Diseases Of The Nervous System Short Answers
Question 1. Name First 4 cranial nerves
Answer:
First 4 Cranial Nerves
- Olfactory nerve
- Optic nerve
- Oculomotor nerve
- Trochlear nerve
Diseases of the nervous system short questions and answers
Question 2. Four causes of meningitis
Answer:
Causes Of Meningitis
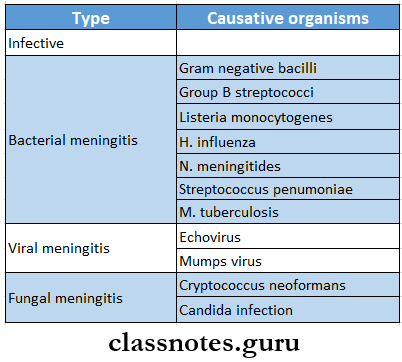
Question 3. Indications of lumbar puncture
Answer:
Indications Of Lumbar Puncture
- Diagnostic
- CNS infection/ inflammation
- Encephalitis
- Meningitis
- Myelitis
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Infiltrative conditions
- Carcinomatous meningitis
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- To confirm raised intracranial pressure
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
- Installation of contrast media
- Myelography
- CNS infection/ inflammation
- Therapeutic
- Administration of intrathecal antibiotics
- Administration of antileukemic drugs
- Spinal anaesthesia
- Removal of CSF to lower the pressure in benign intracranial hypertension
Nervous system disorders short answer questions
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
Question 4. Treatment of migraine
Answer:
Treatment Of Migraine
- Treatment of migraine includes
- Removal of aggravating factors like alcohol, oral contraceptives, and dietary factors
- Aspirin – 600-900 mg/ day
- Paracetamol – 1 g/day
- Antiemetics like metoclopramide
- Ergotamine tartrate 0.5-1 mg sublingually/ orally/ rectally
- Serotonin agonist sumatriptan 50-100 mg orally 23 times a day
Question 5. Evaluation of coma
Answer:
Evaluation Of Coma
- Evaluation of come is done through the Glasgow coma scale
- It is as follows:
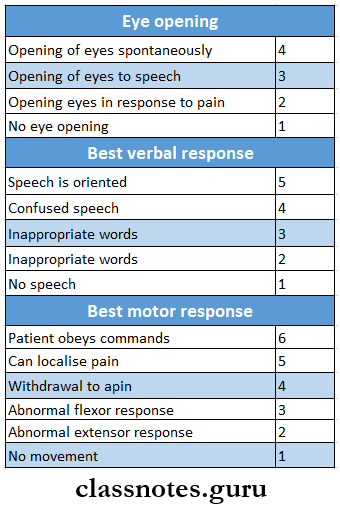
Question 6. Syncope
Answer:
Syncope
- Syncope refers to generalized weakness of muscles, loss of postural tone, inability to maintain an erect posture, and loss of consciousness
- Syncope is a transient loss of consciousness with an inability to maintain postural tone due to an acute decrease in cerebral blood flow
Syncope Clinical Features:
- Tingling or numbness in the limbs
- The patient feels cold and becomes unconscious
- Sowing of pulse
- Limbs become cold and clammy
Syncope Management:
- Elevation of the foot end of the bed
- Administration of 4 glucose
Neurology short Questions & Answers for medical students
Question 7. Causes of syncope
Answer:
Causes Of Syncope
- Standing for a long time
- Starvation
- Excessive heat “ Exhaustion “ Fear
- Sudden anxiety
- Blood loss
- Hypoglycaemia
Question 8. Bell’s palsy
Answer:
Bell’s Palsy Clinical Features:
- Pain in post auricular region
- Sudden onset
- Unilateral loss of function
- Loss of facial expression
- Absence of wrinkling
- Inability to close the eye
- Watering of eye
- Inability to blow the cheek
- Obliteration of nasolabial fold
- Loss of taste sensation
- Hyperacusis
- Slurring of speech
Question 9. Bell’s Palsy management
Answer:
Physiotherapy:
- Facial exercises
- Massaging
- Electrical stimulation B Protection to eye
- Covering of eye with bandage
- Medical management
- Prednisolone 60-80 mg per day
- 3 tablets for 1st 4 days
- 2 tablets for 2nd 4 days
- 1 tablet for 3rd 4 days
- Surgical treatment
- Nerve decompression
- Nerve grafting
Question 10. Clinical features of trigeminal neuralgia
Answer:
Clinical Features Of Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Age: around 35 years
- Sex: common in female
- Site: right lower portion of the face, usually unilateral
- Duration: a few seconds to a few minutes
- As time passes duration between the cycles decreases
- Nature: stabbing or lancinating
- Aggravating Factors: activation of Trigger zones
- These are the vermillion borders of the lip, around the eyes, and the nose
- Interference With Other Activities:
- The patient avoids shaving, washing their face, chewing, and brushing, as these may aggravate pain
- These lead to a poor lifestyle
- Extreme cases: leads to frozen or mask-like face.
Short notes on nervous system diseases
Question 11. Hysteria
Answer:
Hysteria
- Hysteria is a syndrome characterized by a loss or distortion of neurological function
Hysteria Clinical Features:
- Conversion disorder
- Gait disturbances
- Loss of function in limbs
- Aphonia
- Pseudo seizures
- Sensory Joss
- Blindness
- Dissociation disorder
- Memory loss
- Loss of personal identity
- Amnesia
Question 12. Schizophrenia
Answer:
Schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia is a group of disorders characterized by perturbations in language, perception, cognition, and behavior
Etiology:
- Genetic
- Emotional disturbances
- Psychological stress
Schizophrenia Types:
- Catatonic
- Disorganized
- Paranoid
- Undifferentiated
Schizophrenia Symptoms:
- Auditory hallucinations
- Delusion
- Catatonia
- Thought disorder
- Social withdrawal
- Poverty of speech
Schizophrenia Management
- Neuroleptic drugs like Chlorpromazine-100 mg tid
Peripheral nervous system diseases short answers
Question 13. Babinski’s sign
Answer:
Babinski’s Sign
- Extension of the great toe with fanning of other toes is called Babinski’s sign
Babinski’s sign Causes:
- Physiological- infants and children upto 2 years of age during deep sleep
- Pathological- lesions of corticospinal tract above SI segment
Question 14. Four signs of Horner’s syndrome
Answer:
Four Signs Of Horner’s Syndrome
- Ptosis of eyelid
- Enophthalmos
- Loss of ciliospinal reflex
- Anhydrosis of the ipsilateral half of the face
- Miosis
Question 15. Headache
Answer:
Headache
- Headache is a symptom with numerous possible causes
Headache Classification:
- Physiological
- Primary headache
- Secondary headache
- Intracranial pathology
- Extracranial pathology
- Systemic causes
- Depression
Question 16. Tension headache
Answer:
Tension Headache
- Tension headache is usually bilateral
- It is gradual in onset
- Pain continues for weeks or months
- Precipitating factors- stress and anxiety
Tension Headache Clinical Features:
- Dull ache
- Fullness of head
- Pressure overhead
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Nervousness
- Insomnia
Tension Headache Treatment:
- Anxiolytic drugs- Alprazolam-0.25-0.5 mg twice a day
- Antidepressants- Amitriptyline
Short answer questions on brain disorders
Question 17. Facial pain-four causes
Answer:
Facial Pain-Four Causes
- Neuritis of cutaneous nerves of the face and scalp
- Arthralgia of temporomandibular joint
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Post hepatic neuralgia
- Temporal arthritis
Question 18. Anxiety disorder-symptoms any three
Answer:
Anxiety Disorder-Symptoms
- Muscle tension
- Impaired concentration
- Autosomal arousal
- Restlessness
- Insomnia
- Tachycardia
- Dyspnoea
Question 19. Meningitis
Answer:
Meningitis:
- Meningitis is defined as inflammation of the pia-arachnoid and the fluid contained in the space
Meningitis Clinical Features:
- Classical triad – fever, headache, and neck rigidity
- Tachycardiardia, tachypnoea
- Convulsions in children
- Headache
- Blurring of vision
- Papilloedema
- Ixchymosis
- Associated lung, ear, and sinus infection
Short questions on spinal cord disorders
Question 20. Dilantin sodium
Answer:
Dilantin Sodium
- Dilantin Sodium is an anti-epileptic drug
Dilantin Sodium Action:
- Has good antiseizure activity
- Effective against generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures
Dilantin Sodium Mechanism Of Action:
- Causes blockade of voltage-dependent sodium channels
- Stabilizes the neuronal membrane
- Inhibits the generation of repetitive action potentials
Dilantin Sodium Uses:
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures and partial seizures
- Status epilepticus
VIVA VOCE
- Kernig’s sign and Brudzinski’s sign is svn in bacterial meningitis
- H. influenza meningitis in children causes upper respiratory and ear infection
- Nucleusens of the 7th cranial nerve lie in the pons
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome includes Bell’s palsy, herpetic vesicles in the external auditory meatus, and deafness
- Postherpetic neuralgia occurs due to a previous herpetic zoster infection
- A seizure is an episode of abnormal subchondral neuronal discharge in the brain
- Convulsions are seizures accompanied by motor manifestations
- Absence seizures occur in childhood
- Aphasia is a disorder of the language content of speech
- Phenobarbitone is the drug of choice in pregnancy
- Vasovagal syncope occurs due to stress or severe pain
- Postural hypotension syncope occurs following chronic illness
- Micturition syncope occurs in elderly patients during or after urination
- Cardiac syncope occurs due to a sudden reduction in cardiac output
- Syncope of cerebrovascular disease occurs due to the narrowing of large arteries
