Oral Medicine Drugs Short Essays
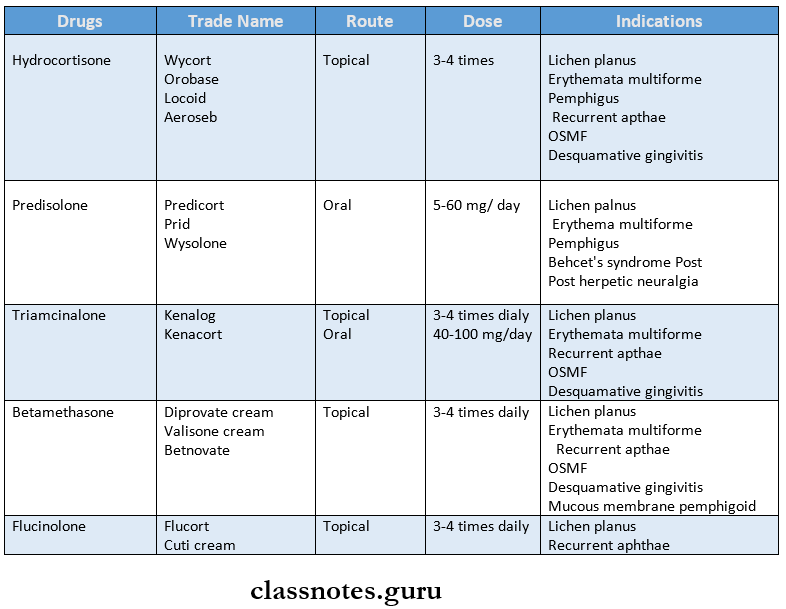
Question 1. Steroids in density. (or) steroids.
Answer:
Steroids In Density
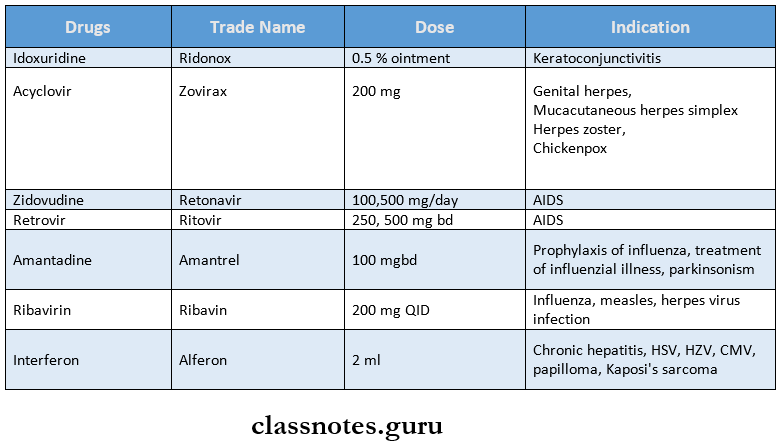
Question 2. Antiviral drugs, (or) Mention four anti-viral drugs.
Answer:
Antiviral Drugs
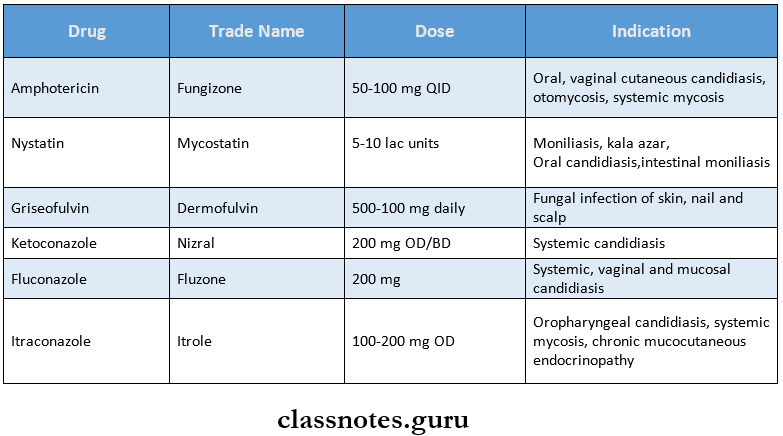
Question 3. Antifungal drugs.
Answer:
Antifungal Drugs
Question 4. Classification uses and adverse effects of Oral Penicillins.
Answer:
Oral Penicillins Classification:
- Natural
- Penicillin G
- Semi-Synthetic
- Acid resistant: Penicillin V
- Penicillinase resistant: Methicillin, Oxacillin
- Aminopenicillin: Ampicillin, Bacampicillin
- Antipsuedomonal penicillin:
- Carboxypenicillin: carbenicillin
- Ureidopenicillin: Azlocillin, Mazlocillin
Read And Learn More: Oral Medicine Question and Answers
Oral Penicillins Uses:
- Orodental Infection:
- It is effective against a variety of aerobic and anaerobic infections
- For pneumonia, meningitis, and osteomyelitis. Penicillin G is the drug of choice
- Periodontal abscess response to Penicillin G
- Penicillin G is the drug of choice for actinomycosis
- Penicillin G is the drug of choice for anthrax, trench mouth
- Benzathine penicillin is used as a prophylactic antibiotic
Oral Penicillins Adverse Effects:
- Hypersensitivity reactions:
- Manifestations range from skin rashes, urticaria, fever, bronchospasm, serum sickness and rarely exfoliative dermatitis, and anaphylaxis
- Large doses of penicillin may produce confusion, muscle twitchings, convulsions, and coma
- Suprainfections are rare due to their narrow spectrum of activity
- Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction:
- When penicillin is injected in a patient with syphilis, there is sudden destruction of spirochaetes and release of its lytic products
- This triggers a reaction with fever, myalgia, shivering, exacerbation of syphilitic lesions, and vascular collapse.
Question 5. Indications and Contraindication of Corticosteroids.
Answer:
Corticosteroids Indications:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: in progressive disease, steroids are given along with NSAIDs
- Osteoarthritis: it is given intra, particularly with a minimum of 3-month intervals between two injections of steroids into the joints
- Allergic diseases: steroids are given in cases with angioneurotic edema, hay fever
- Bronchial asthma: acute exacerbations of asthma are treated with prednisolone
- Collagen diseases: glucocorticoids are the first line of drugs
- Eye diseases: allergic conjunctivitis is treated with steroid eye drops
- Renal diseases: steroids are the first line of drug
- Skin diseases: systemic steroids are life-saving in pemphigus
- Liver diseases: steroids are useful in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis
- Large doses of dexamethasone reduce cerebral edema
- Steroids are useful in the treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia
Corticosteroids Contraindications:
- Peptic ulcer
- Hypertension
- Infections
- Diabetes mellitus
- Ocular infections
- Osteoporosis
- Psychoses
- Epilepsy
- CCF
- Glaucoma
- Renal failure
Oral Medicine Drugs Short Answers
Question 1. Acyclovir.
Answer:
Acyclovir
- Acyclovir is effective against herpes simplex virus, Varicella Zoster virus, and Epstein Barr virus
Acyclovir Mechanism:
- Acyclovir is taken up by the various infected cells
- Acyclovir is converted to acyclovir triphosphate
- This inhibits viral DNA synthesis by inhibiting viral; DNA polymerases and causing DNA chain termination
Acyclovir Adverse Effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Rashes
- Burning and itching
- It may cause renal and neurotoxicity
Acyclovir Uses:
- Herpes simplex virus infections
- Diseases of the mouth, face, skin, esophagus, and brain
- It is effective against primary and recurrent genital and labial herpes
- Acyclovir eye drops are effective against HSV kerato-conjunctivitis
- Herpes zoster
- Acyclovir shortens the duration of illness
- Chickenpox
- Acyclovir reduces the duration and severity of illness
Question 2. Diclofenac sodium.
Answer:
Diclofenac Sodium
- Diclofenac Sodium is an analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory agent
- Its tissue penetrability is good
- Diclofenac Sodium attains good concentration in synovial fluid
- Adverse effects are mild
Diclofenac Sodium Dose:
- 50 minds/ tds
- The gel is available for topical application
Diclofenac Sodium Uses:
- Treatment of chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis
- Acute musculoskeletal pain, painful dental lesions
- Postoperatively for relief of pain and inflammation
Question 3. NSAIDs
Answer:
NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are aspirin-type or non-opioid analgesics
NSAIDs Classification:
1. Nonselective COX Inhibitors
- Salicylic acid derivatives
- Aspirin, sodium salicylate, diflunisal
- Para-aminophenol derivatives
- Paracetamol
- Pyrazolone derivative
- Phenylbutazone, azapropazone
- Indole acetic acid derivative
- Indomethacin. etodolac
- Aryl acetic acid derivative
- Diclofenac, aciclofenac, ketorolac
- Propionic acid derivative
- Ibuprofen, carprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen
- Anthranilic acids
- Plufenamic acid, mefanamic acid
- Oxicams
- Piroxicam tenoxicam
- Alkanones
- Nabumetone
2. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors
- Nimesulide, celecoxib, rofecoxib
Mechanism Of Action:
- NSAIDs inhibit the prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme cyclo-oxygenase
Question 4. Anti-oxidants.
Answer:
Anti-oxidants
- Antioxidants a molecules capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules
Anti-oxidants Uses:
- Inhibit oxidation reactions
- Used as an ingredient in dietary supplements
- Prevents cancer, coronary heart disease
- Industrial use as preservatives in food and cosmetics
- Prevents degradation of rubber and gasoline
Anti-oxidants Agents:
- Thiols
- Ascorbic acid
- Polyphenols
- Glutathione
- Superoxide dismutase
Question 5. Analgesics for pulpal pain
Answer:
Analgesics For Pulpal Pain
- Analgesics used for pulpal pain are
1. Opioids
- They have short half-lives
- Require repeated dosing
- Side effects are dose-dependent
- Have high abuse potential
- Ex: Morphine
2. NSAIDs- Like celecoxib, diclofenac, ibuprufen, naproxen
- Act by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase enzyme responsible for the formation of prostaglandin that promotes pain and inflammation
- It is used along with acetaminophen- Ibuprufen 600 mg plus acetaminophen 1000 mg administered every 6 hours for 24 hours is effective
Question 6. Clindamycin
Answer:
Clindamycin
- Clindamycin is a congener of lincomycin
- Bonds to 50S ribosomal subunit
Clindamycin Actions:
- Suppresses protein synthesis
- Inhibits streptococci, staphylococci, and pneumococci, and anaerobes
Clindamycin Uses:
- Anaerobic infections
- Streptococcal and staphylococcal infections
- P.jiroveci infection
- T.gondii
- Prophylaxis in valvular heart disease patients
Clindamycin Adverse effects:
- Diarrhea
- Skin rashes
- Neuromuscular blockade
- Intravenous administration causes thrombophlebitis
Oral Medicine Drugs Viva Voce
- The required adult dose of acyclovir in severe herpes zoster is 800 mg 5 times daily
- The use of corticosteroids is contraindicated in primary herpes
- Atropine used in peptic ulcer may lead to Xerostomia
- Isoniazid hydrochloride may induce hepatitis
- Azathioprine can produce stomatitis and Xerostomia
- Pilocarpine and cevemeline are contraindicated in patients with pulmonary disease
- The required adult dose of acyclovir in severe herpes zoster is 800 mg 5 times daily
- The use of corticosteroids is contraindicated in primary herpes
- Atropine used in peptic ulcer may lead to Xerostomia
- Isoniazid hydrochloride may induce hepatitis
- Azathioprine can produce stomatitis and Xerostomia
- Pilocarpine and cevemeline are contraindicated in patients with pulmonary disease
