given in the supporting documents submitted along with DIN application.
- Residence proof like :
- Bank statement
- Electricity bill
- Telephone bill
- Utility bill etc.
Submitted are older than 2 months of submitting the application for verification.
- The supporting document are not duly attested that is:
- Name
- Designation
- Membership
- Practicing certificate number etc. are not clearly indicated
- Passport/Driving License/Identity proofs etc. attached are expired only such documents which are currently valid should be attached..
Viewing public documents is open to any member of public because the very term ‘public document’ means a document to which a member of public has access. There is no issue on eligibility to view public document. Any member of public or citizen can access MCA portal for viewing public documents of any company registered with ROC.
The feature of viewing is available after login. One who wishes to view will select the company concerned after login. Then the documents under each category will come on the screen. Contents of the documents can be seen only after payment of requisite fee. Once payment is made the person can view the documents during the next 7 days and once the view is started then it is available for a maximum of 3 hours.
The documents can be viewed from anywhere i.e. from any online facility available without visiting Registrar of Companies’ office, using the ‘My documents’ tab available after logging into the portal. Apart from viewing public documents, a person can also obtain certified copies of documents of payment. In this regard, an application is to be made to the concerned ROC within whose jurisdiction the company’s registered office is situated. Examples of public documents are:
Documents relating to incorporation of a company
Annual returns and balance sheets
Note: Examples of public documents are given below:
- Documents relating to incorporation of company.
- Annual returns and financial statement. Space to write important points for revision
Mca 21 And Xbrl Questions
Question 4. What is the general structure of e-filing process under MCA-21?
Answer:
Question 5. “XBRL offers major benefits at all stages of business reporting and analysis”. Discuss.
Answer:
Benefits of XBRL
XBRL offers major benefits at all stages of business XBRL reporting and analysis. The benefits are seen in automation, cost saving, faster, more reliable and more accurate handling of data, improved analysis and in better quality of information and decision- making.
- It saves costs and improves efficiency in handling business and financial information.
- It is extensible and flexible which can adapt any changes according to the requirements.
- It enables producers and consumers of financial data to switch resources away from costly manual processes, typically involving time-consuming comparison, assembly and re-entry of data.
- The users of financial data are able to make more effort on analysis.
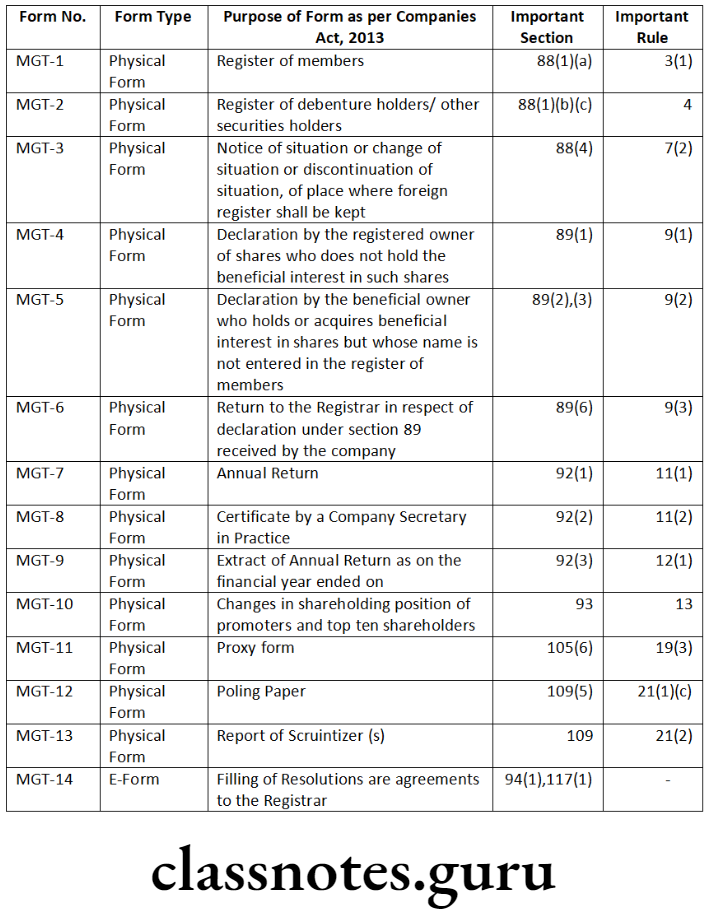
Question 6. List out the resolutions which require filing of e- Form MGT-14 with the Registrar of Companies.
Answer:
Section 117 of the Companies Act, 2013 provides that a copy of every resolution and an agreement in respect of matters specified therein together with a explanatory statement shall be filed in Form No. MGT-14 with the Registrar within thirty days of its passing.
Resolutions and agreements to be filed with the Registrar are as under:
- special resolutions;
- resolutions which have been agreed to by all, the members of a company, but which if not so agreed to, would not have been effective for their purpose unless they had been passed as special resolutions;
- any resolution of the Board of Directors of a company or agreement executed by a company, relating to the appointment, re-appointment or renewal of the appointment or variation of the terms of appointment, of a managing director;
- resolutions or agreements which have been agreed to by any class of members but which, if not so agreed to, would not have been effective for their purpose unless they had been passed by a specified majority or otherwise in some particular manner and all resolutions or agreements which effectively bind such class of members though not agreed to by all those members;
- resolutions passed by a company according consent to be exercised by its Board of Directors of any of the powers under clause (a) and clause (c) of Sub-Section (1) of Section 180;
- resolutions requiring a company to be wound up voluntarily passed in pursuance of Section 304;
- resolutions passed in pursuance of Sub-Section (3) of Section 179, and
- any other resolution or agreement as may be prescribed and placed in the public domain.
Question 7. “The e-forms are required to be authenticated by the authorised signatories using digital signatures.” With reference to e-filing of documents with the Registrar of Companies, identify the users of digital signature who are required to obtain Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and enlist the requirements of obtaining DSC in the case of foreign directors.
Answer.
The following four types of users are identified as users of Digital Signatures and are required to obtain digital signature certificate:
- MCA (Government) Employees.
- Professionals (Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, Cost Accountants and Lawyers) who interact with MCA and companies in the context of Companies Act.
- Authorized signatories of the Company including Managing Director, Directors, Manager or Secretary.
- Representatives of Banks and Financial Institutions.
Requirements for obtaining DSC in case of foreign directors: Foreign directors are required to obtain Digital Signature Certificate from an Indian Certifying Authority (List of Certifying Authorities is available on the MCA portal). The process of registration of DSC is same as applicable to others.
In case of Foreign Director, the DSC application is to be made to one of the Indian Certifying Authorities which is licensed u/s 24 of the Information Technology Act, 2000 and mentioned in the list available on the MCA portal. The said application should be duly filled by such applicant with the relevant enclosures.
Such DSC application then to be physically submitted with the necessary documents. Further, the said documents be attested and notarized by the Notary Public by the Foreign Ambassador/Diplomatic. In this manner, the Foreign Director can obtain the DSC from C.A. on the successful verification of the Application along with the documents and information.
Question 8. CIN, issued by MCA, the unique identifier, provides the key profile of companies – Explain.
Answer:
Every company incorporated on or after Nov 1, 2000 is allotted a 21.digit Corporate Identity Number (CIN) by the ROC, which indicates the listing status, economic activity (industry), State, Year of incorporation, ownership and sequential number assigned by the ROC. This number is to be quoted in all e-forms and once the number is typed, MCA site automatically pre-fills the essential particulars.
CIN is structured as under to indicate the profile of the company:
1st digit Listing Status
Next 5 digits: Economic activity (industry to which the company belongs) Next 2 digits: State in which Company is registered
Next 4 digits: Year of incorporation
Next 3 digits: Ownership
Next 6 digits: Sequential number assigned by the ROC (Registration Number)
CIN can also be searched in MCA site based on ROC registration number, existing company name or old name, if any. Keeping in view the said specifications, CIN can be considered the unique identifier.
Cs Company Law Mca 21
Question 9. Filing of financial statements in XBRL mode and by using XBRL taxonomy is mandatory to certain companies. Discuss, referring to the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
Answer:
As per Rule 3 of the Companies (Filling of Documents and Forms in Extensive Business Reporting Language) Rules, 2018 mandates the following select class of companies mentioned below to file financial statements in XBRL (extensible Business Reporting Language) mode and by using the XBRL taxonomy:
- All companies listed with any Stock Exchange(s) in India and their Indian subsidiaries; or
- All companies having paid-up capital of Rupees five crore and above; or
- All companies having turnover of Rupees one hundred crore and above; or
- All companies who were required to file their financial statements for F.Y. 2010-11, using XBRL mode.
But, the companies in banking, insurance, power sector, non-banking financial companies and housing finance companies are exempted from XBRL filing till further orders.
Question 10. Shalini, practicing Company Secretary, has disclosed information acquired in the course of her professional engagement to a person other than the client, without the consent of such client. Can she do so? Can she retain the digital signature of her client for uploading e-forms on MCA portal?
Answer:
Clause 1 of Part I of Second Schedule to the Company Secretaries Act, 1980 provides that a Company Secretary in Practice shall be deemed to be guilty of professional misconduct, if he discloses information acquired in the course of his professional engagement to any person other than the client so engaging him, without the consent of such client, or otherwise than as required by any law for the time being in force. This clause indicates the position of trust and confidence reposed by the client in a Company Secretary in practice. Therefore, Shalini is guilty under the above mentioned clause.
It is suggested that Shalini may retain digital signature of client after obtaining a formal letter signed by his client authorising PCS to make use of his Digital signature..
Question 11. Who are all the persons required to obtain Digital Signature Certificates?
Answer:
The e-forms are required to be authenticated by the authorized signatories using Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) as defined under the Information Technology Act, 2000. A digital signature is the electronic signature duly issued by a certifying authority that shows the authority of the person signing the same.
It is an electronic equivalent of a written signature. Every user who is required to sign an e-form for submission with MCA is required to obtain a Digital Signature Certificate. For MCA-21, the following four types of users are identified as users of Digital Signatures and are required to obtain digital signature certificate:
- MCA (Government) Employees.
- Professionals (Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, Cost Accountants and Lawyers) who interact with MCA and companies in the context of Companies Act.
- Authorized signatories of the Company including Managing Director, Directors, Manager or Secretary.
- Representatives of Banks and Financial Institutions.
All companies (Public Company, Private Company, Company not having share capital, Company limited by share or guarantee, Unlimited Company) must comply with this requirement of registration of DSC by the director, manager and secretary. Foreign directors are required to obtain Digital Signature Certificate from an Indian Certifying Authority (List of Certifying Authorities is available on the MCA portal). The process of registration of DSC is same as applicable to others.
Xbrl Filing In Companies Act
Question 12. Every company is required to get pre-scrutiny and pre- certification of e-forms by a practising professional before filing with the Registrar of Companies (ROC). Is this true? Explain the relevant legal provisions.
Answer:
Pre-Scrutiny: Pre-scrutiny is a functionality that is used checking whether certain core aspects are properly filled in the e-form. It can be done by the company itself and no professional is required. Pre scrutiny function is available for all forms and is to be done by all class of companies.
Pre-Certification: Apart from authentication of e-forms by authorized signatories using digital signatures, some e-forms are also required to be pre-certified by practicing professionals. Pre-certification means certification of correctness of any document by a professional before the same is filed with the Registrar of Companies. E-forms mentioned in Rule 8(12) of the Companies (Registration Offices and Fees) Rules, 2014 such as INC-22, AOC-4, MGT-14, DIR-12 etc., are required to be pre-certified by Company Secretaries or Chartered Accountants or Cost Accountants who are in whole-time practice by all class of companies except One Person Company and Small Companies.
Consequently, every company is required to do pre-scrutiny of e-forms but pre-certification of certain forms is not mandatory for every class of company. Space to write important points for revision
Question 13. Assistant Company Secretary of JKL Ltd. has made excess payment of 1 lakh to MCA for filing of e-forms. What is the procedure of refund of MCA-21 fees?
Answer:
In order to claim refund of multiple payments or incorrect payment or excess payment of MCA-21 fees, while using MCA services, following procedure is required to be followed:
- The Person is required to file the ‘Refund Form’ available on MCA21 portal for claiming refund.
- The refund of MCA21 fees is available in the following cases:
- Multiple Payments This includes cases where service seeker does multiple filings such as in e-Form No. SH-7 and makes payments more than once (multiple times) for the same service. Although, refund shall not be allowed in respect of approved e-Forms.
- Incorrect Payments This includes cases where the service seeker has made payment in respect of an e-Form or Stamp duty through an incorrect option under Pay miscellaneous fee facility.
- Excess Payments- This includes cases where any excess fee has been paid by the service seeker due to some incorrect data entered in the e-Form or incorrect data in MCA-21 system due to migration of data from legacy system.
- The refund form is to be filed within the stipulated time period. Also, there shall be deduction in the amount to be refunded based on time period within which refund e-form is filed. Space to write important points for revision-
MCA 21 And Filling In XBRL Practical Questions
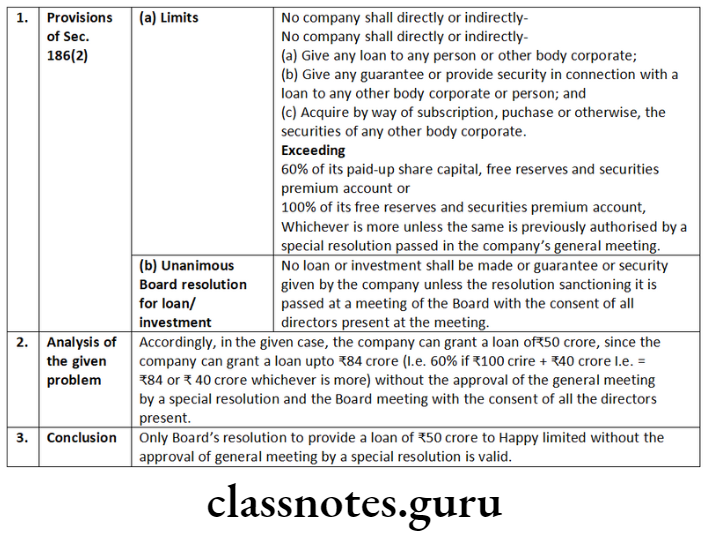
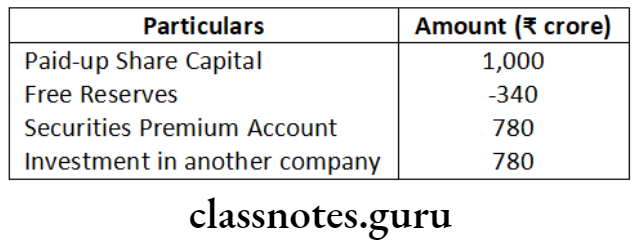
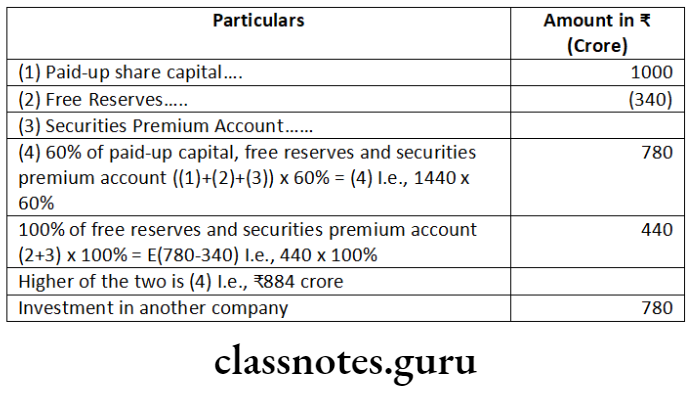
Question 1. Prudent General Insurance Company Ltd. is engaged in the general insurance business. The company is not listed in any stock exchange in India but is a subsidiary of Reliable General Insurance Company Ltd., listed at Bombay Stock Exchange. The turnover of Prudent General Insurance Company Ltd. is 330 crore. Examining the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013, state whether the company is required to file XBRL enabled balance sheet.
Answer:

Question 2. In relation to filing of financial statements of a company in XBRL mode and by using the XBRL taxonomy, decide whether the following companies are required to file the financial statements in the said mode:
- Grand Ltd., the subsidiary company of Tiny Ltd. which is listed at Kolkata Stock Exchange.
- Prime Ltd., a company which has paid-up share capital of 100 crore.
- Crafty Ltd., a company which has a turnover of 400 crore.
- Comfort Ltd., a non-banking financial company.
Answer:
XBRL Filing: The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has mandated the following select class of companies mentioned below to file financial statements in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language) mode and by using the XBRL taxonomy:
- all companies listed with any Stock Exchange(s) in India and their Indian subsidiaries; or
- all companies having paid-up share capital of rupees five crore and above; or
- all companies having turnover of rupees one hundred crore and above; or
- all companies who were required to file their financial statements for F.Y. 2010-11; using XBRL mode.
However, banking companies, insurance companies, power companies and Non-Banking Financial Companies are exempted from XBRL filing till further orders.
- Yes, Company is required to file financial statements through XBRL mode.
- Yes, Company is required to file financial statements through XBRL mode.
- Since in this case the turnover is more than 100 crore, the company is required to file the financial statements through XBRL mode.
- This company is exempted from filing the financial statements through XBRL mode.
How To File Xbrl With Mca
Question 3. ABC Ltd. has not satisfied any conditions specified as per section 137 of the Companies Act for current financial year.. The company has filed financial statement as per XBRL Taxanomy for the previous financial year. Is ABC Ltd. still required to file financial statements as per XBRL. Taxanomy for the current financial year?
Answer:
Rule 3 of the Companies (Filing of Documents and Forms in XBRL) Rules, 2015
- The following class of companies shall file their financial statements and other documents under section 137 of the Act with the Registrar in e-Form AOC-4 XBRL:
- companies listed with stock exchanges in India and their Indian subsidiaries
- companies having paid up capital of five crore rupees or above;
- companies having turnover of one hundred crore rupees or above;
- all companies which are required to prepare their financial statements in accordance with Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015.
- Provided that the Companies preparing their financial statements under the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2006 shall file the statements using the Taxonomy provided in Annexure-Il and companies preparing their financial statements under Companies (Indian Accounting Standards) Rules, 2015, shall file the statements using the Taxonomy provided in Annexure-II A of the Companies (Filing of Documents and Forms in XBRL) Rules, 2015
- Further non-banking financial companies, housing finance companies and companies engaged in the business of banking and insurance sector are exempted from filing of financial statements under these rules.
- The companies which have filed their financial statements under sub-rule (1) of Rule 3 of XBRL Rules, shall continue to file their financial statements and other documents though they may not fall under the class of companies specified therein in succeeding years. The companies which have filed their financial statements under the erstwhile rules, namely the Companies (Filing of Documents and Forms in Extensible Business Reporting Language) Rules, 2011, shall continue to file their financial statements and other documents as prescribed in Rule 3(1) of XBRL Rules though they do not fall under the class of companies specified therein.
Therefore, as per the above provisions ABC Ltd. though has not satisfied any conditions specified as per Section 137 of the Companies Act, 2013 for current financial year, yet the company is required to file financial statements as per XBRL Taxonomy for the current financial year as it has filed the financial statements as per XBRL Taxonomy for the previous financial year.