Radiation Protection Important Notes:
- Lead aprons and collars
Advantages:- Lead aprons reduce 94% if scattered radiation to the gonads
- Protects gonads from radiation exposure
- Thyroid collars reduce the exposure of this gland by 92%
- Position distance rule
- The operator should stand at least 6 feet from the patient, at an angle of 90 degrees to 135 degrees to the central ray beam when the exposure is made.
- This called as Position – – distance rule.
- E speed films
Advantages:- The most effective method of reducing patient dose
- The risk is reduced by a factor of 2
- Contains large tubular grains which increase the speed
- The exposure time is 0.2 sec compared to regular film which is 9 sec
- Disadvantage
- Decreases image sharpness.
Essay on radiation protection in radiology
Radiation Protection Long Essays
Question 1. Enumerate hazards of radiation. Describe protective measures for the patient and the operator against it.
Answer.
Hazards Of Radiation:
- Biologic changes:
- Changes in DNA:
- Change in base
- Disruption of hydrogen bonds
- Breakage of DNA strands
- Cross-linking of DNA strands
- Proteins:
- Denaturation of proteins
- Changes in DNA:
- Cellular changes
- Nuclear changes
- Chromosome aberration
- Cytoplasmic changes
- Tissue changes:
- Non stochastic Effects
- Stochastic Effects
Read And Learn More: Oral Radiology Question and Answers
Radiation Protection:
- Radiation protection for the patient:
- Patient selection:
- Professional judgment should be used to select the patient for an X-ray examination
- Choice of equipment:
- Image receptor – to reduce the exposure time
- A focal spot to film distance
- With the increase in distance, the exposure time reduces
- Collimation – it reduces the size of the X-ray beam
- Filtration – to remove low-energy photons
- Use of lead aprons and collars
- It minimizes unnecessary radiation exposure
- Choice of intraoral technique:
- Parallel radiographic technique causes less exposure, hence used
- X-ray equipment:
- Make use of:
- High kVp
- Increased made
- Reduced exposure time
- Patient selection:
- Processing of film:
- Make use of the proper method of processing
- Avoid repetition of X-ray
- Interpretation of image:
- Properly interpreted the X-ray in a semi-darkened room
- Note down all the necessary details
- Processing of film:
Radiation safety measures long and short notes
- Radiation protection to the operator:
- The following measures must be carried out by the operator to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure
- During exposure, the operator must leave the room/stand behind a suitable barrier
- The operating room should meet the minimum shielding requirements
- The position of the operator during exposure should be 6 feet away from the source
- At an angle of 90 – 135°
- Avoid holding the film intraorally
- Avoid stabilizing the tube during exposure
- Use a lead apron in the absence of a barrier
- Avoid the use of fluorescence mirror during exposure
- Make use of filtration
- Carry out personal radiation monitoring periodically
Question 2. Discuss various measures for radiation protection.
Answer.
- Radiation protection for the patient:
- Patient selection:
- Professional judgment should be used to select the patient for an X-ray examination
- Choice of equipment:
- Image receptor – to reduce the exposure time
- A focal spot to film distance
- With the increase in distance, the exposure time reduces
- Collimation – it reduces the size of the X-ray beam
- Filtration – to remove low-energy photons
- Use of lead aprons and collars
- It minimizes unnecessary radiation exposure
- Choice of intraoral technique:
- Parallel radiographic technique causes less exposure, hence used
- X-ray equipment:
- Make use of:
- High kVp
- Increased mA
- Reduced exposure time
- Make use of:
- Processing of film:
- Make use of the proper method of processing
- Avoid repetition of X-ray
- Interpretation of image:
- Properly interpret the X-ray in a semi-darkened room
- Note down all the necessary details
- Patient selection:
Radiation protection in dentistry essay
- Radiation protection to the operator:
- The following measures must be carried out by the operator to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure
- During exposure, operator must leave the room/stand behind a suitable barrier
- The operating room should meet the minimum shielding requirements
- The position of the operator during exposure should be 6 feet away from the source
- At an angle of 90 – 135°
- Avoid holding the film intraorally
- Avoid stabilizing the tube during exposure
- Use a lead apron in the absence of a barrier
- Avoid the use of fluorescence mirror during exposure
- Make use of filtration
- Carry out personal radiation monitoring periodically
- Radiation protection to the public:
- X-ray room must be
- Lined with lead
- Constructed with gypsum
- Painted with barium
Radiation Protection Short Essays
Question 1. Radiation protection for patients.
Answer.
- Patient selection:
- Professiojudgmentment should be used to select the patient for an X-ray examination
- Choice of equipment:
- Image receptor – to reduce the exposure time
- A focal spot to film distance
- With the increase in distance, the exposure time reduces
- Collimation – it reduces the size of the X-ray beam
- Filtration – to remove low-energy photons
- Use of lead aprons and collars
- It minimizes unnecessary radiation exposure
- Choice of intraoral technique:
- Parallel radiographic technique causes less exposure, hence used
- X-ray equipment:
- Make use of:
- High kVp
- Increased made
- Reduced exposure time
- Processing of film:
- Make use of the proper method of processing
- Avoid repetition of X-ray
- Interpretation of image:
- Properly interpret the X-ray in a semi-darkened room
Note down all the necessary details
- Properly interpret the X-ray in a semi-darkened room
Principles of radiation protection essay
Question 2. Radiation protection for the operator.
Answer.
Radiation protection for the operator
- The following measures must be carried out by the operator to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure
- During exposure, the operator must leave the room/stand behind a suitable barrier
- The operating room should meet the minimum shielding requirements
- The position of the operator during exposure should be 6 feet away from the source
- At an angle of 90 – 135°
- Avoid holding the film intraorally
- Avoid stabilizing the tube during exposure
- Use a lead apron in the absence of a barrier
- Avoid the use of fluorescence mirror during exposure
- Make use of filtration
- Carry out personal radiation monitoring periodically
Question 3. Image receptors.
Answer.
- E-speed films:
- Used to reduce the exposure time
- Double-sided emulsion:
- Reduces exposure
- Double film packets:
- Reduces the radiation needed
- Xeroradiography
- Good edge enhancement
- Good image quality
- Reduces exposure
- Intensifying screens:
- Used in extraoral radiography
- Contains phosphors that fluorescence on exposure to the x-ray beam
- The intensity of it is directly proportional to the intensity of the x-ray beam
Radiation protection in medical imaging
Question 4. Intensifying Screens.
Answer.
Intensifying Screens
These are used with all extraoral radiographs
Intensifying Screens Types:
- Blue emitting
- Green emitting
Intensifying Screens Mechanism:

Intensifying Screens Composition:
- Base
- Reflecting layer
- Phosphor layer
- Protective coat
Radiation Protection Short Answers
Question 1. ALARA principle.
Answer.
ALARA principle
- It is the abbreviation of “As Low As Reasonably Achievable”
- It suggests that no matter how small the dose is, the stochastic effect may result.
- Following are the guidelines of the ALARA principle
- For radiation workers
- For occupational exposure – 50 mSv in 1 year
- For reproductive age – 10 mSv in 1 year
- For general public
- Annual effective dose – 1 mSv
Question 2. Dosimetry
Answer.
Dosimetry
- It is the measurement of the quantity of the radiation exposure or the amount of the energy absorbed per unit mass at an interest site
Dosimetry Techniques:
- Ionization chamber:
- Plates with opposite charges are connected to an electrometer
- These are separated by a standard volume of air
- The X-ray beam is passed through the air
- This leads to the generation of positive and negative ions
- These are attracted to the plates
- The potential difference between the plates is measured
- Film badges:
- A worn film with metallic badges is used
- It is processed along with the films of known amount of exposure
- Next, the degree of darkening is measured and compared
- Thermoluminescent dosimeters:
- Crystals like lithium fluoride are used
- These crystals absorb radiation energy:
- It results in the release of visible light
- This is proportional to the absorbed energy
Personal protective equipment in radiology essay
Question 3. Leakage radiation/Stray radiation.
Answer.
Leakage radiation/Stray radiation
- It is defined as radiation emitted by any other part of the X-ray tube other than the focal spot
- It can be prevented by
- Avoid holding of the tube during exposure
- Check the X-ray machine periodically for leakage
Question 4. Thermoluminescence dosimeter.
Answer.
Thermoluminescence dosimeter
- Crystals like lithium fluoride are used
- These crystals absorb radiation energy
- It results in the release of visible light
- This is proportional to the absorbed energy
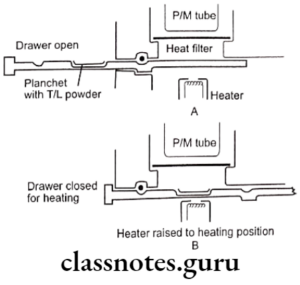
Radiation protection methods in diagnostic radiology
Question 5. Position & distance rule.
Answer.
Position & distance rule
- The operator should stand at least 6 feet from the patient, at an angle of 90 – 135° to the central ray beam when the exposure is made.
- This is called the position and distance rule.
Radiation Protection Viva Voce
- The gonadal dose is 1/1000 of exposure to skin
- Dosimetry – Determining the quantity of radiation exposure or does.
- The distance of the safe light from the working area in a dark room is 4 feet
