Ventricles Of Brain Question And Answers
Question 1. Write a note on the third ventricle.
Answer:
Third Ventricle
- The third Ventricle is the cavity of the diencephalon
- The third Ventricle is a slit-like cavity present between two thalami and the hypothalamus
- Third Ventricle extends from the lamina terminalis anteriorly to the superior end of the cerebral aqueduct posteriorly
- Its cavity is lined by ependymal cells and traversed horizontally by interthalamic adhesion (mass of gray matter) connecting two thalami.
Third Ventricle Boundaries
- The third ventricle has anterior and posterior walls, roof and floor, and two lateral walls
- The anterior wall is formed by the anterior column of the fornix, anterior commissure, and lamina terminalis
- The posterior wall is formed by the pineal gland, posterior commissure, and commencement of cerebral aqueduct
- The lateral wall is divided into upper and lower halves by the hypothalamic sulcus which extends from the interventricular foramen to the cerebral aqueduct
- The upper part of the lateral wall is large and is formed by the medial surface of the anterior 2/3rd of the thalamus
- The smaller lower part of the lateral wall is formed by the hypothalamus.
- The roof is formed by ependyma extending between two thalami
- The floor is formed by optic chiasma, tuber cinereum, mammillary bodies, posterior perforated substance, and tegmentum of the brain.
Third Ventricle Communications
- Anteriorly, the 3rd ventricle communicates with the lateral ventricle on each side through the interventricular foramen of Monro
- Posteriorly, it communicates with the 4th ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius.
Third Ventricle Recesses
- The cavity extends to surrounding structures as pockets like protrusions called recesses.
- The following recesses are associated with 3rd ventricle:
- Infundibular Recess: Tunnel shaped recess extending through tuber cinereum to infundibulum
- Optic Recess: Angular recess located at the junction of the anterior wall and floor of the ventricle
- Anterior Recess: Triangular recess located between diverging anterior columns of fornix and anterior commissure anteriorly and interventricular foramen posteriorly
- Suprapineal Recess: It is a blind diverticulum extending between the stalk of the pineal gland and the tela choroidea
- Pineal Recess: A small diverticulum extending between the superior and inferior lamellae of the stalk of the pineal gland.
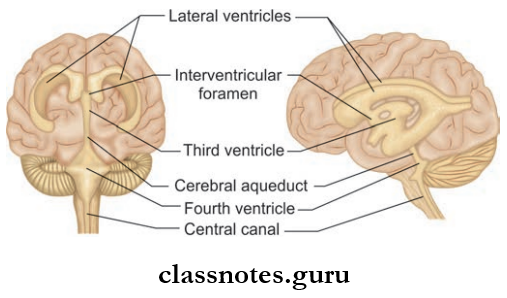
Question 2. Write a note on the lateral ventricle.
Answer:
Lateral Ventricle
- Each lateral ventricle is a C-shaped cavity present in each cerebral hemisphere
- It is lined by ependymal cells.
Lateral Ventricle Communications: Each ventricle communicates with 3rd ventricle through the interventricular foramen.
Lateral Ventricle Parts: Each ventricle consists of the following parts
- Central Part
- Anterior Horn
- Posterior Horn
- Inferior Horn
1. Central Part
- The Central Part is located within the parietal lobe extending from the interventricular foramen to the splenium of the corpus callosum
- The Central Park is triangular in cross-section and consists of a roof, floor, and a medial wall
- The floor is formed by the body of the caudate nucleus, stria terminalis, thalamostriate vein, and thalamus
- The roof is formed by the body of the corpus callosum and the medial wall by the septum pellucidum.
2. Anterior Horn
- The anterior Horn is the anterior prolongation of the central part into the frontal lobe
- The anterior Horn lies in between the interventricular foramen and genu of corpus callosum
- Anterior Horn consists of a roof, floor, anterior, medial, and lateral walls
- Roof: Formed by the body of corpus callosum
- Floor: Formed by rostrum of corpus callosum
- Anterior wall by genu of corpus callosum
- Medial wall by septum pellucidum
- Lateral wall by the head of caudate nucleus.
3. Posterior Horn
- The posterior Horn is the posterior prolongation of the central part into the occipital lobe
- Posterior Horn consists of a roof, floor, medial and lateral wall
- Roof, floor, and lateral wall are formed by the tapetum of the corpus callosum
- The medial wall is formed by forceps of the corpus callosum and calcarine sulcus.
4. Inferior Horn
- Inferior Horn is the largest horn
- Inferior Horn appears as a slit and consists of a roof and floor
- The roof is formed by the tapetum of the corpus callosum, stria terminalis, and tail of the caudate nucleus
- The floor is formed by the hippocampus and collateral eminence.
Ventricles Of Brain Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 1. Regarding the cavities of the brain, all of the following statements are correct except:
- Right and left lateral ventricles are cavities within the right and left cerebral hemispheres respectively
- Third ventricle is a cavity within the diencephalon
- The cerebral aqueduct is the cavity within the pons
- The fourth ventricle is the cavity within the hindbrain
Answer: 3. Cerebral aqueduct is the cavity within the pons
Question 2. An infant with hydrocephalus was diagnosed to have a blocked outlet passage from the third ventricle. The blocked passage is:
- Central canal of medulla
- Foramen of Monro
- Aqueduct of Sylvius
- Foramen of Magendie
Answer: 3. Aqueduct of Sylvius
