Pathology Miscellaneous Long Essays
Question 1. Discuss the causes of hemorrhage and describe the complications.
Answer:
Causes of Hemorrhage:
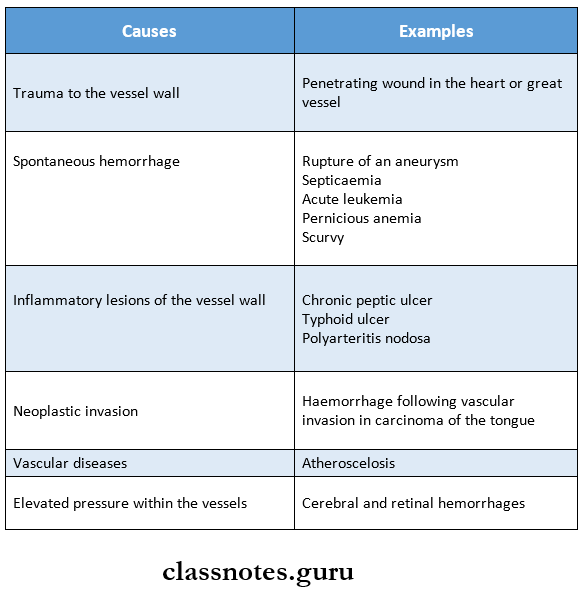
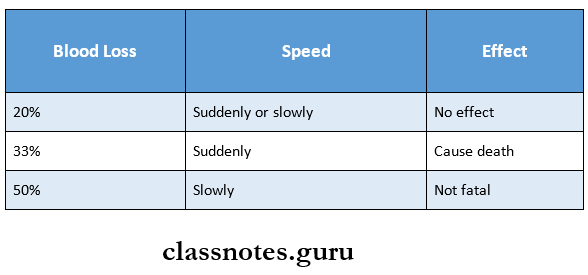
Hemorrhage Complications:
- It depends on
- Amount of blood loss
- Speed of blood loss
- Site of hemorrhage
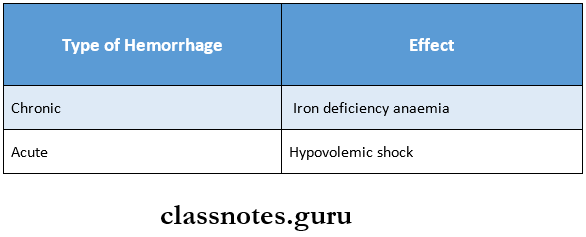
Pathology Miscellaneous Short Essays
Question 1. Thyrotoxicosis
Answer: Thyrotoxicosis is a syndrome resulting from an increased level of free thyroxin
Thyrotoxicosis Clinical Features:
- Hyperactivity
- Irritability
- Heat intolerance
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Tachycardia
- Systolic hypertension
- Presence of tremors
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Excessive sweating
- Exophthalmos
Read And Learn More: Pathology Question And Answers
Thyrotoxicosis Management:
1. General management:
- Rest
- Nutritious diet
2. Drug therapy:
- Carbimazole- Initial dose of 30 mg/day, maintenance dose of 10-20 mg/day is given
- Potassium perchlorate -800 mg/day in divided doses
- Sodium or potassium iodide 6-10 mg/day
3. Surgical treatment: Subtotal thyroidectomy
4. Radioiodine treatment: Iodine is given in doses of 8-10 millicuries
Question 3. Mention the diseases transmitted through blood transfusion and screening tests.
Answer:
Diseases Transmitted Through Blood Transfusion: The common diseases transmitted through blood transfusion are as follows:
- AIDS
- Hepatitis B and C
- CMV
- Syphilis
- Malaria
- Toxoplasmosis
Screening Tests:
- The usual screening TESTS performed before blood transfusion are
- ELISA for HIV and Hepatitis B
- VDRL for syphilis
- PS for malarial parasites
Pathology Miscellaneous Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Antioxidants
Answer: Antioxidants are endogenous or exogenous substances
Antioxidants Importance:
- Inactivate free radicals
- Play an important role in net effect of free radical in-jury
- It influence the rate of elimination of free radicals
Antioxidants Examples:
- Vitamin E, A, and C
- Sulfhydryl-containing compounds like cysteine and glutathione
- Serum proteins- ceruloplasmin and transferrin
Question 2. Idiopathic hemochromatosis
Answer:
- A form of hemosiderosis in which there is excessive intestinal absorption of iron even when intake is normal, it is called idiopathic hemochromatosis
- It is an autosomal dominant disease associated with much more deposits of iron
- It is characterized by a triad of
- Pigmentary liver cirrhosis
- Pancreas damage resulting in diabetes mellitus
- Skin pigmentation
Idiopathic hemochromatosis Synonyms:
- Hereditary hemochromatosis
- Bronze diabetes
Question 3. Immunization of rabies
Answer:
Rabies vaccines are two types
- Neural
- Non-neural
1. Neural Vaccines:
- Semple vaccine:
- The most widely used vaccine
- Developed by Semple at Central Research Institute, Kasauli.
- It is a 5% suspension of infected sheep brain and inactivated by 5% phenol at 37°C leaving no residual live virus.
- Beta Propiolactone (BPL) Vacine:
- Modified semple vaccine
- Instead of phenol, BPL is used as inactivating agent.
- Infant brain vaccine:
- Used widely in south America
- Reduce neurological complications.
- Vaccination Schedules:
- Now a days not used.
- In the past they were given subcutaneously on the anterior abdominal wall.
- 7 – 14 injections depends on the degree of risk.
- Vaccination Schedules:
2. Non-Neural Vaccines:
- Duck Egg Vaccine:
- BPL is used as an inactivating agent
- It has poor immunogenicity so not used now.
- Tissue culture vaccines: Following cell culture vaccines are available in India.
1. Human diploid cell strain vaccine [HDCS]
- The HDCS vaccine is prepared by growing the rabies virus on human diploid cells and is inactivated with BPL.
- This vaccine is highly antigenic and free of side effects
2. Purified chick embryo cell vaccine [PCEC]
- PCEC is now widely used.
- It is cheaper
- It contains BPL inactivated flurry LEP strain
- 3. Purified Vero cell vaccine [PVC]
- This vaccine is under study
Question 4. Bombay blood group
Answer:
- Red blood cells of type 0 have large amounts of another antigen called H substance
- This is different from ABO
- It is the precursor of A and B antigens
- An O-group individual who inherits A or B genes but fails to inherit the H gene from either parent is called the Bombay blood group
- It contains anti-A, anti-B, and anti-H antibodies in serum
- But red cells are not agglutinated by them
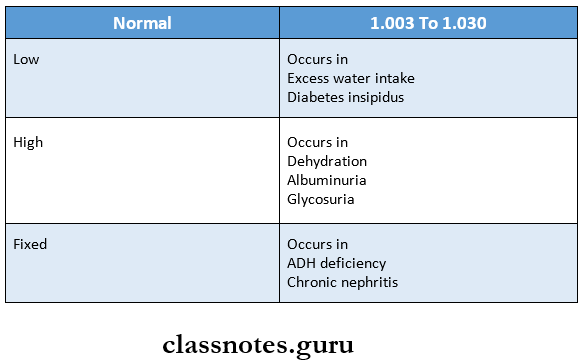
Question 5. The specific gravity of urine
Answer:
- The specific gravity of urine is the ratio of the weight of 1 ml volume of urine to that of 1 ml of distilled water
- it depends upon the concentration of various particles or solutes in the urine
Urine Uses: Use to measure concentrating and diluting power of the kidneys
Urine Methods:
- It is measured by
- Urinometer
- Refractometer
- Reagent strips
Urine Significance:
Question 6. Anticoagulants used in blood bank
Answer: Anticoagulants are substances which prevent or postponed the coagulation of blood
Anticoagulants Types:
- Natural anticoagulants
- Anticoagulants used in blood banks
- Anticoagulants used in laboratory
- Therapeutic Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants Used In Blood Banks: Anticoagulants used in blood banks are
- Acid citrate dextrose (ACD)
- Citrate phosphate dextrose (CPD)
- They are used to store blood in the blood bank
- Citrates combine with calcium ions in the blood to form a calcium citrate complex
- This decreases ionic calcium levels and prevents coagulation
