Structure And Functions Of The Immune System Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. T-Lymphocytes.
Answer:
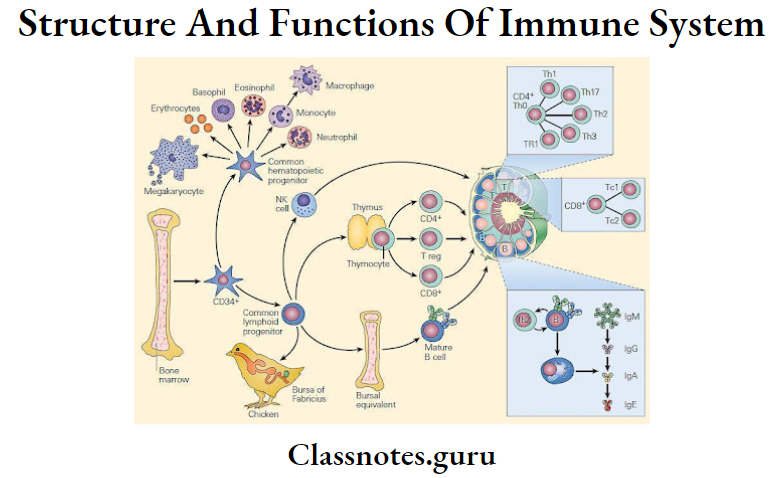
T-Lymphocytes
- T-lymphocytes constitute 70% of total lymphocytes.
- They are derived from the thymus, thus called T- T-lymphocytes.
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question and Answers
T-Lymphocyte Types:
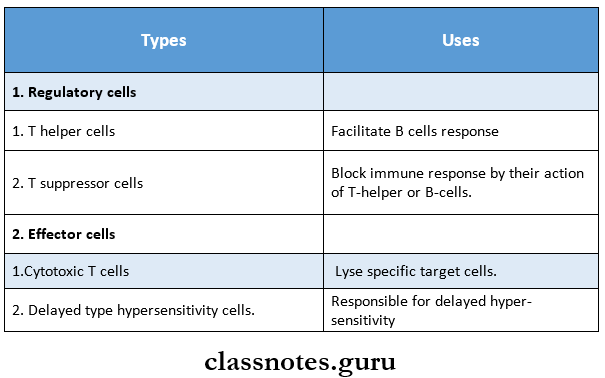
Immune system short notes
Question 2. B-lymphocytes.
Answer:
B-lymphocytes
B-lymphocytes constitute 20% of total lymphocytes.
- They are derived from ‘Bursa’ or bone marrow, thus the name B-lymphocytes.
- Antigenically stimulated B-lymphocytes undergo blast transformation to become plasma cells.
B-lymphocytes Functions:
B cells produce an antibody-mediated immune response by specific differentiation and proliferation of plasma cells, which produce antigen-specific antibodies
Question 3. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC).
Answer:
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
The cell surface antigens that induce an immune response leading to rejection of allografts are known as histocompatibility antigens.
- The group of such antigens is called the major histocompatibility complex (MHC).
- MHC in humans is known as the human leucocyte antigen (HLA complex.
- The HLA complex of genes is located on the short arm of chromosome 6 and is grouped into 3 classes.
1. Class 1 MHC Antigens (A, B, C]
- Present on the surface of all nucleated cells.
- Involved in graft rejection and cell-mediated cytolysis.
Structure and function of the immune system
2. Class 1 MHC Antigens (DR, DQ, And DP]
- Found on the surface of macrophages, monocytes, activated T-lymphocytes, and B-lymphocytes.
- Responsible for graft-versus-host response.
3. Class 3 MHC Antigens.
- Encode C2 and C4 complement components of the classical pathway and properdin factor B of the alternative pathway.