Infections And Infestation Short Essays
Question 1. Lab diagnosis of enteric fever
Answer:
Enteric fever Lab Diagnosis:
1. Isolation of bacilli.
- For isolation of bacteria, specimens are obtained from blood, faeces, urine, aspirated duodenal fluid, bile, bone marrow or rose spot.
- These specimens are then cultured.
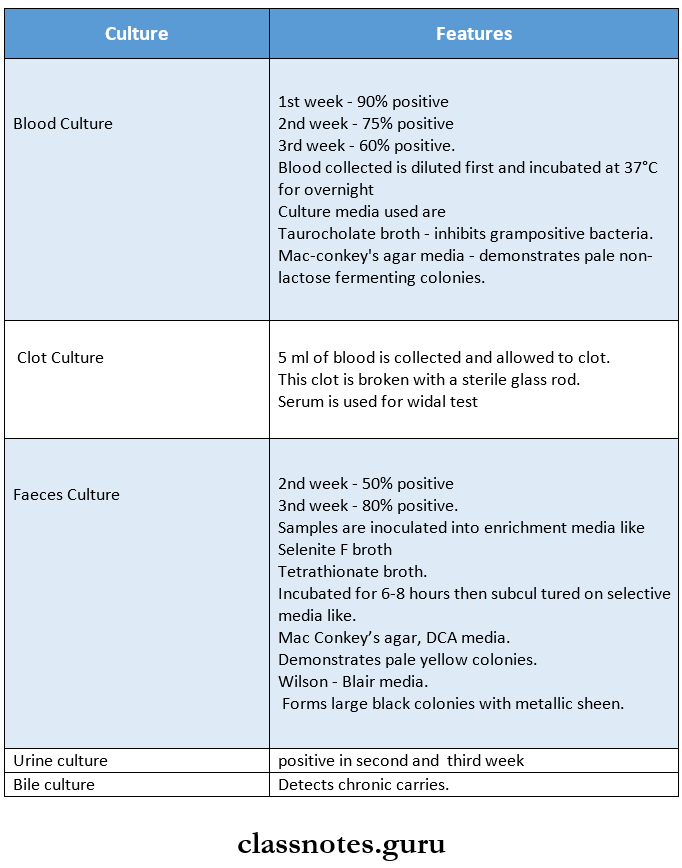
2. Demonstration of Antibodies
1. Widal test.
It is an agglutination for the detection of agglutinins H and 0 in patients with enteric fever
Widal test Method:
- Equal volumes f0.4 ml) serial dilutions of serum from 1:10 to 1: 640 and H and O antigens are mixed.
- One control tube containing antigen and normal saline is used.
- All these tubes are incubated in a water bath at 37°C.
Read And Learn More: Pathology Question And Answers
Widal test Results:
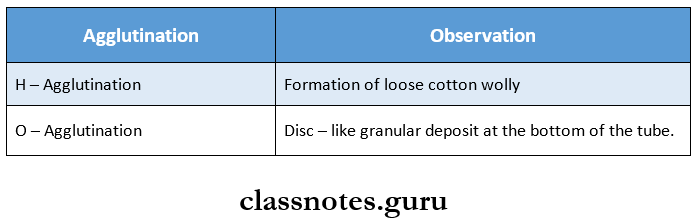
Widal test Interpretation:
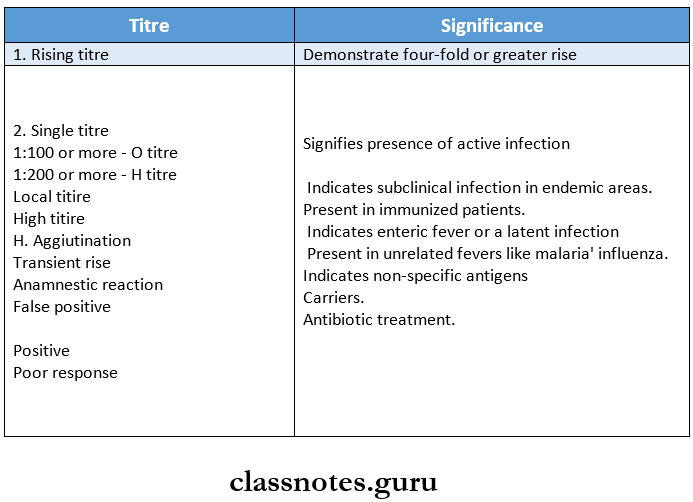
3. Demonstration of circulating antigen.
Done by counterimmunoelectrophoresis and ELISA.
Question 2. Urinary sediment
Answer:
Urinary sediment contains the following constituents
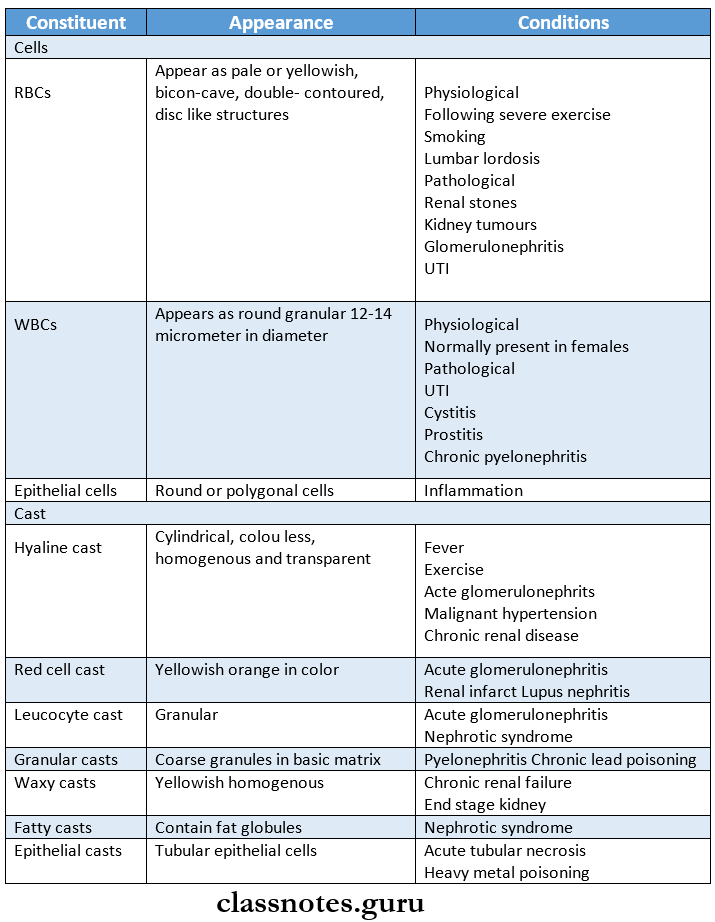
- It also contains
- Crystals of
- Calcium oxalate
- Uric acid
- Amorphous urate
- Tyrosine
- Calcium carbonate
- Miscellaneous structures like
- Spermatozoa
- Parasite
- Fungus
- Tumour cells
- Crystals of
Infections And Infestation Short Question And Answers
Question 1. Amoebiasis
Answer:
- Caused by entamoeba histolytica
- E. Histolytica can cause two types of pathological lesions as follows

- This condition is called as amoebic dysentery.
- These ulcers may be generalised (or) may be localised to the ileo-caecal (or) sigmoidorectal region.
- Occasionally ulcers may involve deeper tissues and may cause perforation (or) peritonitis.
- Erosion of blood vessels may lead to haemorrhage.
- The superficial lesions generally heal without scarring.
- Deep ulcers form scars leading to strictures, partial obstruction and thickening of gut wall.
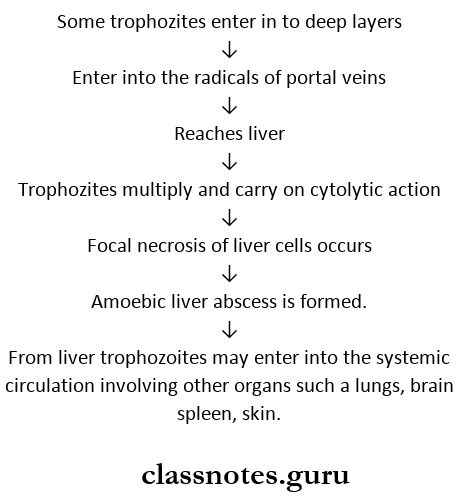
2. Extra-intestinal amoebiasis (or) secondary (or) metastatic lesions.
Amoebic liver abscess:
Question 2. Candidiasis
Answer:
- Candidiasis is caused by Candida albicans and occasionally by other Candida species
- It is an opportunistic endogenous infection.
Candidiasis Predisposing Factors:
- Diabetes
- Immunodeficiency
- Malignancy
- Prolonged administration of antibiotics
- Patients on immunosuppressive drugs and intravenous catheters
Candidiasis Treatment:
- Removal of predisposing factors
- For superficial infections- Topical application of polyene and imidazole is used
- For systemic infections- Amphotericin B + 5- fluoroscopy- tosine is used
Question 3. Rhinosporidiosis
Answer:
Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic granulomatous disease.
Rhinosporidiosis Causative Organism:
Rhinosporidium seeberi.
Rhinosporidiosis Mode of Infection:
Frequent contact with stagnant water.
Rhinosporidiosis Features:
- Friable polyps
- Sites involved- nose, mouth and eye
- Oral manifestations are Oropharyngeal lesions
- They appear as soft red polypoid growth and spread to the pharynx and larynx.
- These lesions contains mucoid discharge and are vascular.
Rhinosporidiosis Diagnosis:
- H and E stained tissue sections shows a large number of endospores within the sporangia
- These are embedded in a stroma of connective tissue, and capillaries
Question 4. Cysticercus cellulose
Answer:
- Cysticercus cellulose is the larval stage of taenia solium
- It develops in the muscles of the pig which is intermediate host
- A mature cyst is an opalescent ellipsoidal body and the long axis of the cyst is parallel to the muscle fibre.
- A dense milky white spot is present at the side where the scolex with its hooks and suckers remains invalidated.
- The cyst develops further when ingested by man which is the definitive host
- It may develop in any organ but are usually present in the subcutaneous tissues and muscles.
Various features of cysticercosis:
- They causes palpable nodule in sub-cutaneous tissues and muscles
- In brain leads to epileptic attacks.
- Neurocysticercosis involving the nervous system is the most serious form
Question 5. Fungi infecting hair
Answer:
- Dermatophytes are the group of fungi affecting the hair.
- Favus is a chronic type of ringworm involving the hair follicles
Fungi infecting hair Features:
- Alopecia
- Scarring
- Sparse hyphal growth
- Formation of air spaces within the hair shaft
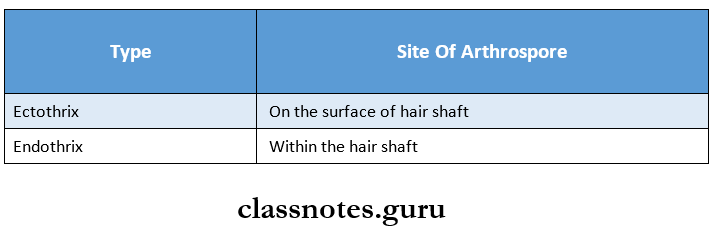
Fungi infecting Hair Types:
Question 6. Urinometer.
Answer:
- It is an equipment for determining urine specific gravity
- It is composed of
- Float – It is air filled glass tube
- Weight – It is a bulb filled with ball bearings
- Stem – It has calibrated graduation and numbers marked off to indicate specific gravity measurements
- Urinometer is placed in a tube of urine and where the meniscus of the urine reaches displays the specific gravity of the urine
