Thyroid Hormones And Anti Thyroid Drugs Important Notes
1. Thyroid Hormones And Anti Thyroid Drugs Thyroid storm
- It means thyrotoxicosis
- Treatment is to reduce the production and conversion of thyroid hormones
- Drugs used for it are
- Inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Propylthiouracil
- Methimazole
- Carbimazole
- Inhibiting hormone release
- Iodine
- Iodide
- Destroying thyroid tissue
- Radioactive iodine
- To counteract adrenal insufficiency
- Corticosteroids
- To control sympathetic symptoms
- Propanolol
- Inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question and Answers
2. Thyroid Hormones And Anti-thyroid drugs
- Propylthiouracil, carbimazole, and radioactive iodine are anti-thyroid drugs
- Used in the treatment of
- Hyperthyroidism
- Preparation of patients for thyroid surgery
Thyroid hormones: question and answer
Thyroid Hormones And Anti-Thyroid Drugs Long Essays
Question 1. Enumerate antithyroid drugs. Explain the action of the thioamides giving the indications, advantages, and adverse effects of each.
Answer:
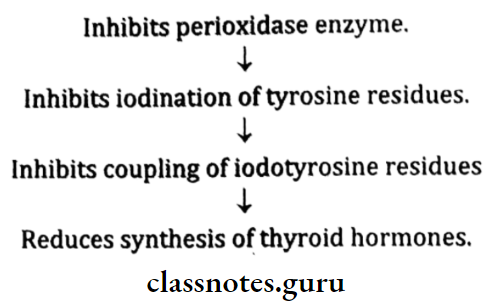
Antithyroid drugs:
- These drugs inhibit hormone synthesis.
- They are thioureylenes or thionamides which includes.
- Propylthiouracil.
- Methimazole.
- Carbimazole.
Antithyroid drugs Actions:
Antithyroid drugs Indications/uses:
1. Graves disease or diffuse toxic goiter.
- Needs long-term treatment with antithyroid drugs.
2. Toxic nodular goiter.
- Used when surgery is not indicated like in elderly patients.
3. Preoperatively in hyperthyroid patients.
- Used along with radioactive iodine to hasten recovery in thyrotoxicosis.
4. Rarely used in hyperthyroidism in pregnancy.
5. Thyroid storm or thyrotoxic crisis.
- It is a sudden, severe, exacerbation of thyrotoxicosis.
- Propylthiouracil is used IV.
Antithyroid drugs Advantages:
- No surgery is required.
- No injury to parathyroid or recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- Hypothyroidism, if occurs, is reversible.
- Can be used in children and young adults also.
Antithyroid drugs Disadvantages:
- Long-term treatment is required.
- Poor patient compliance.
- Drug toxicity.
Antithyroid drugs Adverse effects:
- Allergic reactions – skin rashes.
- Jaundice
- Headache.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Agranulocytosis.
- GIT disturbances.
- Joint pain.
- Nephritis, hepatitis
- Loss of hair, loss of taste.
Mechanism of thyroid hormone action
Thyroid Hormones And Anti Thyroid Drugs Short Essays
Question 1. Radioactive iodine.
Answer:
Radioactive iodine is a thyroid tissue-destroying agent
- When given orally, it is rapidly absorbed and is concentrated by the thyroid in the follicles.
- It emits X-rays as well as β particles.
- It is used as a sodium salt of 31I dissolved in water.
Radioactive iodine Uses:
1. Small doses – 25 -100 m curie.
- Used for diagnosis in thyroid function tests.
2. Large doses – 3 – 6 cm curie.
- Used for treatment of hyperthyroidism.
- β particles emitted destroy thyroid cells.
- Thus, it is used in carcinoma of the thyroid.
Radioactive iodine Advantages:
- Simple and convenient
- Inexpensive.
- No surgical risks.
- Hyperthyroidism is permanently cured.
Radioactive iodine Disadvantages:
- Slow-acting.
- The long latent period of response.
- Hypothyroidism develops.
- Not suitable for pregnant women, children, and young adults.
Thyroid Hormones And Anti Thyroid Drugs Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Lugol’s iodine.
Answer:
Lugol’s iodine is a solution of 5% iodine in 10% potassium iodide solution.
- A daily dose of 5 -15 drops can be used.
Lugol’s iodine Uses:
- As expectorant
- In preoperative preparation for thyroidectomy.
- Thyroid storm.
- Prophylactic in endemic goiter.
- As antiseptic.
Anti-thyroid drugs classification
Question 2. Iodine.
Answer:
Iodine inhibits the release of thyroid hormone
- In thyrotoxic patients, symptoms subside in 1 – 2 days.
- The gland becomes firm and shrinks in size in 10 -14 days.
- Effects decrease after 15 days.
Iodine Uses:
- Preoperatively in thyroidectomy.
- In thyroid storm.
- Prophylactically in endemic goiter.
- As antiseptic
- As expectorant.
Iodine Adverse effects:
- Allergic reactions – skin rashes, conjunctivitis.
- Swelling of lips and salivary glands.
- Fever
- Lymphadenopathy.
Thyroid drugs pharmacology
Question 3. Carbimazole.
Answer:
Carbimazole is a thioamide.
- Act as thyroid hormone synthesis inhibitor.
- It is more potent and long-acting.
- It crosses the placental barrier.
Carbimazole Uses:
- long-term therapy of thyrotoxicosis.
- To hasten recovery in thyrotoxicosis.
- Used in thyrotoxic crisis.
Carbimazole Adverse effects:
- Allergic reactions
- Hypothyroidism.
- GI intolerance
- Hepatitis, nephritis.
- Joints pain.
- Agranulocytosis.
Question 4. Alendronate.
Answer:
- It is second generation bisphosphonate
- Mainly used in osteoporosis
- Advice to be given on an empty stomach in the morning with plenty of water
- Avoid lying or having food for at least 30 minutes to avoid oesophagitis
- Calcium and iron preparation and NSAIDs should not give along with it
