Acute Poisoning And Environmental Emergencies Important Notes
Different Poisoning
Fluorosis
- Dental fluorosis is caused by excessive intake of fluoride during tooth development
- Features:
- Dental Fluorosis
- Mottled enamel
- Presence of hypoplastic areas
- Mottled areas may stain yellow/ brown
- Fluoride occurs symmetrically within dental areas, commonly affecting premolars
- Skeletal Fluorosis
- Severe pain in
- Backbones
- Joints
- Hips
- Severe pain in
- Stiffness in joints and spine
- Knock-knee syndrome
- Outward bending of legs and hands
- Damage to fetus
- Blocking and calcification of blood vessels
- Cripping fluorosis
- Effect On Kidney
- May aggravate renal disease
Acute poisoning viva questions
Management of Acute Poisoning
Acute Poisoning Steps Of Management:
- Resuscitation and initial stabilization
- Maintain airway, breathing, and circulation
- Blood sample collection for examination
- Rectal temperature is obtained
- Treatment of hypotension with crystalloids
- Administration of a cocktail of 50% dextrose, naloxone, and thiamine
- Diagnosis of various types of toxins
- History
- Reveals type of poison and amount of overdose taken
- Examination
- Helps to detect a syndrome associated with certain poisons
- Investigations
- Colour of urine
- Colour of blood
- Crystals in urine
- Ketonuria
- Anion gap
- History
- Nonspecific treatment
- Reduces levels of toxin in the body
- Gastric decontamination- includes
- Removal of unabsorbed poison from the gut
- Induction of emesis
- Gastric lavage
- Cathartics
- Use of activated charcoal
- Whole bowel irrigation
- Enhancement of excretion of absorbed toxins from the body
- Forced diuresis- alkaline diuresis
- Use of multiple doses of activated charcoal
- Peritoneal and hemodialysis
- Dialysis
- Specific therapy
- A specific antidote is administered
Important MCQs on acute poisoning
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Signs, Symptoms, And Management Of Fluorosis
Fluorosis
- Excessive intake of fluoride causes fluorosis
Fluorosis Types:
- Dental Fluorosis
- Caused by fluoride intake above 2 ppm
- Its symptoms are:
- Mottling of enamel
- Discoloration of teeth
- Teeth become weak and rough
- Brown or yellow patches appear on their surfaces
- Skeletal Fluorosis
- Caused by fluoride intake above 20 ppm
- It causes:
- Pathological changes in the bone
- Hypercalcification
- Bone density of limbs, pelvis, and spine increases
- Ligaments of the spine and collagen of bones get calcified
- Neurological disturbances may also occur
- Genu valgum
- It is an advanced stage of Fluorosis
- In it, individuals are unable to perform their routine work
- Joints become stiff
- Individuals are crippled
Fluorosis Management:
- Vomiting is induced wi a syrup of ipecac or digital or mechanical stimulation the of tongue or throat
- Decrease the absorption of fluoride by administering fluoride-binding liquids like warm water, calcium hydroxide, antacids containing aluminum or magnesium hydroxide, or milk
- The stomach should be thoroughly washed with additional lime water
- Calcium gluconate should be administered intravenously along with lime to prevent shock
Short answer questions on acute poisoning
Atropine
- Atropine is a natural anticholinergic drug
Atropine Mechanism Of Action:
- Bind to muscarinic receptors
- Blocks the effects of acetylcholine
Atropine Actions
- Increases heart rate
- Vasodilation
- hypotension
- Reduces all secretions
- Muscle relaxation
- Bronchodilation
- Relaxes ureter
- Produces mydriasis
- CNS stimulant
Case-based questions on acute poisoning
Atropine Uses
- Anti-spasmodic
- Mydriatric and cycloplegic
- Preanaesthetic medication
- Organophosphorous poisoning
- Bronchial asthma
- Peptic ulcer
- Parkinsonism
- Motion sickness
- During labor
Frequently asked questions in acute poisoning
Atropine Adverse Reactions
- Blurring vision
- Dry mouth
- Dysphagia
- Dry skin
- Fever
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Skin rashes
- Palpitation
- Flushing
- Restlessness
- Delirium
- Hallucination
- Psychosis
- Convulsion
- Coma
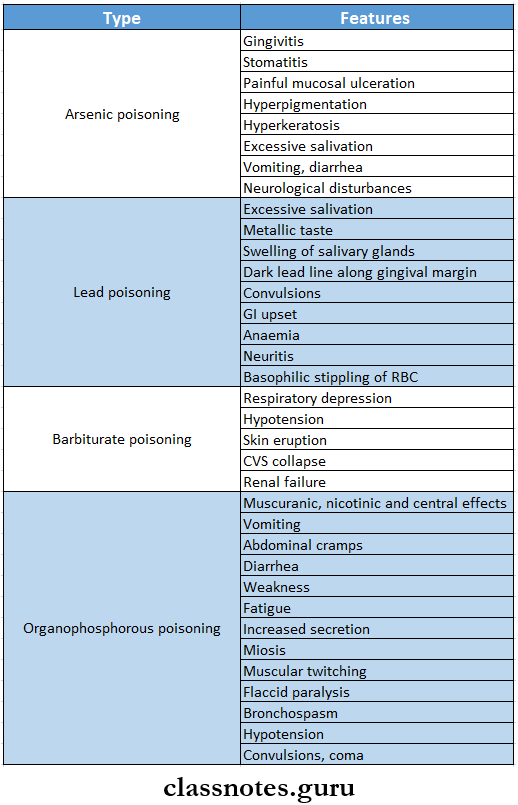
Arsenic Poisoning Features
- Gingivitis
- Stomatitis
- Painful mucosal ulceration
- Hyperpigmentation and hyperkeratosis
- Excessive salivation
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Neurological disturbances
Oral exam questions on acute poisoning
Symptoms Of Lead Poisoning
Symptoms Of Lead Poisoning Features:
- Excessive salivary secretions
- Metallic taste in the oral cavity
- Swelling of the salivary glands
- Development of the dark lead line along the gingival margin
- Convulsions
- GI upset
- Anaemia
- Neuritis
- Basophilic stippling of the RBC cells
Fluorides in Health and Disease
Importance Of Fluoride In Health:
- The kidney excretes it
- Fluoride passes the placental barrier
- Fluoride prevents the development of dental caries
- Fluoride converts hydroxyapatite to fluorapatite
- Fluoride is mostly found in bones and teeth
- Fluoride is deposited in other calcified tissues also
- Fluoride is required for the proper development of bones
- Fluoride inhibits the activities of certain enzymes
- Sodium fluoride inhibits enolase in glycolysis
- Fluoroacetate inhibits aconitase in TCA cycle
Fluoride In Disease:
- Excess of fluoride causes fluorosis
- Drinking water containing less than 0.5 ppm of fluoride causes development of caries in children
Previous year acute poisoning questions
Dental care in mental retardation
Dental Care In Mental Retradation
- Familiarise the patient with the office and dental personnel to reduce his/her fear of the unknown before undertaking any treatment
- Speech must be slow and simple
- Only one instruction at a time should be given
- Tell, show, and do technique is used in mild cases and sedation in moderate cases
- Carefully listen to the patient
- Appointments should be short and scheduled during the early part of the day
- Children should be managed with a blend of kindness and firmness
- General anesthesia may be indicated in cases where adequate levels of cooperation cannot be achieved
