Pediatric Endodontics Definitions
1. Pulpotomy
- It is defined as the complete removal of the coronal portion of the dental pulp, followed by the placement of a suitable dressing or medicament that promotes healing and preserves tooth vitality.
2. Pulpectomy
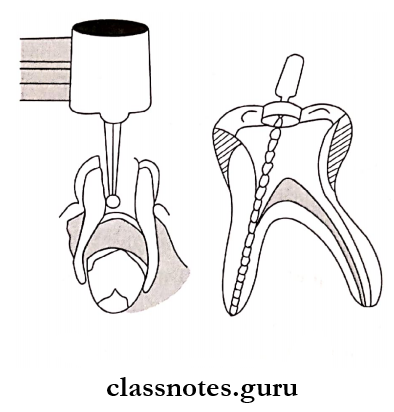
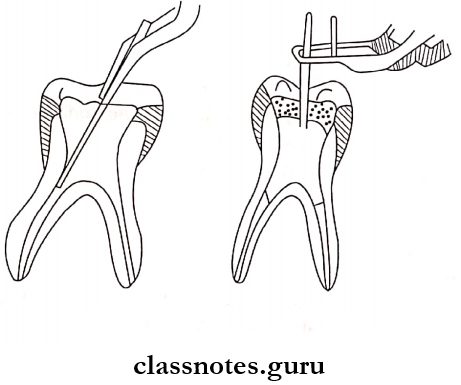
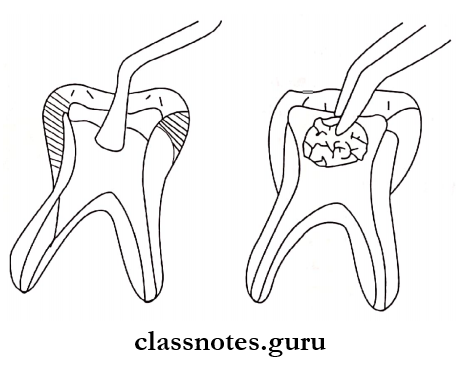
- It involves the removal of the roof and contents of the pulp chamber in order to gain access to the root canals which are debrided, enlarged, and disinfected.
3. Indirect Pulp capping
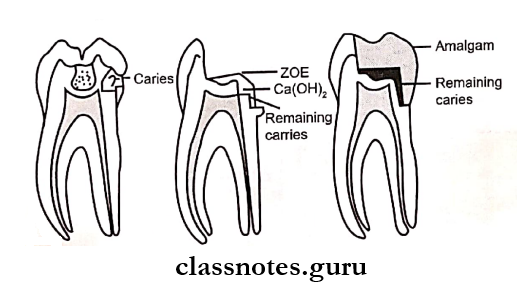
- It is the procedure involving a tooth with a deep carious lesion where carious dentin removal is left incomplete and the decay process is treated with a biocompatible material to avoid pulp tissue exposure
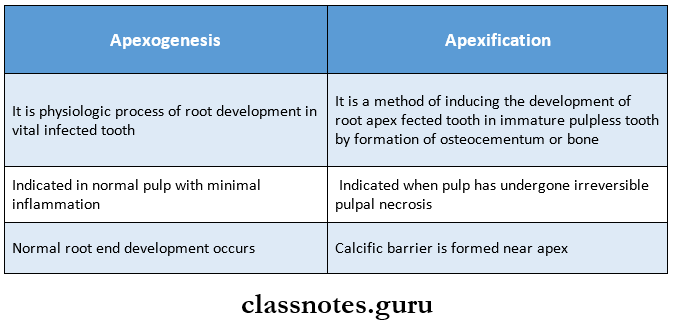
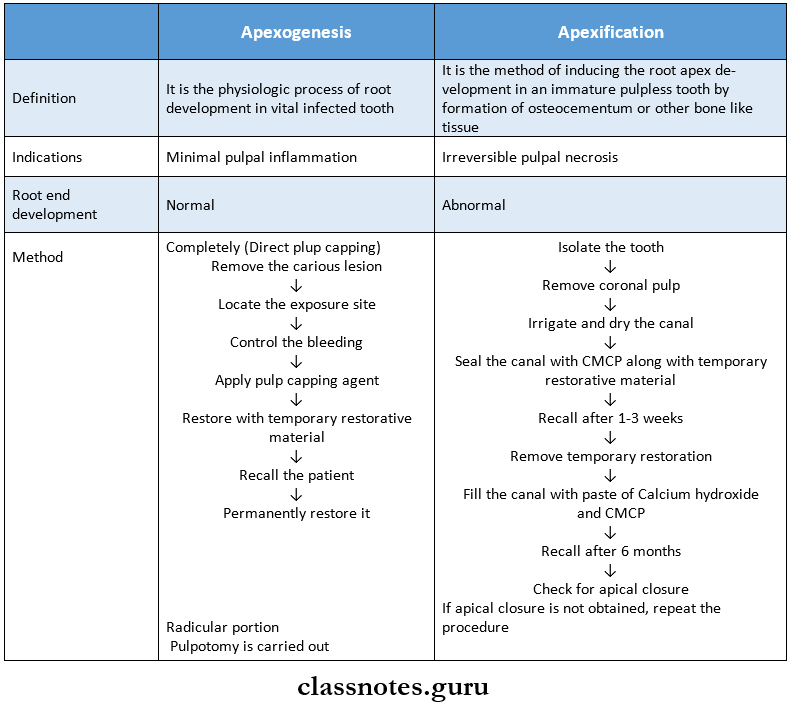
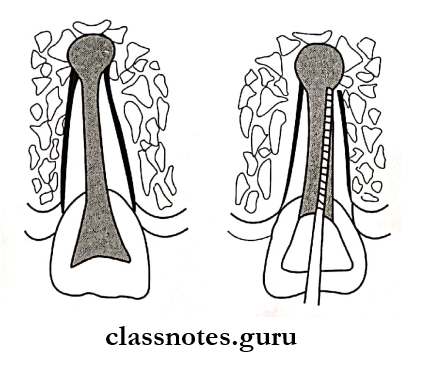
4. Apexification
- It is a method of inducing the development of root apex in an immature pulpless tooth by the formation of osteocytes- tum or bone
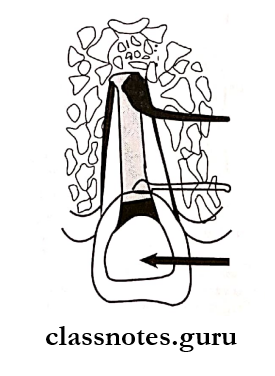
5. Apexogenesis
- It is the physiologic process of root development in the vital infected tooth
Read And Learn More: Pedodontics Short Essays Question And Answers
Pediatric Endodontics Important Notes
1. Pulpotomy techniques
- Vital Pulpotomy
- Devitalization
- Single sitting-formoterol
- Two-stage – paraformaldehyde
- Preservation
- Glutaraldehyde
- Ferric sulfate
- MTA
- Regeneration
- Bone morphogenetic proteins
- Devitalization
- Nonvital Pulpotomy
- Beechwood cresol
- Formocresol
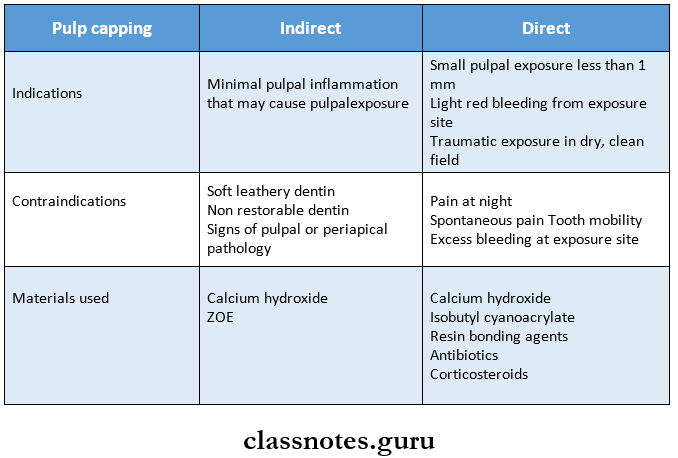
2. Direct v/s indirect pulp capping
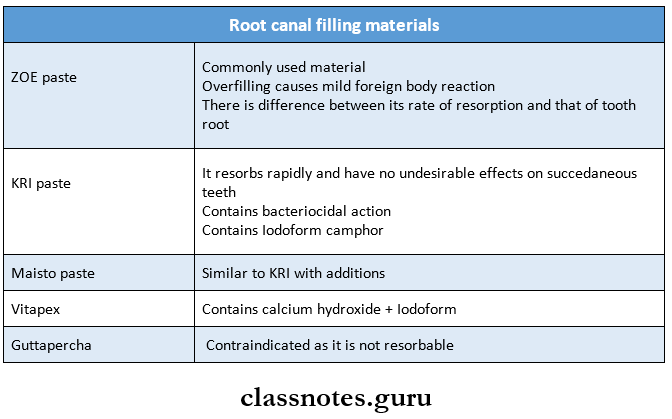
3. Root canal filling materials
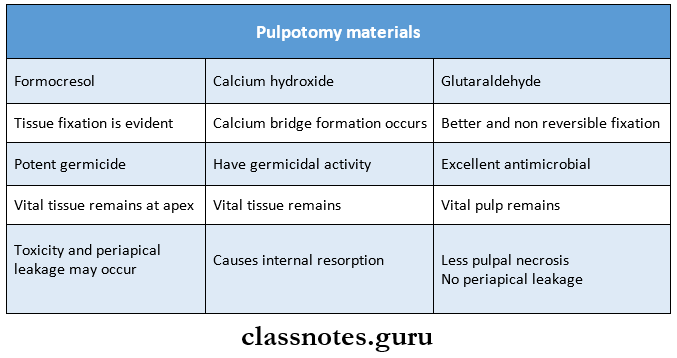
4. Pulpotomy materials
5. Apexogenesis v/s apexification
6. Contraindications of Pulpotomy
- Spontaneous pain
- Hemorrhage that is bright red in colour and not easy to control
- Internal resorption
- Existence of abscess or fistula
7. Composition of Buckley’s solution
- 19% – Formaldehyde
- 35% – Cresol
- 15% – glycerine
- Water
8. Mummifying paste
- Introduced by Hobson
Composition
- Paraformaldehyde – active devitalizing agent
- Lignocaine
- Propylene glycol
- Carbowax
- Carmine
Pediatric Endodontics Long Essays
Question 1. Define pulpotomy. Describe indications and contra-indications for pulpotomies. Explain formocresol pulpotomy procedure.
Answer:
- Pulpotomy: It is defined as the complete removal of the coronal portion of the dental pulp, followed by the placement of a suitable dressing or medicament that promotes healing and preserves tooth vitality.
Pulpotomy Indications
- Vital teeth that are free of radicular pulpitis are considered suitable for pulp capping
- Pain, if present is neither spontaneous nor persistent
- The tooth is restorable and possesses at least two-thirds of its root length
- There is no evidence of internal resorption, inter radicular bone loss, abscesses or fistulas
- The hemorrhage from the amputation site is easy to control
Pulpotomy Contraindications
- The tooth crown is non-restorable and tender on percussion
- Highly viscous hemorrhage seen at the radicular canal orifices
- Mobility or radiolucency with marked root resorption exists
- Persistent toothaches and coronal pus
Pulpotomy Technique:
- Anesthetized and isolate the tooth
- Remove the carious lesion
- The entire roof of coronal pulp is removed
- With the help of a spoon or excavator cut out the coronal pulp
- Irrigate the pulp chamber
- Control the bleeding with the help of a moist cotton pellet
- Dry the pulp chamber
Read And Learn More: Pedodontics Short Essays Question And Answers
- Now place cotton moistened with 1.5 concentration of Buckley’s formocresol solution into the canal
- Keep it for 5 minutes
- Now remove it and dry the canal
- Restore the tooth with a thick paste of zinc oxide eugenol
- Place the base of zinc polycarboxylate cement over it
- Finally, permanently restored with stainless steel crown
Pediatric Endodontics Short Essays
Question 1. Materials used for pulpotomy.
(or)
Pulpotomy medicaments
Answer:
- Devitalizing Agents
- Formocresol:
- Potent germicidal
- Maintains tissue vitality
- May lead to periapical leakage
- Gysi Triopaste:
- Composition:
- Tricresol
- Cresol
- Glycerin
- Paraformaldehyde
- Zinc Oxide
- Composition:
- Easlick’s paraformaldehyde paste:
- Paraformaldehyde
- Procaine base
- Powdered asbestos
- Petroleum jelly
- Carimine to color
- Formocresol:
- Preservative Agents:
- Glutaraldehyde:
- Better tissue fixation
- Excellent antimicrobial
- Maintains pulp vitality
- This leads to minimal pulpal necrosis
- Ferric Sulphate:
- Favorable pulpal response
- Causes internal resorption
- MTA (Mineral Trioxide Aggregate):
- Biocompatible
- Better sealing
- Promotes regeneration
- Glutaraldehyde:
- Regenerative Agents:
- Bone Morphogenic protein:
- Induce differentiation of adult pulp cell into odontoblast
- This leads to dentin bridge formation
- Bone Morphogenic protein:
Question 2. Apexification.
Answer:
- It is a treatment of non-vital immature teeth to induce root end closure by suitable medicament
Apexification Procedure

Question 3. Obturating materials.
Answer:
1. Zinc oxide Eugenol paste:
Introduced into the root canal with the help of a syringe
- Zinc oxide Eugenol paste Problems:
- Underfilling – frequently accepted
- Overfilling – causes mild foreign body reaction
- Differences occur between its rate of resorption and that of tooth root
- Iodoform paste/KRI paste
- Zinc oxide Eugenol paste Composition:
- Iodoform
- Camphor
- Parachlorophenol
- Menthol
Zinc oxide Eugenol paste Properties:
- Resorbs rapidly
- Extruded periapical KRI. the paste is replaced with a normal tissue
- Has long-lasting bactericidal potential
- Has good success rate
2. Calcium Hydroxide:
- Easy to apply
- Rapidly resorbed
- Has no toxic effects
- It is radiopaque
3. Collacote:
- It is a soft, white, biocompatible
- Can be applied to bleeding canals
- Provides scaffold for bone growth
Collacote Composition:
- Synthetic collagen
4. Endoflas:
- Composition:
- Zinc oxide
- Barium sulfate
- Iodoform
- Calcium hydroxide
- Eugenol
- Pentachlorophenol
- It prevents microleakage
- Placed after the elimination of inflammation
Question 4. Obturation Techniques.
Answer:

1. With the help of a syringe:
- An endodontic pressure syringe loaded with Vitapex is used
- Introduce the syringe up to 1/5th the distance from the apex of the canal
- Slowly inject the material

Question 5. Apexification and Apexogenesis.
Answer:
Question 6. Indirect Pulp Capping-
Answer:
- Definition – It is the procedure involving a tooth with a deep carious lesion where carious dentin removal is left incomplete and the decay process is treated with a biocompatible material to avoid pulp tissue exposure
Indirect Pulp Capping Indications:
- Irreversible pulpitis
- Presence of adequate bone support
- Root length available at least 2/3rd of its total length
- Internal resorption
Indirect Pulp Capping Contraindications:
- Mobile tooth
- Non-restorable tooth
- Presence of cyst
- Less than 2/3rd of root length remaining
- Perforation of the pulpal floor
Indirect Pulp Capping Procedure:

Question 7. Formocresol v/s Glutaraldehyde.
Answer:
Question 8. Pulpectomy in 85.
Answer:
- Pulpectomy – It involves the removal of the roof and contents of the pulp chamber in order to gain access to the root canals which are debrided, enlarged, and disinfected.
Procedure:

Question 9. Bleaching.
Answer:
- It is a procedure by which the discoloration of teeth are managed by the application of a bleaching agent
Bleaching Types:
1. For vital teeth:
- For non-vital teeth
2. Extracoronal bleach:
- Intracoronal bleach
Agents Used:
- Superoxol
- Sodium perborate
- Sodium peroxide
- Hydrogen peroxide
Question 10. Define Apexogenesis and write in detail about the procedure of Apexogenesis.
Answer:
Apexogenesis
- It is the physiologic process of root development in the vital infected tooth
Apexogenesis Indications
- Traumatized or palpably involved vital permanent tooth
Apexogenesis Contraindications
- Presence of degenerative changes in radicular pulp
- Purulent discharge
- Necrotic debris in the canal
- Periapical radiolucency
Apexogenesis Technique
- The operated area is anesthetized
- A rubber dam is applied
- Remove all carious portions of the tooth and open up the pulp chamber
- Remove coronal pulp leaving behind the radicular portion
- Rinse thoroughly all the debris
- Control bleeding by placing a moist cotton pellet over the amputated pulp
- Calcium hydroxide is placed over the pulp
- Restore with a temporary restoration
- Follow-up radiographs are taken to check the root development periodically
- Once root formation is completed, conventional root canal treatment is done
Pediatric Endodontics Short Answers
Question 1. Glutaraldehyde.
Answer:
- Better tissue fixation
- Excellent antimicrobial
- Maintains pulp vitality
- Leads to minimal pulpal necrosis
Question 2. Obturation.
Answer:
- Obturation of primary teeth is done with resorbable material that will give way for the erupting permanent tooth
Obturation Procedure
- First, a thin mix of zinc-oxide eugenol is used to coat the walls of the canals using a reamer
- First, the reamer is rotated clockwise inside the canal for 10-15 rotations
- Use a thick mix of zinc oxide eugenol and fill the canal using leptospiral
- Seal the pulp chamber with a temporary restoration
- Recall after a week, if the patient is totally asymptomatic, restore permanently with stainless steel crown
Question 3. Vitality test.
Answer:
Heat Test:
- Done by
- Hot gutta-percha
- Hot burnisher
- Hotair
- Hot compound
- Hot water
- Result:
- No response – necrosed pulp
- Mild response – Normal pulp
- Painful response – Pulpitis
- Cold Test:
- Done using ethyl chloride spray, pencil sticks of ice, carbon dioxide snow at -78°C
- Electric Pulp Test:
- Most useful tool
- Execute neural elements of pulp
- Other methods:
- Anesthetic test
- Transillumination
- Test cavity
Pediatric Endodontics Viva Voce
- Direct pulp capping and calcium hydroxide Pulpotomy are contraindicated in primary teeth as they cause internal resorption
- Pulp testing gives false results if root formation is incomplete or the tooth has a temporary crown or splint
- If an injured tooth requires more current than normal it indicates pulp death
- If less current is needed it indicates pulpal inflammation
- Tooth tested immediately after trauma may give a negative response
- A laser Doppler flow meter and pulse oximeter determine vitality based on the blood supply to the pulp
- Calcium hydroxide-iodoform mixture- vitapex is considered as nearly ideal filling material
- KRI paste has long-lasting germicidal potential
- ZOE paste is a commonly used filling material in primary teeth
- Gutta-percha is contraindicated as it is not resorbable
