Planning Survey And Evaluation Definitions
Planning
- Planning is a systemic approach to defining the problem, setting priorities, developing specific goals and objectives, and determining alternative strategies and methods of implementation.
Survey
- Survey is a non-experimental type of research that attempts to gather information about the status quo for a large number of cases by describing present conditions without directly analyzing their causes
Evaluation
- Evaluation measures the degree to which objectives and targets are fulfilled and the quality of the results obtained
Planning Survey And Evaluation Mcqs
Planning Survey And Evaluation Important Notes
1. Types of survey
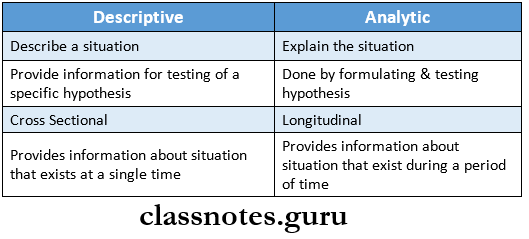
Read And Learn More: Percentive Communitive Dentistry Question And Answers
2. Pathfinder survey
- Pathfinder survey was put forth by WHO
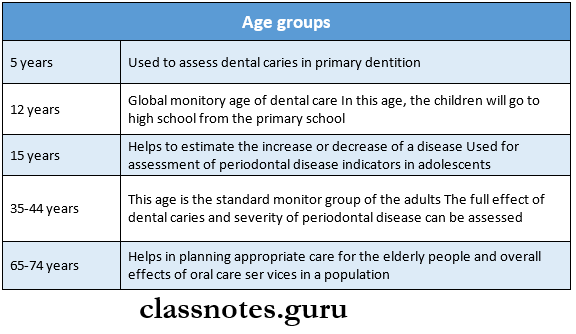
- In this survey, 0.1%-1% of the population is assessed by 4 specific groups of different ages
- Age groups:
Planning Survey And Evaluation Long Essays
Question 1. Define survey. How do you conduct an oral health survey of a town having a 3 lac population?
Answer:
Definition Of Survey:
- Survey is a non-experimental type of research that attempts to gather information about the status quo for a large number of cases by describing present conditions without directly analyzing their causes
Survey Steps
- Establishing the objectives
- The objective must be clear before the start of the study
- The objectives can be stated in the form of a null hypothesis or by describing what is to be measured
- Designing the investigation
- Protocol: it should contain
- Main objective and purpose of the survey
- Type of the study to be used- descriptive or analytic
- Type of information to be collected and methods to be used- case-control or cohort
- Sampling method used
- Personnel and physical arrangement
- Statistical methods to be used
- Budget
- Schedule of the activities
- Selection of control group or cohort
- Protocol: it should contain
- Selecting the sample
- Selecting the sample is done as it is impossible to study every individual in the study population
- Along with this, it saves resources in terms of time, money, and manpower
- Sample i.e. reference population is selected using any of the sampling methods
- Conducting the examination
- Organize the survey as follows
- Before the examination obtain approval from the authorities
- The budget is made according to the resources required
- Schedule the program as the time required for oral examination
- Prepare a list of emergency care and referral services
- The diagnostic method used should be valid and reliable
- Organize the personnel such as clerks to manage the patients
- Instruments and supplies needed
- Plain mouth mirror- 30/ examiner
- Periodontal probe-30/examiner
- Several pairs of tweezer
- Container and concentrated sterilizing solution
- A wash basin
- Cloth/ paper hand towels
- Gauze
- Infection control
- Including the use of protective barriers, sterilization, waste disposal
- Examination area- includes
- An adjustable chair
- A source of illumination
- A recorder to receive information from the examiner
- Precautions
- Minimize the number of examiners
- Use of a similar design to the explorer
- Minimum divergences of opinion
- Discuss the interpretation of borderline cases
- Circulate rules among examiners
- Supervises should recheck an occasional case
- Analyzing the data
- The data is analyzed manually or mechanically
- Tabulation and graphical presentation are done for an easy conclusion
- Drawing the conclusion
- Drawing the conclusion is related to the investigation
- No exploration of the population as a whole is made
- Publishing the report
- Publishing the report should be clear and simple
- Publishing the report should contain
- Purpose of the survey
- Materials and methods used
- Diagrammatic presentation of the result
- Discussion and conclusion
- Summary/abstract
Health Survey And Evaluation Questions
Question 2. What do you mean by planning? Write about the stages of planning
Answer:
Definition Of Planning:
- Planning is a systemic approach to defining the problem, setting priorities, developing specific goals and objectives, and determining alternative strategies and methods of implementation.
Planning Steps:
Identify The Problem:
- It includes
Determining Priorities:
- A health advisory committee is established for it
- Priorities are determine
- To allow the most efficient allocation of resources
- For ranking solutions to the problem
- Factors considered are
- Severity of disease
- Who needs care most
- Percentage of people affected
- High-risk group
Development of Program Goals, Objectives, and Activities:
- Goal: it is defined as the ultimate desired state towards which objectives and resources are directed
- Objective: it should be precise
- It should specify
- Nature of situation/ condition
- The extent of the situation/ condition
- Desired population
- Desired geographic area
- The desired time of the situation is intended to exist
- Types: outcome and process
- Activities include
- What is going to be done
- Who will be doing it
- When will it be done
Resources Identification:
- Resources should be
- Appropriate
- Adequate
- Effective
- Efficient
Identifying Constraints:
- Constraints that commonly occur are
- Lack of funding
- Lack of inadequate facilities
- Lack of time
- Inadequate transport
- Labor shortage
- Negative community attitudes
Identify Alternative Strategies:
- To overcome the existing constraints and available resources
Develop Implementation Strategies:
- Includes
- Why? – objective of the study
- What?- activities required
- Who?- Individuals responsible
- When?- Sequence of activities
- How?- Materials and method used
- How much?- Cost and time spent
Implementation:
- Implementation is the process of putting the plan into operation
- Implementation involves individuals, organizations, and the community
Monitoring, Evaluating, and Revising The Program:
- Monitoring refers to the maintenance of an ongoing watch over the activities of a health service
- It is the basis for the continual modification of goals, plans, or activities
- The program requires continuous surveillance of all activities
Program Planning And Evaluation Quiz
Planning Survey And Evaluation Short Essays
Question 1. Calibration of examiners in surveys.
Answer:
Objectives
- To ensure uniform interpretation, understanding and application by all examiners of the codes and criteria for various diseases and conditions to be observed
- To ensure that each examiner can examine consistently
Features:
- To measure intra-examiner variability each examiner should carry out reproducibility
- One of many examiners must be carefully standardized
- To measure inter-examiner variability examiner should undergo a training and calibration exercise
Precautions:
- Minimize the number of examiners
- Use of a similar design to the explorer
- Minimum divergences of opinion
- Discuss the interpretation of borderline cases
- Circulate rules among examiners
- Supervises should recheck an occasional case
Question 2. Importance of pilot survey/ Pilot survey.
Answer:
Importance of pilot survey
- The pilot survey includes only the most important subgroups in the population
- Provide the minimum amount of data needed for planning
- Includes only one or two index ages out of which one is 12 years
- Additional data should then be collected for the implementation and monitoring of services
Question 3. Evaluation.
Answer:
Evaluation Definition:
- Evaluation measures the degree to which objectives and targets are fulfilled and the quality of the results obtained
- It measures the productivity of available resources in achieving clearly defined objectives
- It measures how much output or cost-effectiveness is achieved
- It makes possible the reallocation of priorities and of resources on the basis of changing health needs- WHO
Evaluation Purpose:
- Determine the value of the program
- Provide information for decision-making
- Measure the effect
- Modification can be done
- Measure the progress of each activity
Evaluation Criteria:
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- Appropriateness
- Adequacy
Evaluation Types:
- Formative
- It refers to the internal evaluation of a program
- Evaluation is an examination of the process/ activities of a program as they are taking place
- Evaluation aids in the development of a program in its early phases
- Evaluation concerns whether various components of a program are workable or whether changes should be made
- Summative
- Evaluation judges the worth of a program
- Evaluation is aimed at program decision-makers
Evaluation Elements:
- Relevance
- Adequacy
- Accessibility
- Acceptability
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- Impact
Evaluation Steps:
- Determine what is to be evaluated
- Establishment of standard criteria
- Planning of methodology
- Gathering information
- Analysis of results
- Taking action
- Revaluation
Health Program Evaluation Questions
Planning Survey And Evaluation Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Evaluation.
Answer:
Evaluation Definition:
- Evaluation measures the degree to which objectives and targets are fulfilled and the quality of the results obtained
- Evaluation measures the productivity of available resources in achieving clearly defined objectives
- Evaluation measures how much output or cost-effectiveness is achieved
- Evaluation makes possible the reallocation of priorities and resources based on changing health needs- WHO
Evaluation Purpose:
- Determine the value of the program
- Provide information for decision-making
- Measure the effect
- Modification can be done
- Measure the progress of each activity
Evaluation Criteria:
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- Appropriateness
- Adequacy
Evaluation Types:
- Formative
- Summative
Question 2. Plan.
Answer:
- A plan is a decision about a course of action
Question 3. Pathfinder survey.
Answer:
Pathfinder survey
- It is a stratified cluster sampling technique that aims to include the most important population subgroups likely to have differing disease levels
- It is a practical and economical method
- It provides the following information
- Prevalence of oral diseases
- The severity of oral diseases
- Need for treatment
- Progression of oral diseases
Classification:
- Pilot survey
- National pathfinder survey
Monitoring And Evaluation In Public Health
Question 4. Formative evaluation.
Answer:
Formative evaluation
- Formative evaluation refers to the internal evaluation of a program
- Formative evaluation is an examination of the process/ activities of a program as they are taking place
- Formative evaluation aids in the development of a program in its early phases
- Formative evaluation concerns whether various components of a program are workable or whether changes should be made
Question 5. Uses of the survey.
Answer:
Monitoring Trends In Oral Health and Disease:
- When surveys are repeated over time they give information about how oral health varies by geographic area, social class, race, or ethnic group
Policy Development:
- A survey can be used to establish oral health strategies and develop an oral health policy
Program Evaluation
- Survey data are often used to evaluate program
- However, inferences in a survey need to be made with caution
Assessment Of Dental Needs
- The survey can be used for the assessment of needs with differences in criteria used in the survey and for individual patient care
Provide Visibility To Dental Issues From A
National Survey:
Question 6. Summative evaluation
Answer:
Summative evaluation
- Summative evaluation judges the worth of a program
- Summative evaluation is aimed at program decision-makers
- Summative evaluation provides information on program effectiveness
- Conducted after the completion of the program design
Summative evaluation Uses:
- To help decide whether to continue or end a program
- To help determine whether a program should be expanded to other locations
Planning, Survey, And EvaluatioN Viva Voce
- The analytical survey is conducted to assess the determinants of the diseases
- The Pathfinder survey employs a stratified cluster sampling technique
- 15 The age group is considered a global age index age to monitor oral health
- 15 years index age is important to assess periodontal disease indicators in adolescent
- 35-44 years index group is used to assess the full effect of dental caries and the severity of periodontal involvement
- 25-50 subjects in each index age group are to be examined in the Pathfinder survey
- Calibration is done to ensure uniform interpretation of codes and criteria for various diseases and conditions
- 5-10 minutes are taken for a basic oral health examination of the child
- 15-20 minutes is taken for a basic oral health examination of adults
- The validator in a survey is an experienced epidemiologist
- The recording clerk is instructed to record data on the assessment form in a survey
- The pilot survey includes the most important subgroups and one or more index ages
- Children are examined at 5 years of age in the Pathfinder survey to estimate the level of dental caries in primary dentition
