Diseases Of The Gastrointestinal System Important Notes
- Barium Swallow
- Uses
- To study the gastrointestinal tract
- Visualize break in the gut mucosa
- Detects mucosal abnormalities
- Detects motility disorders
- Shows filling defect caused by varices or tumor
- Detects hiatus hernia or diverticulum
- Uses
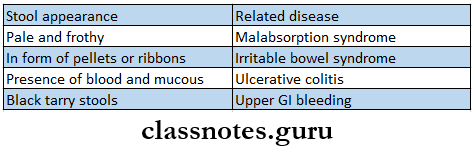
- Stool Examination
- Dental Caries
- It is progressive destruction of mineral and organic constituents of both enamel and dentin
- Fluoride is used to protect it
- Etiological agent
- Bad oral hygiene
- Staph. Aureus responsible for initiation of caries activity
- Lactobacillus leads to acid formation
- Progression of disease
- Dental caries → acute pulpitis → periapical granuloma → periapical cyst
- Ludwig’s Angina
- It is a subcutaneous infection involving all three salivary glands – parotid, submandibular and sub lingual
- Clinical features
- Swelling on floor of mouth
- Elevation of tongue
- Difficulty in breathing or chewing
- Periodontal Disease
- Progression of disease
- Gingivitis → involvement of alveolar bone and periodontal ligament → bone resorption → loss of attachment of periodontal ligament → pocket formation
- Result
- Mobile teeth
- Recurrent abscess formation
- Poor prognosis
- Progression of disease
- Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
- Etiology
- Fusiform spirochaetes
- Clinical features
- Gingival bleeding
- Gingival necrosis
- Ulceration
- Halitosis
- Regional lymphadenopathy
- Etiology
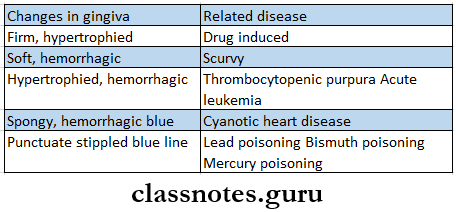
- Changes In Gingiva In Different Diseases
- Causes Of Stomatitis
- Infective
- Bad oral hygiene
- Low immunity
- Nutritional
- Iron deficiency
- Vitamin B complex deficiency
- Infective
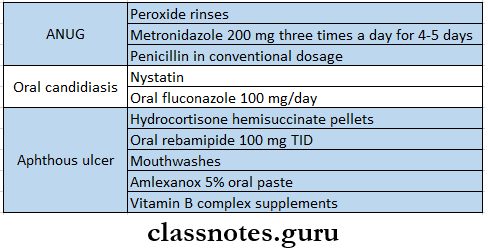
- Drugs Used In Different Diseases Of Oral Cavity
- Dysphagia
- It is defined as a sensation of obstruction of the passage of food through the mouth, pharynx, or esophagus
- Causes
- Extrinsic pressure – mediastinal glands, goiter, enlarged left atrium
- Intrinsic lesion – foreign bodies, stricture, lower oesophageal rings, pharyngeal pouch
- Oesophageal motility disorders – scleroderma, diabetes mellitus
- Plummer Vinson Syndrome
- It is characterized by dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia, dystrophy of nails and glossitis
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Characterised by haematemesis and melaena
- Causes
- Peptic ulcer
- Gastric erosion
- Varices
- Oesophagitis
- Cancer of stomach or esophagus
- Mallory Weiss Tear
- It is one of the cause of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding
- It occurs at the oesophagogastric junction
- GERD
- Burning pain is produced by bending, stooping, or lying down
- Pain seldom radiates to arm
- Pain precipitates by drinking hot liquids or alcohols
- Relieved by antacids
- Dyspepsia Or Peptic Ulcer
- It Means An Ulcer In The Wall Of Stomach Or Duodenum Caused By The Digestive Action Of Gastric Juice
- Types
- Gastric ulcer
- It is peptic ulcer occurring in stomach
- In it pain occurs while eating or drinking and is relieved by vomiting
- It is associated with anorexia and weight loss
- Duodenal ulcer
- It is peptic ulcer found in the duodenum
- In it pain is felt 1-2 hours after food intake and during night
- Pain is relieved by taking food
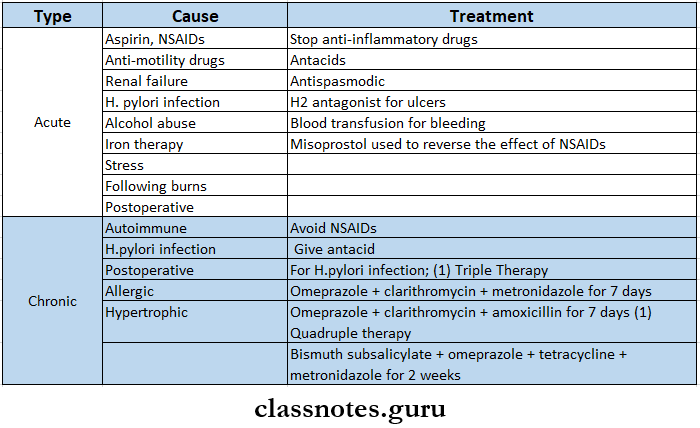
- Gastritis
- It is acute or chronic inflammation of stomach
- Types:
- Diarrhea
- It refers to frequent loose stools
- Bacteria causing it are
- Staph. Aureus
- Bacillus cereus
- CI. perfringens
- Cl. Botulinum
- Salmonella
- Vibrio cholera
- Treatment
- Fluid replacement
- Antibiotics
- Oxytetracycline, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole
- Traveller’s Diarrhea
- Acute diarrhea seen in tourists
- May resolve spontaneously
- Drug used is loperamide in adults

gastrointestinal pathology notes
Read And Learn More: General Medicine Question and Answers
- Malabsorption Syndrome
- Refers to defective absorption of one or more essential nutrients through the intestine
- Etiology
- Disorders of maldigestion
- Deficiency of bile acids
- Genetic abnormality
- Metabolic defects
- Treatment
- Gluten-free diet
- Vitamin and mineral supplements
- Corticosteroids
- Lactose Intolerance
- Occurs due to a deficiency of lactose
- Clinical features
- Intestinal colic
- Distension of abdomen
- Increased flatus
- After ingestion of milk
- Followed by diarrhoea
- Treatment
- Intake of lactose-restricted diet
- Amoebiasis
- Caused by entamoeba histolytica
- Clinical features
- Fever, nausea, vomiting
- 2-4 loose stools per day mixed with blood and mucous
- Pam in abdomen
- Necrotizing colitis with mucosal sloughing, ulceration, and bleeding
- Drugs used
- Oral metronidazole 800 mg TID for 5 days or
- Oral tinidazole 2 g daily for 3 days or
- Oral secnidazole 2 g single dose
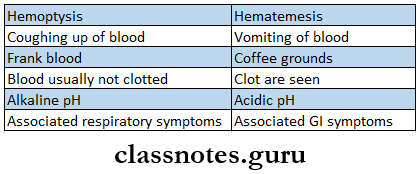
- Hematemesis And Hemoptysis
gastrointestinal system diseases notes
