Vibrio Long Essays
Question 1. Describe morphology, cultural characteristics, taxing, and laboratory diagnosis of vibrio cholera.
Answer:
Vibrio Cholera Morphology:
- Vibrio cholera is a gram-negative, non-capsulated, and non-sporing organism.
- It is motile and possesses a single polar flagellum, thus called darting motility.
- Size: 1.5 mm x 0.2 – 0.4 mm.
- Shape: curved or comma-shaped rod.
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question and Answers
Vibrio Cholera Cultural Characteristics:
- Vibrio cholera is strongly aerobe
- Grows within a temperature range of 16-40°C and alkaline pH of 8.2
Vibrio bacteria
Vibrio Cholera Toxins:
- Vibrio cholera produces enterotoxin known as cholera toxin (CT)
- It is heat-labile
- Protein in nature.
- Molecular weight – 90,000
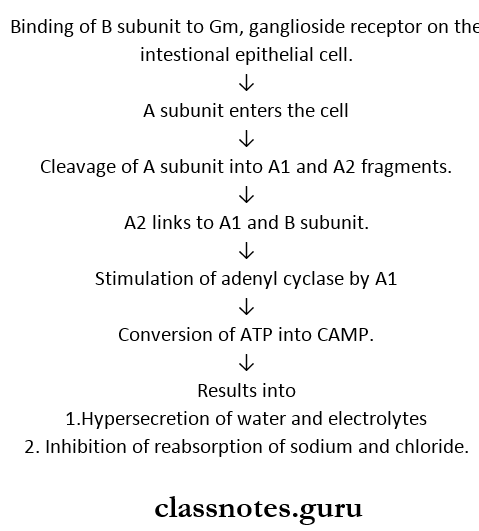
- It has two fractions.
- A (active) subunit – one.
- B (binding) subunit – five.
- Its production is determined by phage integrated with bacterial chromosomes.
Vibrio Cholera Mechanism:
Laboratory Diagnosis:
1. Direct Microscopy.
- Not reliable.
- Characteristic motility of the vibrios is demonstrated by dark field or phase contracts microscope.
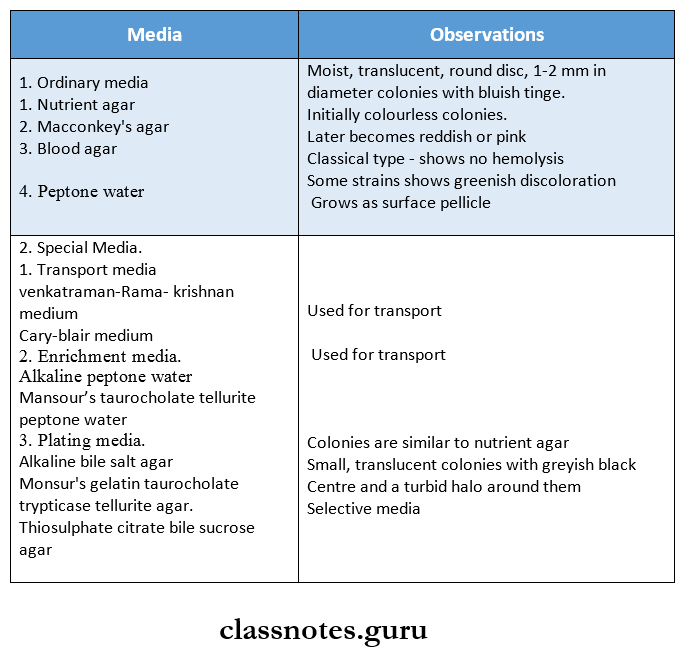
2. Culture.
- Nutrient agar.
- Shows moist, translucent, round disc colonies.
- Selective media – Monsur’s GTTA media.
- Shows small, translucent colonies with a greyish-black center and turbid halo.
- Macconkey’s agar media.
- Shows initially colorless colonies which later become reddish.
3. Agglutination Test
- Colonies from selective media are picked up with a straight wire and tested by slide agglutination with cholera 0 subgroup I serum.
- If positive, the agglutination test is repeated using monospecific Ogawa and Inaba sera for serotyping.
4. Serological Tests – Includes.
- Agglutination using live or killed vibrio suspension.
- Indirect haemagglutination.
- Vibriocidal test.
- Antitoxin assay.
5. Biochemical Test.
- Fermentation of glucose, mannitol, maltose, sucrose.
- Indole positive.
- Reduction of nitrates.
- Catalase and oxidase positive. Voges – Broskauer negative.
Vibrio morphology
Vibrio Short Essays
Question 1. Cholera.
Answer:
Cholera Etiology:
- Cholera is caused by vibrio cholera.
- The route of infection is contaminated food and water.
- Alkaline pH in the stomach and intestine appears to be more easily infected.
Cholera Pathogenesis:
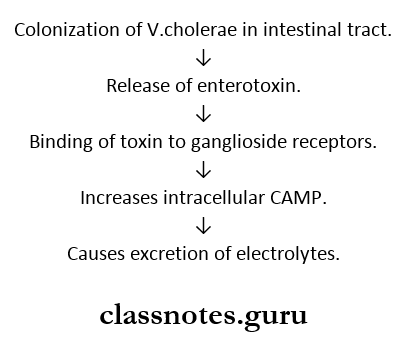
Cholera Features:
- Diarrhea is the major symptom.
- Feces contain epithelial cells, mucus, and a large number of V. Cholera.
- Profuse watery diarrhea – rice water stools occur.
- In severe cases, there may be one liter of fluid loss each hour.
- Abdominal pain.
- Death due to electrolyte abnormalities and fluid loss.
Treatment, Prevention, And Control:
- Intravenous administration of fluids.
- Oral administration of a solution containing glucose and electrolytes.
- Antibiotics.
- Doxycycline – In adults.
- Sulphamethethoxazole – In children.
- Furazolidone – In pregnant women.
- Improved – hygiene.
- Water purification, immunization.
Vibrio characteristics
Vibrio Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Whooping Cough.
Answer:
Whooping cough is predominantly a childhood disease.
Whooping Cough Causative Agents:
- B. Pertusis – 95% cases.
- B. Parapertusis – 5% cases.
- B. Bronchiosepetica – 0.1% cases.
Whooping Cough Features:
- Incubation period – 1 – 2 weeks.
- Infection is transmitted by droplets.
- Diseases usually last for 6 – 8 weeks.
- It consists of 3 stages.
1. Catarrhal.
- Clinical diagnosis is difficult.
2. Paroxysmal.
- Whooping cough occurs.
3. Convalescent.
- Frequently and severity of coughing decreases.
Whooping Cough Complications:
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage.
- Subcutaneous emphysema.
- Bronchopneumonia.
- Convulsions, coma.
Whooping Cough Prophylaxis:
- Pertussis vaccine is given.
- Three injections at intervals of 4 – 6 weeks are given before the age of 6 months.
- A booster dose is given at the end of the first year.
Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis
Question 2. Castaneda’s method of culture.
Answer:
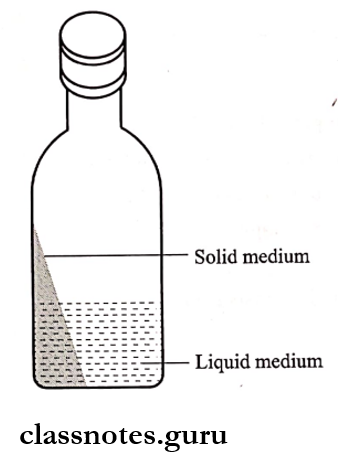
Castaneda’s is used for Brucella.
Culture Composition:
- It contains:
- Liquid media – trypticase soy broth.
- Solid media – trypicase soy agar.
Culture Method:
- Blood is inoculated into liquid media in a bottle.
- Incubate it in an upright position.
- The bottle is tilted and subcultured by solid media.
- Incubate it again in an upright position.