Radiation Physics Definitions
- Ionization
- The conversion of an atom into an ion is called Ionization
- Ionizing radiation
- It is defined as radiation that is capable of producing ions by removing or adding electrons to an atom
- Resolution
- Resolution is the ability of a radiograph to record separate structures that are close together
Radiation physics in radiology
Radiation Physics Important Notes
- The Conversion of an atom into an ion is called Ionization
- The radiation, that brings about the ionization of atoms, is called ionizing radiation.
- Radiation is of two types
- Particulate
- Particulate radiation consists of atomic nuclei that transmit kinetic energy using their small masses moving at very high velocities Eg: Alpha rays, Beta rays, and Cathode rays
- Alpha rays consist of a high-speed stream of doubly ionized helium nuclei.
- Alpha rays have higher LET, thus they are more damaging to the biological systems than X-rays.
- Non – particulate/electromagnetic
- Electromagnetic radiation is produced when the velocity of an electrically charged particle is alerted Eg: Radio, TV, Microwaves, infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma, and Cosmic rays.
- The above examples are in the increasing order of their energy and decreasing order of their wavelengths.
- Particulate
- Types of electromagnetic radiation
- Ionizing radiation
- Nonionizing radiation
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question and Answers
Radiation Physics Short Essays
Question 1. Electromagnetic radiation.
Answer.
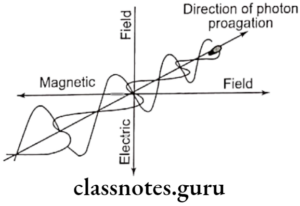
Electromagnetic radiation
- It is a combination of electric & magnetic fields
- Generated when the velocity of an electrically charged particle is altered.
Radiation Physics Types:
- Ionizing radiation
- Nonionizing radiation
Radiation Physics Properties:
- Travel in a straight line
- They travel at the speed of light
- They neither have mass nor weight
- They transfer energy from place to place in the form of photons
- They obey the inverse square law
- These are invisible radiations
Basics of radiation physics
Question 2. Electromagnetic Spectrum
Answer.
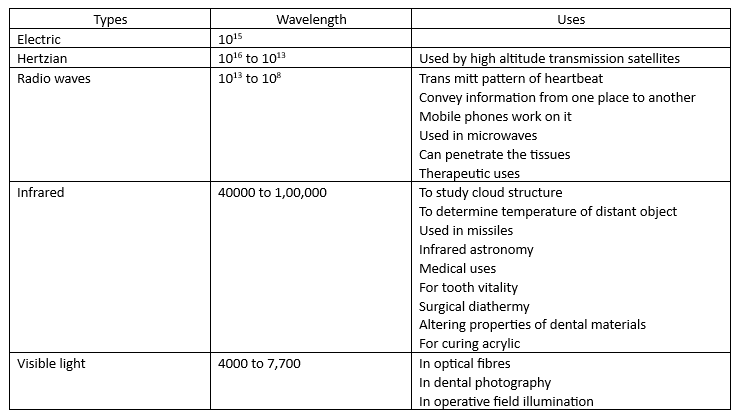
Electromagnetic Spectrum
It comprises of the following radiations
Short Answers
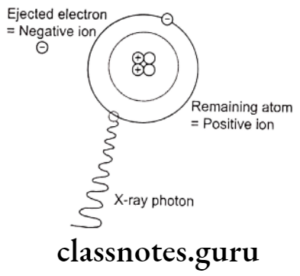
Question 1. Ionizing radiation
Answer.
Ionizing radiation
- It is defined as radiation that is capable of producing ions by removing or adding electrons to an atom
Ionizing radiation Classification:
- Particulate radiation.
- This transmits kinetic energy by extremely fast-moving small masses
- Types are electron, alpha, protons & neutrons
- Electromagnetic radiation
- It is the propagation of wave-like energy through space or matter
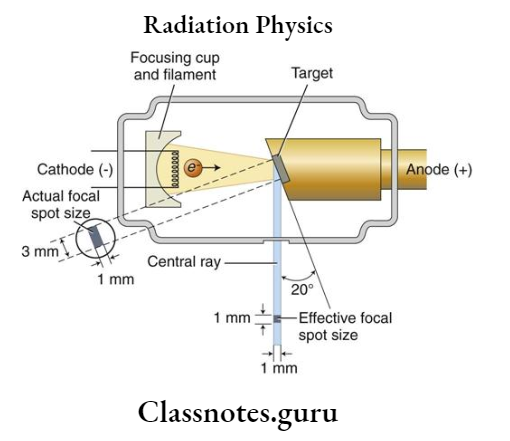
Principles of radiation physics
Question 2. Timer
Answer.
Timer
- A timer is built into high high-voltage circuit to control the duration of the X-ray exposure
- The electronic timer controls the length of time that high voltage is applied to the tube and the time during which tube current flows and x-rays are produced
- Some X-ray machine timers are calibrated in fractions of a second whereas others are expressed as the number of pulses in an exposure
- The number of pulses divided by 60 gives the exposure time in seconds
Question 3. Exposure time
Answer.
Exposure time
- It is one of the factors controlling X-ray beam
- Changing the exposure time modifies the duration of the exposure and thus the number of photons generated
- When the exposure time is doubled, the number of photons generated at all energies in the X-ray emission spectrum is doubled
- The range of photon energies is unchanged.
Radiation physics short notes
Question 4. Resolution
Answer.
Resolution
- Resolution is the ability of a radiograph to record separate structures that are close together
- It is measured by radiographing an object made up of a series of thin lead strips with alternating radiolucent spaces of the same thickness
- The group of lines and spaces are arranged in test targets in order of increasing the number of lines and spaces per millimeter
- It is measured as the highest number of line pairs per millimeter that can be distinguished on the resultant radiograph when examined with low-power magnification
Viva Voice
- X-rays were discovered by Roentgen in 1895
