Staphylococcus Important Notes
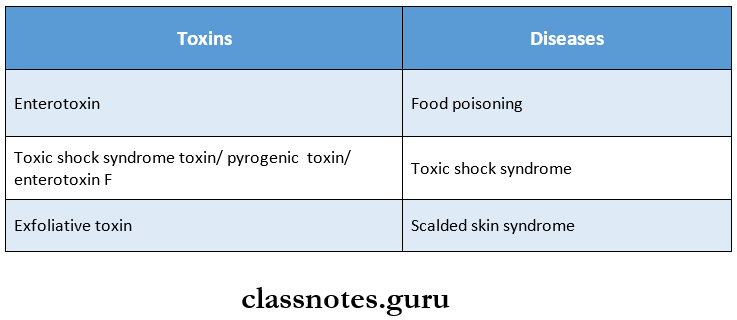
1. Toxins Produced By Staphylococci And Diseases Caused By Them
2. Classification Of Streptococci
- Alpha hemolytic streptococci
- Beta hemolytic streptococci
- Gamma hemolytic/ non hemolytic/ enterococcus group
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question and Answers
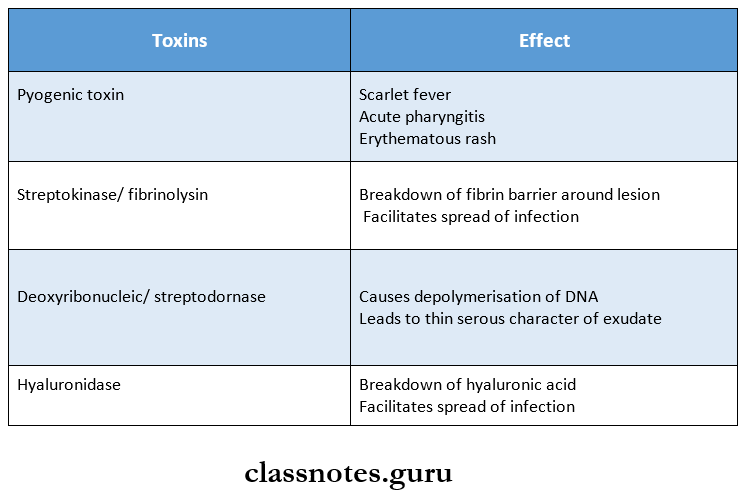
3. Toxins Produced By Streptococci
4. Diseases Caused By Streptococci
- Sore throat
- Ludwig’s angina, otitis media, quinsy, cellulitis
- Erysipelas, impetigo
- Acute glomerulonephritis
- Acute rheumatic fever
5. Toxins Produced By Pneumococci
- Hemolysin
- Leucocidin
Staphylococcus characteristics
6. The OuterMembrane Of Gonococci Consists Of
- Lipopolysaccharides
- Proteins
- Protein 1 – helps in typing of strains, forms pores on the surface
- Protein 2 – helps in adhesion
- Protein 3 – associated with protein 1
7. McLeod Classification
- Gravis
- Intermedius
- Mitis
8. Test Used For Bacillus Anthrax
- M Fadyean’s reaction
- String of pearls reaction
- Ascolis thermoprecipitation test
9. Diseases Caused By Bacillus Anthrax
- Hide Porter’s disease
- Pulmonary anthrax
- Malignant pustule
10. Toxins Produced By Clostridium Tetani
- Tetanolysin
- Tetanospasmin
11. Antigens Of Salmonella Typhi
- H antigen
- O or somatic antigen
- Vi or virulence antigen
12. Types Of E.coli
- Enteropathogenic E.coli
- Enterotoxigenic E.coli
- Entero aggregative E.coli
- Enteninvasive E.coli
- Enterohaemorrhagic E.coli
13. Classification Of Vibrios
- Halophilic vibrios
- V. vulnibicus
- V. alginolyticus
- V. parahemolyticus
- Non halophilic vibrios
- V. cholera
- V. mimicus
14. Diseases Caused By Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
- Infections in burns
- Iatrogenic meningitis
- Nosocomial infection
- Blue pus
- Bed sores
- Shanghai fever
15. Tests Used For Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Catalase peroxidase
- Microscopy
- Petroff s method
- Montouxtest
16. Classification Of Leprosy
- Lepromatous leprosy
- Tuberculoid leprosy
- Dimorphous leprosy
- Indeterminate
- Pure neuritic
17. Lepra Reaction
- Type 1 – reversal reaction
- Type 2 – erythema nodosum leprosum
Staphylococcus identification
Staphylococcus Long Essays
Question 1. Describe the morphology, staining characters, and pathogenicity of Staphylococcus. Add a note on laboratory diagnosis of staphylococcal infections.
Answer:
Staphylococcus Morphology:
- Staphylococcus is
- Gram-positive
- Non-motile
- Non-sporing.
- Non-capsulated
- Aerobic and normally facultative anaerobic.
- Shape: spherical cocci.
- Size: approx 1 micrometer in diameter.
- Arrangement: Arranged in grape-like clusters.
- This arrangement is due to cell division occurring in three planes.
- They may be found singly, in pairs, and in short chains of 3 – 4 cells.
Staphylococcus Staining Characters:
- Staphylococci are gram-positive cocci.
- On gram-staining:
- They resist decolorization with acetone.
- Retain the color of the primary stain.
- Appears violet in color on a pink background.
Staphylococcus Pathogenicity:
Staphylococcus produces two types of diseases.
1. Infections – In It.

2. Intoxications.
In it, the disease is caused by the toxins produced by bacteria.
Staphylococcal Diseases:
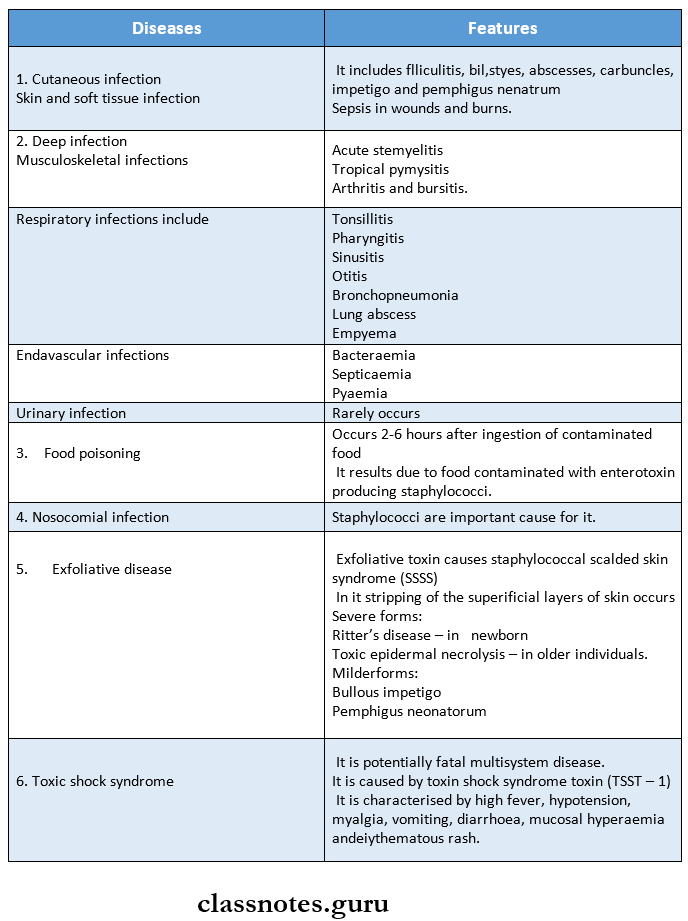
Laboratory Diagnosis:
The specimen to be collected depends on the type of lesion.
Specimen
- Pus
- Sputum
- CSF
- Blood
- Suspected food
Infections
- Suppurative lesions
- Respiratory infections
- Meningitis
- Septicaemia
- Food poisoning
1. Direct Microscopy.
- Gram staining of the smear shows gram-positive cocci arranged in clusters.
2. Culture.
- The inoculated media used are incubated at 37oC for 18 – 24 hours.
- The cultural media used are.
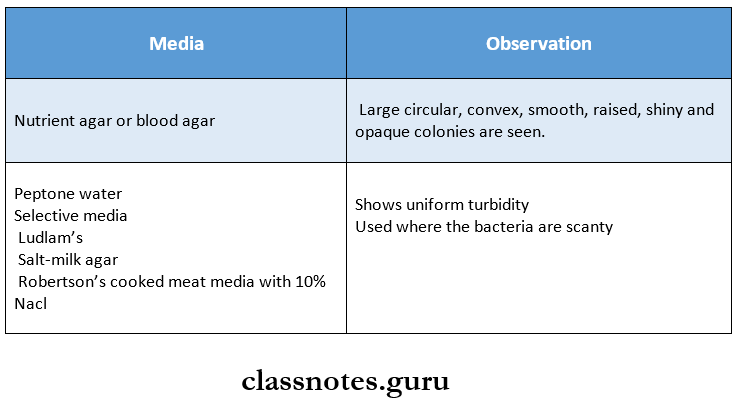
3. Biochemical Reaction
- Catalase test – positive.
- It distinguishes Staphylococcus from Streptococcus
- Coagulase test – positive
- Mannitol fermentation – produces acid without gas
- Gelatin fermentation – positive.
- Tellurite reduction – positive.
- Production of enzyme phosphatase and deoxyribonuclease – positive.
4. Bacteriophage Typing.
- Trace the source of staphylococcus.
5. Antibiotic Susceptibility.
- Determined by Stokes method.
6. Serological tests.
- Helps to diagnose hidden deep infections.
- Also, titer of more than 2 units/ml with rising titer diagnoses deep infections.
Question 2. Classify staphylococci. Describe the morphology, cultural characteristics, and reactions of staphylococcus aureus. Describe the pathological lesions caused by staphylococci.
Answer:
Staphylococci Classification:
- Based on pigment production and virulence.
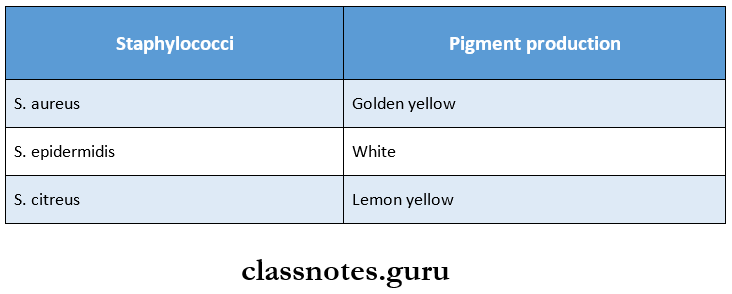
- Based on coagulase production.
- Coagulase positive – St. Aureus.
- Coagulase-negative – other staphylococci
Morphology Cultural Characteristics:
Staphylococci usually grow readily within a temperature range of 10 – 42°C with an optimal temperature of 37°C and pH 7.4 – 7.6.
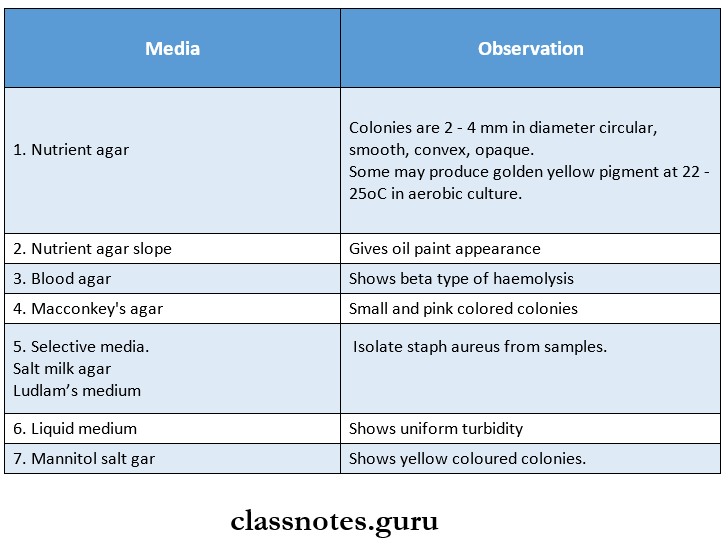
Morphology Reactions:
Staphylococcus aureus undergoes the following, reaction.
- Catalase positive.
- Oxidase negative.
- Fermentation of sugar.
- It ferments sugar without gas.
- This helps to distinguish staphylococcus aureus from. St. Epidermidis.
- Causes beta type of hemolysis.
- Produces.
- Coagulase.
- Phosphatase.
- Enzyme deoxyribonuclease.
- Reduction of tellurite occurs.
Staphylococcus infections
Staphylococcus Short Essays
Question 1. Name enzymes produced by staphylococcus aureus.
Answer:
Enzymes:
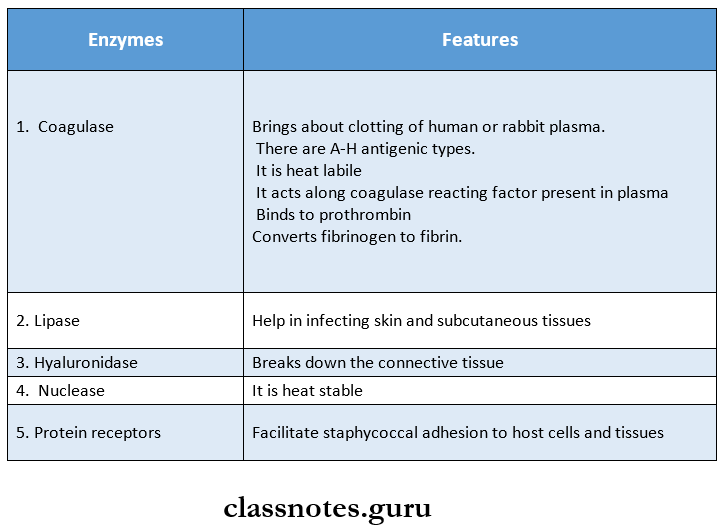
Staphylococcus Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Antigenic structure of staphylococci.
Answer:
Antigenic structure of staphylococci composed on.
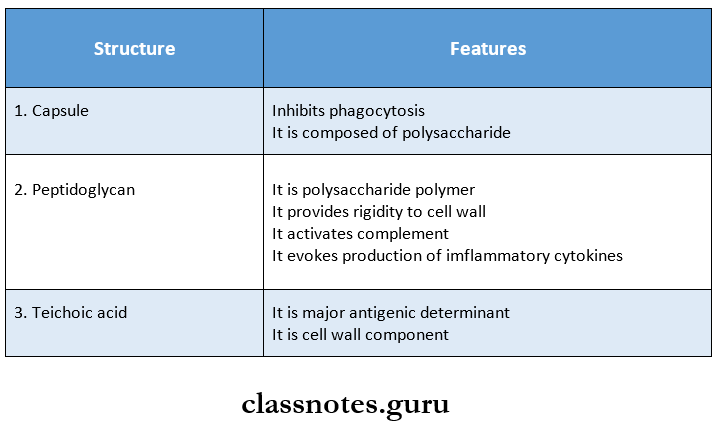
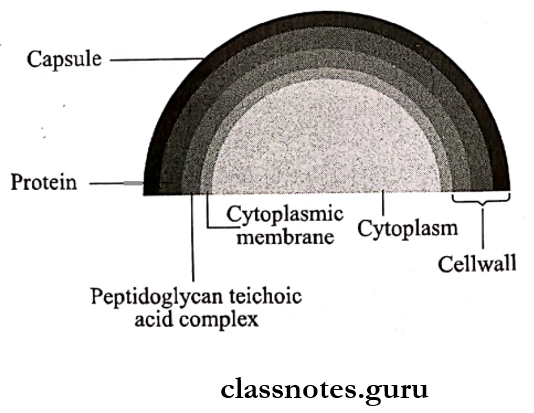
Question 2. Coagulase test.
Answer:
The coagulase test is the standard criterion for the identification of staphylococcus aureus isolates.
It Is Done By Two Methods.
1. Slide Coagulase Test.
- It detects bound coagulase.
- It gives results parallel to the tube test.
- In this method, a few colonies of bacteria are emulsified in a drop of normal saline on a clean glass slide.
- It is mixed with a drop of undiluted rabbit or human plasma.
2. Tube Coagulase.
- It detects free coagulase.
- In this method, 0.1 ml of an overnight broth culture or an agar culture suspension of the organism is mixed with 0.5 ml of 1 in 5 dilutions of human or rabbit plasma.
- Diluted plasma in another tube is used as a control.
- Plasma clots in case of positive reaction.
Staphylococcus classification
Question 3. Bacteriophage typing.
Answer:
- Bacteriophage typing is important in epidemiological studies of staphylococcal infections.
- Strains of S. aureus may be distinguished by their susceptibility to different bacteriophages.
- An internationally accepted set of 23 bacteriophages is employed.
Bacteriophage Typing Method

Centre In India:
Department of Microbiology, Moulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi.
Staphylococcus characteristics
Question 4. Enumerate pyogenic organisms.
Answer:
Pyogenic Organism:
- Staphylococcus Aureus – Gram-positive cocci.
- Streptococcus pyogenes – Gram-positive cocci.
- Klebsiella pneumonia – Gram-negative bacilli.
- Burkholderia mallei – Gram-negative bacilli.
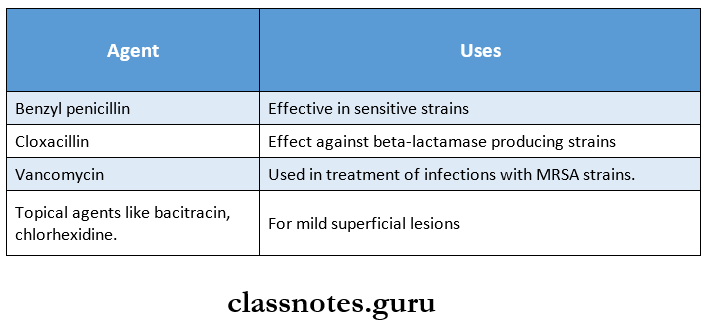
Question 5. Treatment of staphylococcal infections.
Answer: