Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Definitions
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment
Atraumatic restorative is a procedure based on removing carious tooth tissues using hand instruments alone and restoring the cavity with an adhesive restorative material.
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Short Essays
Question 1. Atraumatic restorative treatment.
Answer:
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment
Atraumatic restorative treatment is a procedure based on removing carious tooth tissues using hand instruments alone and restoring the cavity with an adhesive restorative material
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Principles:
- Removing carious tooth tissues using hand instruments
- Restoring the cavity with a restorative material that sticks to the tooth
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Indication:
- Only in small cavities
- Accessible cavities
- Public health programs
Read And Learn More: Percentive Communitive Dentistry Question And Answers
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Contra-Indications:
- Presence of swelling or fistula
- Exposed pulp
- Painful teeth with chronic inflammation of pulp ‘
- Carious cavity with inaccessible area
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Advantages:
- Requires minimal cavity preparation
- Painless technique
- Simplifies infection control
- No electrical driven & expensive dental equipment required
- Simple
- Cost-effective
- Friendly procedure
- Accessible for all population groups
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Notes
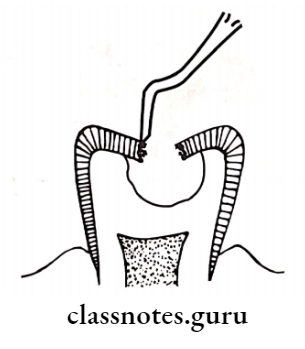
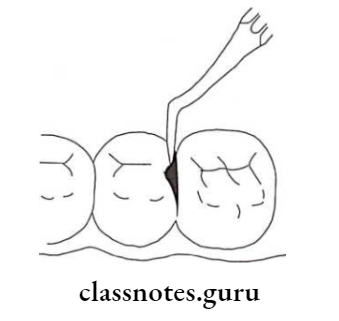
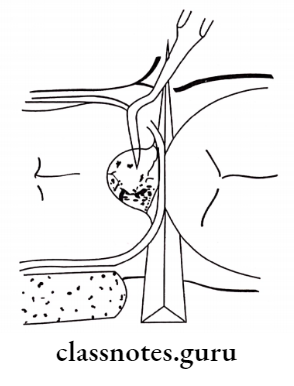
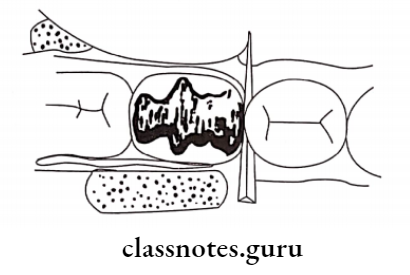
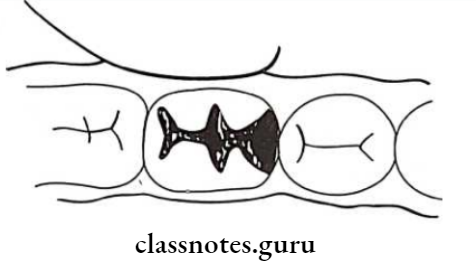
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Procedure:
- Place cotton rolls alongside the tooth to be treated
- Remove plaque wet cotton pellet
- Diy the surface with a dry pellet
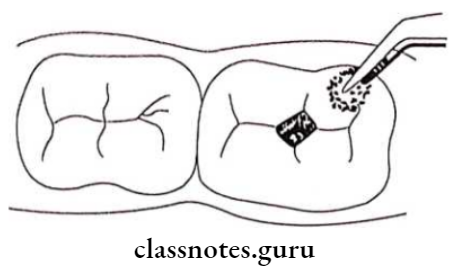
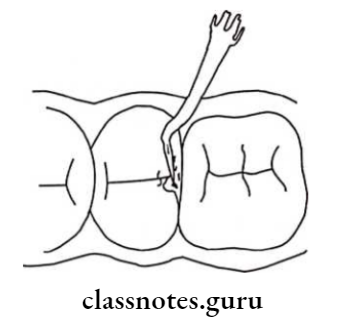
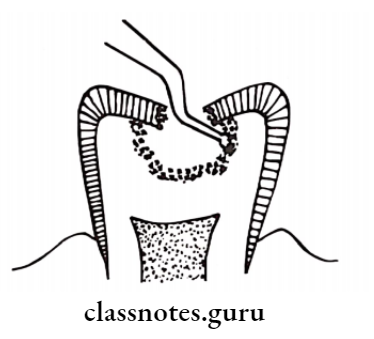
- Caries is removed by dental hatchet
- Next, the cavity is cleaned with wet cotton pellets
- Conditioning the cavity with dentin conditioner
- Mixing of GIC
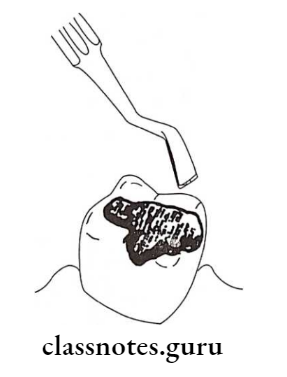
- Restoring the cavity
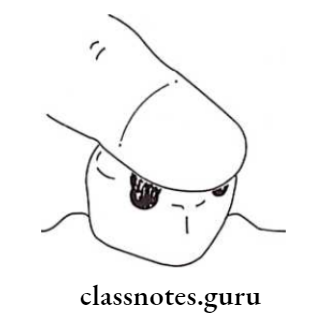
- Rub a small amount of petroleum jelly and press firmly
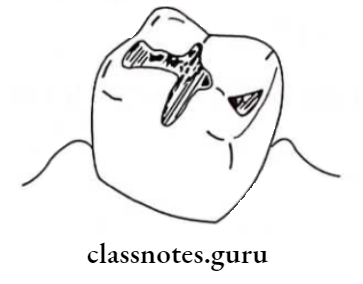
- Remove excess material
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Steps
Atraumatic Restorative Treatment Viva Voce
- Atraumatic restorative treatment [ART) follows the principle of removing carious tooth tissue using a hand instrument only
- ART was a theme of World Health Day in 1992
- ART can be employed when a community cannot afford expensive dental equipment
- ART was pioneered in the 1980s in Tanzania by Joe, Faencken, and Holmgren
- ART can be employed when there is a clear occlusal cavity
- ART is absolutely contraindicated in the presence of swelling or fistula near the carious tooth
- GIC bonding in ART is a chemical
- Control of saliva is an important aspect of the success of ART
- A small spoon excavator is used to clean the enamel dentin junction
- A dental hatchet is used to widen the entrance to the cavity by removing unsupported enamel
- Petroleum jelly is used to keep moisture away from GIC in ART
- A plastic strip is used to contour the proximal surface of multiple surface restoration in ART
- Poor adhesion is the result of over-mixing of GC material.